|
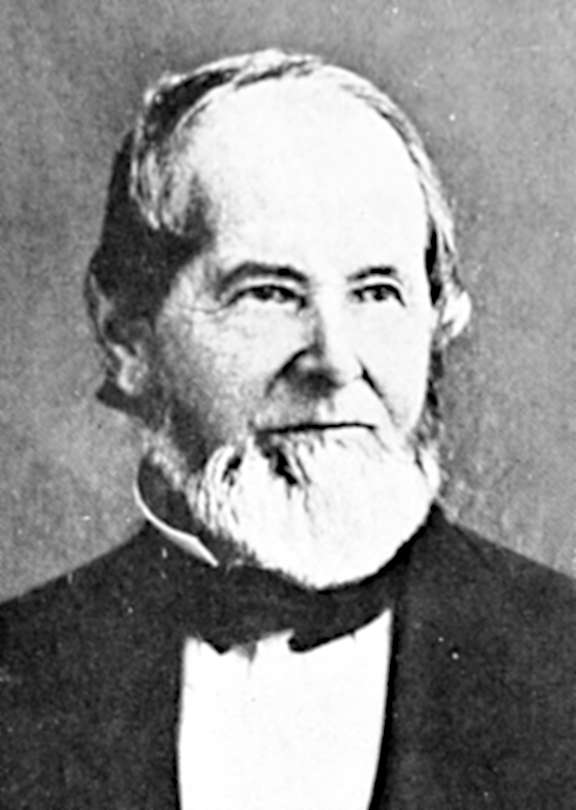
George Washington Bush
George Bush (c. 1779 – April 5, 1863) was an American settler and one of the first African-American (Irish and African) non-Amerindian settlers of the Pacific Northwest. Early life and education George Bush was born in Pennsylvania around 1779. An only child, he was raised as a Quaker and educated in Philadelphia.Tumwater Research Center“History and Background of Pioneer Bush Family”, ''Olympia News'', 1945-07-06, Retrieved on 2008-07-13. Bush's African American father, Matthew Bush, was born in India. Matthew Bush worked for a wealthy English merchant named Stevenson for most of his life. At Stevenson's home in Philadelphia, Matthew Bush met his wife, an Irish maid who also worked for Stevenson, and they married in 1778. Pennsylvania did not repeal its anti-miscegenation law until 1780, suggesting that Matthew Bush was either not considered black, or he was married under the care of Germantown Friends meeting in violation of the law. George's parents served Stevenson unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryland to its south, West Virginia to its southwest, Ohio and the Ohio River to its west, Lake Erie and New York (state), New York to its north, the Delaware River and New Jersey to its east, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario to its northwest via Lake Erie. Pennsylvania's most populous city is Philadelphia. Pennsylvania was founded in 1681 through a royal land grant to William Penn, the son of William Penn (Royal Navy officer), the state's namesake. Before that, between 1638 and 1655, a southeast portion of the state was part of New Sweden, a Swedish Empire, Swedish colony. Established as a haven for religious and political tolerance, the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcated by the Treaty of 1818, consisted of the land north of 42nd parallel north, 42° N latitude, south of 54°40′ N latitude, and west of the Rocky Mountains down to the Pacific Ocean and east to the Continental Divide of the Americas, Continental Divide. Article III of the 1818 treaty gave joint control to both nations for ten years, allowed land to be claimed, and guaranteed free navigation to all mercantile trade. However, both countries disputed the terms of the international treaty. Oregon Country was the American name, while the British used Columbia District for the British Empire, region. British North America, British and French Canadians, French History of Canada (1763–1867), Canadian North American fur trade, fur tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockstock Incident
The Cockstock incident was an altercation between indigenous peoples and settlers in the Willamette Valley. It originated as a dispute between Cockstock, a native, and James D. Saules, a free black settler. On 4 March 1844, conflict erupted between Cockstock's party and settlers; with Cockstock and two white settlers dying. The event has been called "the most significant occurrence of violence" in the Oregon Country between indigenous peoples and settlers prior to the Cayuse War. In the aftermath of the violence, white settlers feared that black settlers could insult local indigenous peoples enough to provoke an uprising. The Cockstock incident influenced the adoption an 1844 black exclusion law that banned black settlers from living in the Oregon Country. Historian Thomas McClintock has written that the connection between the Cockstock incident and the Exclusion Law is "unquestionable". Background Cockstock was a Molala man who lived in the Oregon Country during the first half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Government Of Oregon
The Provisional Government of Oregon was a popularly elected settler government created in the Oregon Country (1818-1846), in the Pacific Northwest region of the western portion of the continent of North America. Its formation had been advanced at the Champoeg Meetings since February 17, 1841, and it existed from May 2, 1843 until March 3, 1849, and provided a legal system and a common defense amongst the mostly American pioneers settling an area then inhabited by the many Indigenous Nations. Much of the region's geography and many of the Natives were not known by people of European descent until several exploratory tours and expeditions were authorized at the turn of the 18th to the 19th centuries, such as Lewis and Clark's Corps of Discovery going northwest in 1804-1806, and United States Army Lt. Zebulon Pike and his party first journeying north, then later to the far southwest. The Organic Laws of Oregon were adopted in 1843 with its preamble stating that settlers onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Bridger
Fort Bridger was originally a 19th-century fur trading outpost established in 1842, on Blacks Fork of the Green River, in what is now Uinta County, Wyoming, United States and was then part of Mexico. It became a vital resupply point for wagon trains on the Oregon, California, and Mormon Trails. The US Army established a military post here in 1858 during the Utah War, until it was finally closed in 1890. A small town, Fort Bridger, Wyoming, remains near the fort and takes its name from it. Bridger's trading post The post was established by the mountain man Jim Bridger, after whom it is named, and Louis Vasquez. In December 1843, Bridger wrote to Pierre Chouteau Jr., "I have established a small fort, with a blacksmith shop and a supply of iron in the road of emigrants on Black Fork of Green River, which promises fairly." According to Stanley Vestal, "His fort consisted simply of an eight-foot stockade, with a corral adjoining on the north. Within that stockade stood four log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in North America that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon Territory. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail crossed what is now the states of Kansas, Nebraska, and Wyoming. The western half crossed the current states of Idaho and Oregon. The Oregon Trail was laid by fur traders and trappers from about 1811 to 1840 and was initially only passable on foot or horseback. By 1836, when the first migrant wagon train was organized in Independence, Missouri, a wagon trail had been cleared to Fort Hall, Idaho. Wagon trails were cleared increasingly farther west and eventually reached the Willamette Valley in Oregon, at which point what came to be called the Oregon Trail was complete, though further improvements in the forms of bridges, cutoffs, ferries, and roads would make the trip faster and safer. From various starting points in Iowa, Missouri, or Nebraska Territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Simmons (pioneer)
Michael Troutman Simmons (August 5, 1814 – November 15, 1867) was an American pioneer and one of the first white men to settle in the Puget Sound.Wilma 2003. Biography Simmons was one of ten children, born in Kentucky in 1814. As a boy, he moved with his mother to Pike County, Illinois. When Michael was 21 years old, he moved to Iowa and married a 15-year-old girl named Elizabeth Kindred. Five years later, the couple moved to Missouri and Michael built a gristmill. In late 1845, at the age of 30, he decided to abandon the Midwest and came to the Puget Sound on a wagon train with a group of settlers (including his friend George Bush). He assumed leadership of the new settlers, who gave him the title of "Colonel". After taking advice from the traders of the Hudson's Bay Company at Fort Nisqually, the new American settlers founded New Market (later Tumwater). Despite its help, three years later Simmons led a campaign of complaints against the "monarchist" Hudson's Bay Company. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Owen Bush
William Owen Bush (July 4, 1832 – February 13, 1907) was an American farmer and politician who was elected to the Washington House of Representatives as part of the inaugural Washington State Legislature in 1889. He was the first African-American to serve in the Washington legislature. He introduced legislation that established Washington State University and tirelessly promoted Washington agriculture. In its obituary, the ''Morning Olympian'' newspaper described Bush as "one of the oldest and most famous pioneers of the state of Washington" and declared that "probably no resident of the state or territory throughout its history has done more to advertise the state than W. O. Bush". Early life Bush was born in Clay County, Missouri. He was the son of George Bush, a celebrated settler and veteran of the War of 1812 who inherited a portion of the substantial fortune of his father, Matthew, and Isabella James. Bush's father was of mixed race, while his mother was of German desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew County, Missouri
Andrew County is a county located in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the county had a population of 18,135. Its county seat is Savannah. The county was organized January 29, 1841, and named for Andrew Jackson Davis, a lawyer and prominent citizen of St. Louis. Andrew County is part of the St. Joseph, MO KS Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Kansas City, MO KS Combined statistical area. History The following material is inscribed on a plaque erected by the State Historical Society of Missouri and State Highway Commission in 1960, now located by the Andrew County Courthouse: Andrew County, organized 1841, is one of six counties in the Indian Platte Purchase Territory annexed to Missouri in 1837. Named for Andrew Jackson Davis, a St. Louis editor, the county was first settled in the middle 1830s. Pioneers were from Ohio, Indiana, Tennessee, Kentucky, Virginia, and other parts of Missouri. Savannah, the county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platte Purchase
The Platte Purchase was a land acquisition in 1836 by the United States government from American Indian tribes of the region. It comprised lands along the east bank of the Missouri River and added to the northwest corner of the state of Missouri. This expansion of the slave state of Missouri was in violation of the Missouri Compromise of 1820, which prohibited the extension of slavery in the former Louisiana Territory north of the parallel 36°30′ north, except within the boundaries of the state of Missouri, as defined at the time of the adoption of the Missouri Compromise. The area acquired was almost as large as the states of Delaware and Rhode Island combined, and extended Missouri westward along the river. St. Joseph, one of the main river ports of departure for the westward migration of American pioneers, was located in the new acquisition. The region of the Platte Purchase includes the following modern counties within its bounds: Andrew (435 square miles, 1127 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White People
White is a Race (human categorization), racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry. It is also a Human skin color, skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view. Description of populations as "White" in reference to their skin color is occasionally found in Greco-Roman ethnography and other ancient or medieval sources, but these societies did not have any notion of a White race or pan-European identity. The term "White race" or "White people", defined by their light skin among other physical characteristics, entered the major European languages in the later seventeenth century, when the concept of a "unified White" achieved greater acceptance in Europe, in the context of racialization, racialized slavery and social status in the European colonies. Scholarship on Race (human categorization), race distinguishes the modern concept from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave State
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were prohibited. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states to be politically imperative that the number of free states not exceed the number of slave states, so new states were admitted in slave–free pairs. There were, nonetheless, some slaves in most free states up to the 1840 census, and the Fugitive Slave Clause of the U.S. Constitution, as implemented by the Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 and the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850, provided that a slave did not become free by entering a free state and must be returned to his or her owner. Enforcement of these laws became one of the controversies that arose between slave and free states. By the 18th century, slavery was legal throughout the Thirteen Colonies, but at the time of the American Revolution, rebel colonies started to abolish the prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |