|
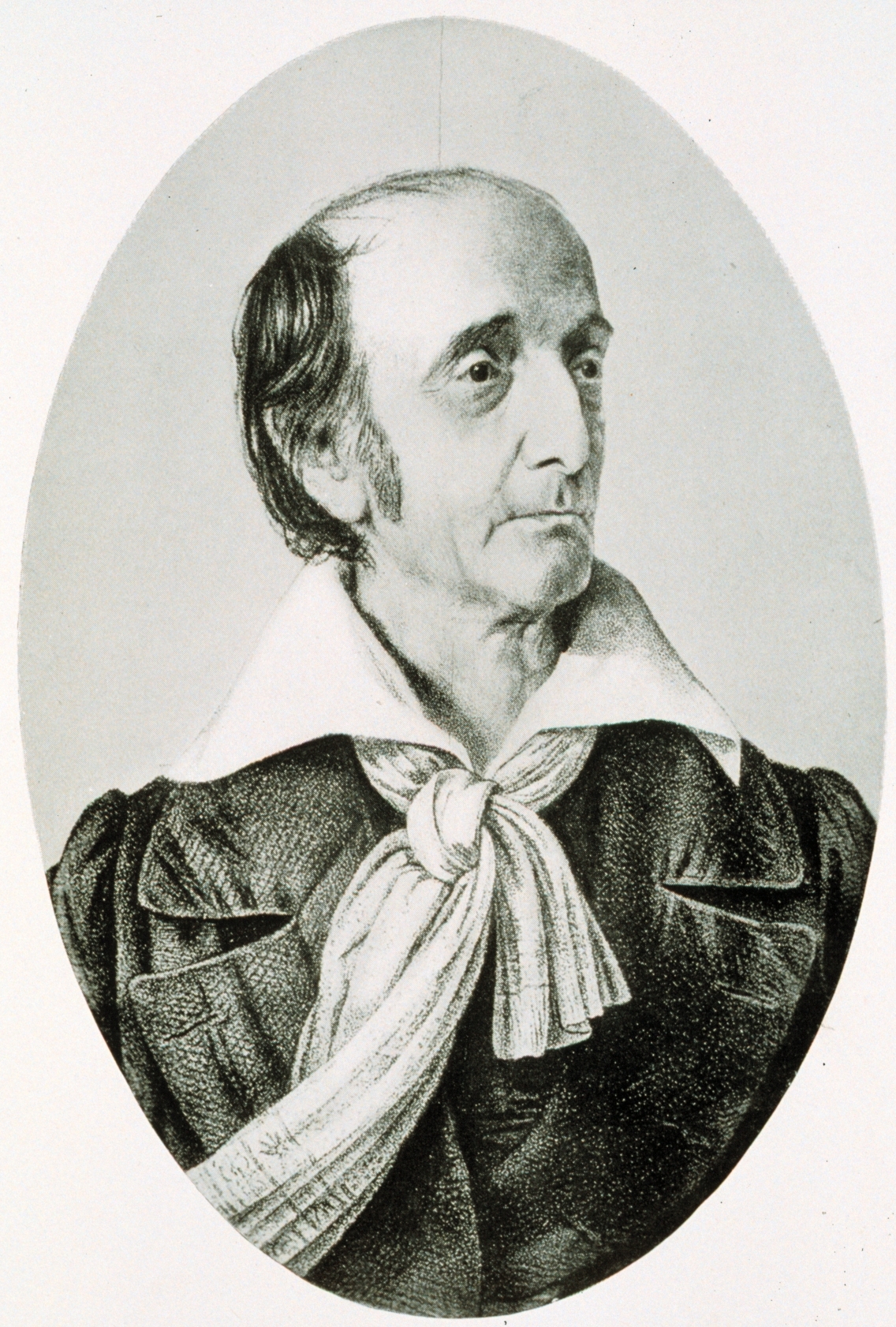
George Mifflin Bache
George Mifflin Bache, Jr. (November 12, 1841 – February 11, 1896) was an officer in the United States Navy, fighting on the Union side in the American Civil War and continuing to serve for a decade after the war's end. The ''Fletcher''-class destroyer was named for him. Early life and ancestors He was born in Washington, D.C., to Lt. George Mifflin Bache, USN, who was lost at sea in 1846, and Elizabeth Catherine Patterson.There is a monument in the Congressional Cemetery on Washington to the elder Lt. Bache and the 22 men under his command who were lost in that incident. He was the grandson of Richard Bache, Jr., who served in the Republic of Texas navy and was an elected representative in the Texas legislature, and Sophia Burrell Dallas, daughter of Arabella Maria Smith and Alexander James Dallas, who served as the U.S. Treasury Secretary under President James Madison. He was also a great-grandson of Sarah Franklin Bache and Richard Bache, and a great-great-grandson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast And Geodetic Survey
The United States Coast and Geodetic Survey ( USC&GS; known as the Survey of the Coast from 1807 to 1836, and as the United States Coast Survey from 1836 until 1878) was the first scientific agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States Government. It existed from 1807 to 1970, and throughout its history was responsible for mapping and charting the coast of the United States, and later the coasts of Territories of the United States, U.S. territories. In 1871, it gained the additional responsibility of surveying the interior of the United States and geodesy became a more important part of its work, leading to it being renamed the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878. Long the U.S. government's only scientific agency, the Survey accumulated other scientific and technical responsibilities as well, including astronomy, cartography, metrology, meteorology, geology, geophysics, hydrography, navigation, oceanography, exploration, Piloting, pilotage, tides, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannon, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured swarm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's Drainage basin, watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky Mountains, Rocky and Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian mountains. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the world's List of rivers by discharge, tenth-largest river by discharge flow, and the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Sloop
Steam frigates (including screw frigates) and the smaller steam corvettes, steam sloops, steam gunboats and steam schooners, were steam-powered warships that were not meant to stand in the line of battle. The first such ships were paddle steamers. Later on the invention of screw propulsion enabled construction of screw-powered versions of the traditional frigates, corvettes, sloops and gunboats. Evolution First steam warships The first small vessel that can be considered a steam warship was the '' Demologos'', which was launched in 1815 for the United States Navy. From the early 1820s, the British Navy began building a number of small steam warships including the armed tugs and , and by the 1830s the navies of America, Russia and France were experimenting with steam-powered warships. Hellenic sloop-of-war '' Kartería'' (Καρτερία; Greek for "Perseverance") was the first steam-powered warship to be used in combat operations in history. It was built in 1825 in an Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Historical Center
The Naval History and Heritage Command, formerly the Naval Historical Center, is an Echelon II command responsible for the preservation, analysis, and dissemination of U.S. naval history and heritage located at the historic Washington Navy Yard. The NHHC is composed of 42 facilities in 13 geographic locations including the Navy Department Library, 10 museums and 1 heritage center, USS ''Constitution'' repair facility and detachment, and historic ship ex-USS ''Nautilus''. Command history The Naval History and Heritage Command traces its lineage to 1800, when President John Adams requested Benjamin Stoddert, the first Secretary of the Navy, prepare a catalog of professional books for use in the Secretary's office. When the British invaded Washington in 1814, this collection, containing the finest works on naval history from America and abroad, was rushed to safety outside the Federal City. After that, the library had many locations, including a specially designed space in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a United States Service academies, federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as United States Secretary of the Navy, Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the second oldest of the five United States service academies, U.S. service academies and it educates midshipmen for service in the officer corps of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. It is part of the Naval University System. The campus is located on the former grounds of Fort Severn at the confluence of the Severn River (Maryland), Severn River and Chesapeake Bay in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, Anne Arundel County, east of Washington, D.C., and southeast of Baltimore. The entire campus, known colloquially as the Yard, is a National Historic Landmark and home to many historic sites, buildings, and monuments. It replaced Philadelphia Naval Asylum in Phila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wainwright (American Civil War Naval Officer)
Commander Richard Wainwright (January 15, 1817 – August 10, 1862) was an officer in the United States Navy during the American Civil War who commanded , flagship of Admiral David G. Farragut's West Gulf Blockading Squadron. Early life Wainwright was born in Charlestown, Massachusetts, on January 15, 1817. He was the son of Robert Dewar Wainwright and Maria Montresor Auchmuty. He was a cousin of Comdr. Jonathan Wainwright (naval officer), Jonathan Mayhew Wainwright. Career Wainwright was commissioned in the United States Navy on May 11, 1831. He attended the naval school at Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk, Virginia, in 1837–1838, and became a passed midshipman on June 15, 1837. From 1838 to 1841, he served with the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, United States Coast Survey in the brig ''Consort''. He was commissioned Lieutenant (naval), lieutenant on September 8, 1841 and commanded the Steamship, steamer in the U.S.Navy's Home Squadron from 1848 to 1849, served again o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master's Mate
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the British Royal Navy, Royal Navy, United States Navy and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of sub-lieutenant in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers. Royal Navy Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a senior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his Commissioned officer#Commissioned officers, commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a First-rate, first rate, three on a Third-rate, third rate, and two on most frigates. Duties Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a Topgallant sail, topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a Course (sail), fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are Gaff rig, gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. Etymology The term "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The term may be related to a Scots language, Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. History The exact origins of schooner rigged vessels are obscure, but by early 17th century they appear in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The earliest known il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all unrated warships, including List of gun-brigs of the Royal Navy, gun-brigs and Cutter (boat), cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fire ships were classed by the Royal Navy as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the role of a sloop-of-war when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of the First World War and the highly successful of the Second World War, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capabilities. They performed similar duties to the destroyer escorts of the United States Navy, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain's Clerk
A captain's clerk was a naval rating, rating, now obsolete, in the Royal Navy and the United States Navy for a person employed by the Captain (nautical), captain to keep his Document, records, communication, correspondence, and Account (accountancy), accounts. The regulations of the Royal Navy demanded that a purser serve at least one year as a captain's clerk, so the latter was often a young man working his way to a purser's warrant. He had high status, with an office on the Deck (ship)#Common names for decks, quarterdeck or Deck (ship)#Common names for decks, upper deck on most ships. He was paid at the same rate as a midshipman in 1800, but by 1815 he had almost the same monthly pay as a Warrant Officer#Standing warrant officers, standing warrant officer. On large ships, he had his own cabin in the gunroom, but on smaller vessels he lived with the midshipmen on the orlop deck. Duties Once commissioned, a ship required a great deal of paperwork to keep her in good order. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |