|
George P. L. Walker
George Patrick Leonard Walker (2 March 1926 – 17 January 2005) was a British geologist who began his career studying mineralogy and later made significant contributions to volcanology. He was widely regarded as one of the pioneers of modern quantitative volcanology. Biography Walker was born in Harlesden, on 2 March 1926. He was the only child of Leonard Walker, an insurance salesman, and Evelyn Frances (nee McConkey), a nurse. He went to school at Acton Lane Elementary School, and won a scholarship to Willesden County School in 1937. In 1939, Walker and his mother were in Ballinderry, County Antrim, when World War II broke out. They stayed in Ballindery, and Walker completed his schooling at Wallace High School, Lisburn. Walker went to Queen's University, Belfast to study geology and graduated with a BSc in 1948, and an MSc in 1949. He then went on to study for a PhD at the University of Leeds, under the supervision of W Q Kennedy. His dissertation focused on the seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College London
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a Public university, public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a Albertopolis, cultural district in South Kensington that included museums, colleges, and the Royal Albert Hall. In 1907, these colleges – the Royal College of Science, the Royal School of Mines, and the City and Guilds of London Institute – merged to form the Imperial College of Science and Technology. In 1988, Imperial merged with St Mary's Hospital, London, St Mary's Hospital Medical School and then with Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School to form the Imperial College School of Medicine. The Imperial Business School was established in 2003 and officially opened by Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Formerly a constituent college of the University of London, Imperial became an independent university in 2007. Imperial is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballinderry, County Antrim
Ballinderry is a civil parish and townland (of 1182 acres) in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is situated in the historic barony of Massereene Upper. Civil parish of Ballinderry The civil parish contains the villages of: *Lower Ballinderry * Upper Ballinderry Townlands The civil parish contains the following townlands: A Aghacarnan, Aghadavy, Aghanamoney, Aghanliss B Ballinderry, Ballykelly, Ballylacky, Ballymaclose, Ballymacrevan, Ballyscolly, Brackenhill C Cluntirriff, Crew Park D Derrykillultagh, Drumanduff G Gortrany K Kilcreeny L Legatirriff, Loughrelisk, Lurganteneil, Lurgill M Moneycrumog, Moygarriff P Portmore T Templecormac, Tullyballydonnell Notable people * Samuel Kelly, coal merchant and businessmanhttps://shippingtandy.com/features/john-kelly-belfast/ See also * List of townlands of County Antrim *List of civil parishes of County Antrim In Ireland County, Counties are divided into civil parishes in Ireland, civil parishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Falcon
The Order of the Falcon () is the only order of chivalry in Iceland, founded by Christian X of Denmark, King Christian X of Denmark and Iceland on 3 July 1921. The award is awarded for merit for Iceland and humanity and has five degrees. Nowadays, appointments are made on the nomination of the President of Iceland and that of a "five-member council." History and appointments Christian X of Denmark, Christian X, the King of Denmark, ruled Iceland until 17 June 1944. During his royal visit to Iceland in 1921, King Christian X issued the royal decree founding the Icelandic Order of the Falcon. When Iceland became a republic, new statutes were incorporated for the Order on 11 July 1944. The Republic of Iceland replaced the King by an elected List of Presidents of Iceland, President of Iceland who is the designated Grand Master (order), Grand Master of this Order. It may be awarded to both Icelanders and citizens of other countries for achievements in Iceland or internationally. A fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of New Zealand
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family or royalty Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), 2021 * Royal (Ayo album), 2020 * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * '' The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * '' The Raja Saab'', working title ''Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
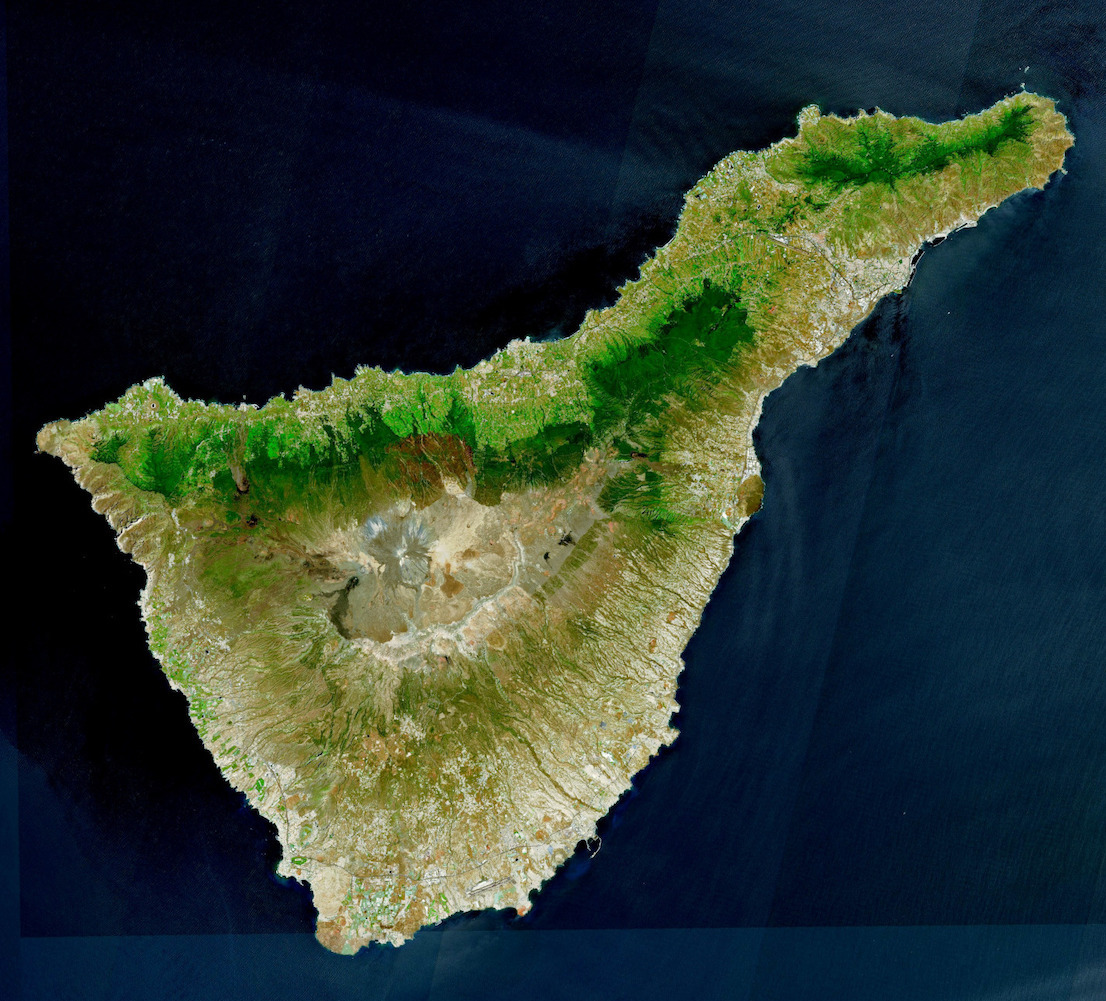
Tenerife
Tenerife ( ; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. With a land area of and a population of 965,575 inhabitants as of April 2025, it is the most populous island in Spain and the entire Macaronesia region. Tenerife is also home to 42.7% of the total population of the archipelago. More than seven million tourists (7,384,707 in 2024) visit Tenerife each year, making it by far the most visited island in the archipelago. It is one of the most important tourist destinations in Spain and the world, hosting one of the world's largest carnivals, the Carnival of Santa Cruz de Tenerife. The capital of the island, , is also the seat of the island council (). That city and are the co-capitals of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Canary Islands. The two cities are both home to governmental institutions, such as the offices of the preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about west of Lisbon, about northwest of Morocco, about southeast of Newfoundland, Canada, and the same distance southwest of Cork, Ireland. Its main industries are agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing, and tourism, which has become a major service activity in the region. In the 20th century and to some extent into the 21st, they have served as a waypoint for refueling aircraft flying between Europe and North America. The government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The largest city of the Azores is Ponta Delgada. The culture, dialect, cuisine, and traditions of the Azorean islands vary considerably, because these remote island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Rocks
Pyroclastic rocks are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater. The word ''pyroclastic'' is derived from the Greek , meaning fire; and , meaning broken. Unconsolidated accumulations of pyroclasts are described as tephra. Tephra may become lithified to a pyroclastic rock by cementation or chemical reactions as the result of the passage of hot gases ( fumarolic alteration) or groundwater (e.g. hydrothermal alteration and diagenesis) and burial, or, if it is emplaced at temperatures so hot that the soft gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( or ; , or ; ; or ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina, Italy, Messina and Catania. It is located above the Convergent boundary, convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is one of the tallest active volcanoes in Europe, and the tallest peak in Italy south of the Alps with a current height (September 2024) of , though this varies with summit eruptions. For instance, in 2021 the southeastern crater reached a height of , but was then surpassed by the Voragine crater after the summer 2024 eruptions. Etna covers an area of with a basal circumference of . This makes it by far the largest of the three volcanism in Italy, active volcanoes in Italy, being about two and a half times the height of the next largest, Mount Vesuvius. Only Teide, Mount Teide on Tenerife in the Canary Islands surpasses it in the whole of the Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surtsey
Surtsey ("Surtr's island" in Icelandic, ) is an uninhabited volcanic island located in the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago off the southern coast of Iceland. At Surtsey is the southernmost point of Iceland. It was formed in a volcanic eruption which began below sea level, and reached the surface on 14 November 1963. The eruption lasted until 5 June 1967, when the island reached its maximum size of . Since then, wave erosion has caused the island to steadily diminish in size: , its surface area was . The most recent survey (2007) shows the island's maximum elevation at above sea level. The new island was named after Surtr, a fire ''jötunn'' or giant from Norse mythology. It was intensively studied by volcanologists during its eruption, and afterwards by botanists and other biologists as life forms gradually colonised the originally barren island. The undersea vents that produced Surtsey are part of the Vestmannaeyjar submarine volcanic system, part of the fissure of the sea floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reader (academic Rank)
The title of reader in the United Kingdom and some universities in the Commonwealth of Nations, for example India, Australia and New Zealand, denotes an appointment for a senior academic with a distinguished international reputation in research or scholarship. In the traditional hierarchy of British and other Commonwealth universities, reader (and principal lecturer in the new universities) are academic ranks above senior lecturer and below Chaired Professor, recognising a distinguished record of original research. Reader is a professor without a chair, similar to the distinction between professor and chaired professor in Hong Kong and between ''professor extraordinarius and'' ''professor ordinarius'' at some European universities. Readership is one/two rank(s) more prestigious than senior/permanent Lecturership, which translate to Associate/Assistant Professorship. Readers in the UK would correspond to the start of full professors in China and the United States.Graham WebbMak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a cultural district in South Kensington that included museums, colleges, and the Royal Albert Hall. In 1907, these colleges – the Royal College of Science, the Royal School of Mines, and the City and Guilds of London Institute – merged to form the Imperial College of Science and Technology. In 1988, Imperial merged with St Mary's Hospital Medical School and then with Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School to form the Imperial College School of Medicine. The Imperial Business School was established in 2003 and officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II. Formerly a constituent college of the University of London, Imperial became an independent university in 2007. Imperial is organised into four faculties: Engineering, Medicine, Natural Sciences, and Business. The university fosters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964. Colonization of the Congo Basin, Colonial rule in the Congo began in the late 19th century. Leopold II of the Belgians, King Leopold II of the Belgians attempted to persuade the Federal Government of Belgium, Belgian government to support colonial expansion around the then-largely unexploited Congo Basin. Their ambivalence resulted in Leopold establishing a colony himself. With support from a number of Berlin Conference, Western countries, Leopold achieved international recognition of the Congo Free State in 1885. By the turn of the century, the violence used by Free State officials against indigenous Congolese and a ruthless system of economic exploitation led to intense diplomatic pressure on Belgium to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |