|
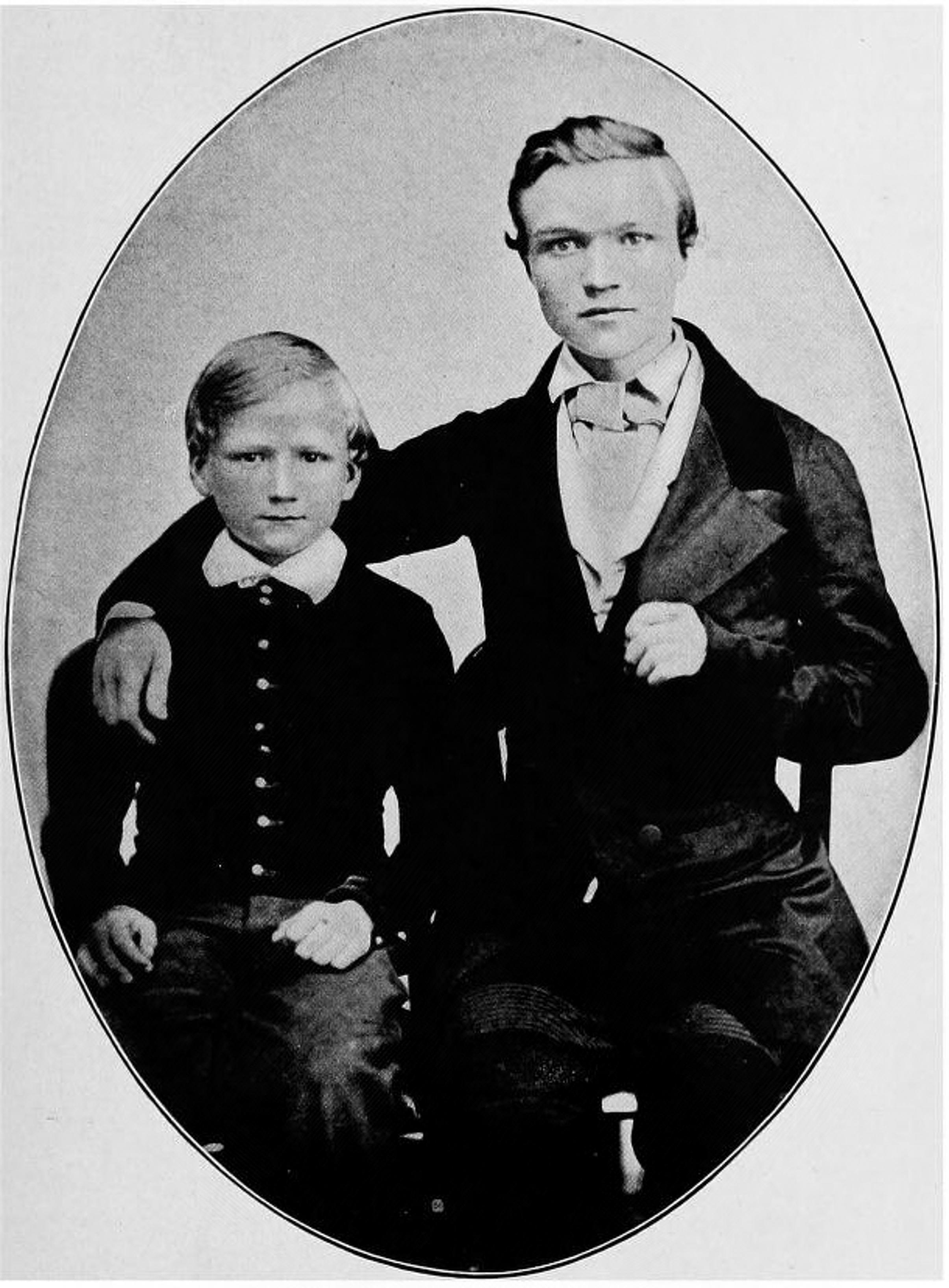
George Lauder, Sr.
George Lauder (9 May 1815 – 18 November 1901) was a political leader in Scotland who was the father of Scottish industrialist George Lauder and surrogate father to his nephew Andrew Carnegie. He was the also the progenitor of the Lauder Greenway Family. Lauder has been described as Carnegie's "intellectual father." Lauder was consistently credited by Carnegie throughout his lifetime, saying in his 1920 autobiography: "...a man whose influence on me cannot be underestimated, my Uncle Lauder." Early life Lauder. was born in Dunfermline, Scotland to George Lauder and Margaret Muir. His father was a well-to-do owner of a snuff mill that he had inherited from his father. At 25, Lauder opened a shop on 8 High Street Dunfermline (which still stands today, although it is now a café) which would become a de facto school for his nephew and son. Civic life As a Chartist, Lauder was deeply involved in securing democratic enfranchisement (voting rights) for all citizens of the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunfermline
Dunfermline (; , ) is a city, parish, and former royal burgh in Fife, Scotland, from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. Dunfermline was the de facto capital of the Kingdom of Scotland between the 11th and 15th centuries. The earliest known settlements around Dunfermline probably date to the Neolithic period, growing by the Bronze Age. The city was first recorded in the 11th century, with the marriage of Malcolm III of Scotland, and Saint Margaret of Scotland, Saint Margaret at Dunfermline. As List of Scottish consorts, Queen consort, Margaret established a church dedicated to the Trinity, Holy Trinity, which evolved into Dunfermline Abbey under their son David I of Scotland, David I in 1128, and became firmly established as a prosperous royal mausoleum for the Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish Crown. A total of eighteen royals, including seven Kings, were buried here between 1093 and 1420 including Robert the Bruce in 1329. By the 18th century, Dunfermline became a regiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauder College
Carnegie College (formerly Lauder College) was a further education college based in Halbeath, Dunfermline, Fife, Scotland. It was established in 1899, with financial support from George Lauder and Andrew Carnegie and named after their father and uncle, respectively, George Lauder, Sr. In 2007, it was renamed Carnegie College in honour of Andrew Carnegie, Lauder's cousin, the steel magnate and philanthropist born in Dunfermline. On 1 August 2013 Carnegie College and Adam Smith College came together to form Fife College, creating a new college for the region in line witGovernment legislation The land-based elements of Scotland’s Rural College, SRUC Elmwood College, were also incorporated in the new Fife College providing a wide range of courses to choose from. Before merging with Adam Smith, Carnegie College had around 11,000 students every year and offered over 350 programs at various levels, from introductory and national qualifications to higher national standards and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Philanthropists
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland * Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland * Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian-era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina (Spanish ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Nationalists
Scottish independence (; ) is the idea of Scotland regaining its independence and once again becoming a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom. The term Scottish independence refers to the political movement that is campaigning to bring it about. Scotland was an independent kingdom through the Middle Ages, and fought wars to maintain its independence from England. The two kingdoms were united in personal union in 1603 when the Scottish King James VI became James I of England, and the two kingdoms united politically into one kingdom called Great Britain in 1707. This movement united the countries which ended the wars of independence and created relative peace. Political campaigns for Scottish self-government began in the 19th century, initially in the form of demands for home rule within the United Kingdom. Two referendums on devolution were held in 1979 and 1997, with a devolved Scottish Parliament being established on 1 July 1999. The pro-independence Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartists
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, with particular strongholds of support in Northern England, the East Midlands, the Staffordshire Potteries, the Black Country and the South Wales Valleys, where working people depended on single industries and were subject to wild swings in economic activity. Chartism was less strong in places such as Bristol, that had more diversified economies. The movement was fiercely opposed by government authorities, who finally suppressed it. Support for the movement was at its highest when petitions signed by millions of working people were presented to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. The strategy employed was to use the scale of support which these petitions and the accompany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Family
Carnegie may refer to: People *Carnegie (surname), including a list of people with the name **Andrew Carnegie, Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist * Clan Carnegie, a lowland Scottish clan Institutions Named for Andrew Carnegie * Carnegie Building (Troy, New York), on the campus of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute * Carnegie College, in Dunfermline, Scotland, a former further education college * Carnegie Community Centre, in downtown Vancouver, British Columbia * Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs *Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, a global think tank with headquarters in Washington, DC, and four other centers, including: **Carnegie Middle East Center, in Beirut ** Carnegie Europe, in Brussels ** Carnegie Moscow Center *Carnegie Foundation (other), any of several foundations *Carnegie Hall, a concert hall in New York City * Carnegie Hall, Inc., a regional cultural center in Lewisburg, West Virginia * Carnegie Hero Fund *Carnegie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1901 Deaths
December 13 of this year is the beginning of signed 32-bit computing, 32-bit Unix time, and is scheduled to end in Year 2038 problem, January 19, 2038. Summary Political and military 1901 started with the Federation of Australia, unification of multiple Crown colony, British colonies in Australia on January 1 to form the Australia, Commonwealth of Australia after a 1898–1900 Australian constitutional referendums, referendum in 1900, Subsequently, the 1901 Australian federal election, 1901 Australian election would see the first Prime Minister of Australia, Australian prime minister, Edmund Barton. On the same day, Nigeria became a Colonial Nigeria, British protectorate. Following this, the Victorian era, Victorian Era would come to a end after Queen Victoria died on January 22 after a reign of 63 years and 216 days, which was List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign, longer than those of any of her predecessors, Her son, Edward VII, succeeded her to the throne. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1815 Births
Events January * January 2 – Lord Byron marries Anna Isabella Milbanke in Seaham, county of Durham, England. * January 3 – Austria, Britain, and Bourbon-restored France form a secret defensive alliance treaty against Prussia and Russia. * January 8 – Battle of New Orleans: American forces led by Andrew Jackson defeat British forces led by Sir Edward Pakenham. American forces suffer around 60 casualties and the British lose about 2,000 (the battle lasts for about 30 minutes). * January 13 – War of 1812: British troops capture Fort Peter in St. Marys, Georgia, the only battle of the war to take place in the state. * January 15 – War of 1812: Capture of USS ''President'' – American frigate , commanded by Commodore Stephen Decatur, is captured by a squadron of four British frigates. February * February 3 – The first commercial cheese factory is founded in Switzerland. * February 4 – The first Dutch student association, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife College
Fife College is a further and higher education college based in various towns across the region of Fife, Scotland. Campuses The college's main campuses are located in Dunfermline, Glenrothes and Kirkcaldy with smaller campuses in Leven, Fife, Leven, and Rosyth. The college also operates community learning centres across Fife. History Fife College was created on 1 August 2013 as a merger of Adam Smith College, Carnegie College and non land based elements of the Elmwood College, Elmwood Campus of the rural college SRUC. When the merger was announced in March of that year the new principal was named as Hugh Logan, formerly principal of Motherwell College. Following the retirement of Hugh Logan, Hugh Hall was appointed as principal, taking office on 1 March 2017. After six years in the role, Hugh Hall stood down to be replaced, in April 2023, by Jim Metcalfe, former Chief Executive at College Development Network. In March 2016, the college announced that it had secured the op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology and began granting four-year degrees. In 1967, it became Carnegie Mellon University through its merger with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. The university consists of seven colleges, including the College of Engineering, the School of Computer Science, and the Tepper School of Business. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from downtown Pittsburgh. It also has over a dozen degree-granting locations in six continents, including campuses in Qatar, Silicon Valley, and Kigali, Rwanda ( Carnegie Mellon University Africa) and partnerships with universities nationally and glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie ( , ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the History of the iron and steel industry in the United States, American steel industry in the late-19th century and became one of the List of richest Americans in history, richest Americans in history. He became a leading philanthropist in the United States, Great Britain, and the British Empire. During the last 18 years of his life, he gave away around $350 million (equivalent to $ billion in ), almost 90 percent of his fortune, to charities, foundations and universities. His 1889 article proclaiming "The Gospel of Wealth" called on the rich to use their wealth to improve society, expressed support for progressive taxation and an Inheritance tax, estate tax, and stimulated a wave of philanthropy. Carnegie was born in Dunfermline, Scotland. He immigrated to what is now Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States with his parents in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |