|
George Clark (historian)
Sir George Norman Clark, (27 February 1890 – 6 February 1979) was an English historian, academic and British Army officer. He was the Chichele Professor of Economic History at the University of Oxford from 1931 to 1943 and the Regius Professor of Modern History at the University of Cambridge from 1943 to 1947. He served as the provost of Oriel College, Oxford, from 1947 to 1957. Early life and education Clark was born on 27 February 1890 in Halifax, Yorkshire, England, to James Walker Clark and his wife Mary Clark (née Midgley). He was educated at Bootham School, a private boarding school in York, and at Manchester Grammar School, a grammar school in Manchester. In 1908, he matriculated into Balliol College, Oxford, to study classics as a Brackenbury Scholar. In 1911, he achieved a first class in '' Literae Humaniores''. He then changed to modern history and graduated in 1912 with a first class honours Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree. In 1912, he was elected to a prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax, West Yorkshire
Halifax is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Calderdale, in West Yorkshire, England. It is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. In the 15th century, the town became an economic hub of the old West Riding of Yorkshire, primarily in woollen manufacture with the large Piece Hall square later built for trading wool in the town centre. The town was a thriving mill town during the Industrial Revolution with the Dean Clough Mill buildings a surviving landmark. In 2021, it had a population of 88,109. It is also the administrative centre of the wider Calderdale Metropolitan Borough. Toponymy The town's name was recorded in about 1091 as ''Halyfax'', most likely from the Old English ''halh-gefeaxe'', meaning "area of coarse grass in the of land". This explanation is generally preferred to derivations from the Old English ' (holy), in ''hālig feax'' or "holy hair", proposed by 16th-century antiquarians. The probably-incorrect interpretation gave rise to two legends. One concern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boarding School
A boarding school is a school where pupils live within premises while being given formal instruction. The word "boarding" is used in the sense of "room and board", i.e. lodging and meals. They have existed for many centuries, and now extend across many countries. Their functioning, codes of conduct, and ethos vary greatly. Children in boarding schools study and live during the school year with their fellow students and possibly teachers or administrators. Some boarding schools also have day students who attend the institution during the day and return home in the evenings. Boarding school pupils are typically referred to as "boarders". Children may be sent for one to twelve years or more in boarding school, until the age of eighteen. There are several types of boarders depending on the intervals at which they visit their family. Full-term boarders visit their homes at the end of an academic year, semester boarders visit their homes at the end of an academic term, weekly boarders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons. These may include isolating them from enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and Repatriation, repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishment, prosecution of war crimes, labour exploitation, recruiting or even conscripting them as combatants, extracting collecting military and political intelligence, and political or religious indoctrination. Ancient times For much of history, prisoners of war would often be slaughtered or enslaved. Early Roman gladiators could be prisoners of war, categorised according to their ethnic roots as Samnites, Thracians, and Gauls (''Galli''). Homer's ''Iliad'' describes Trojan and Greek soldiers offeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
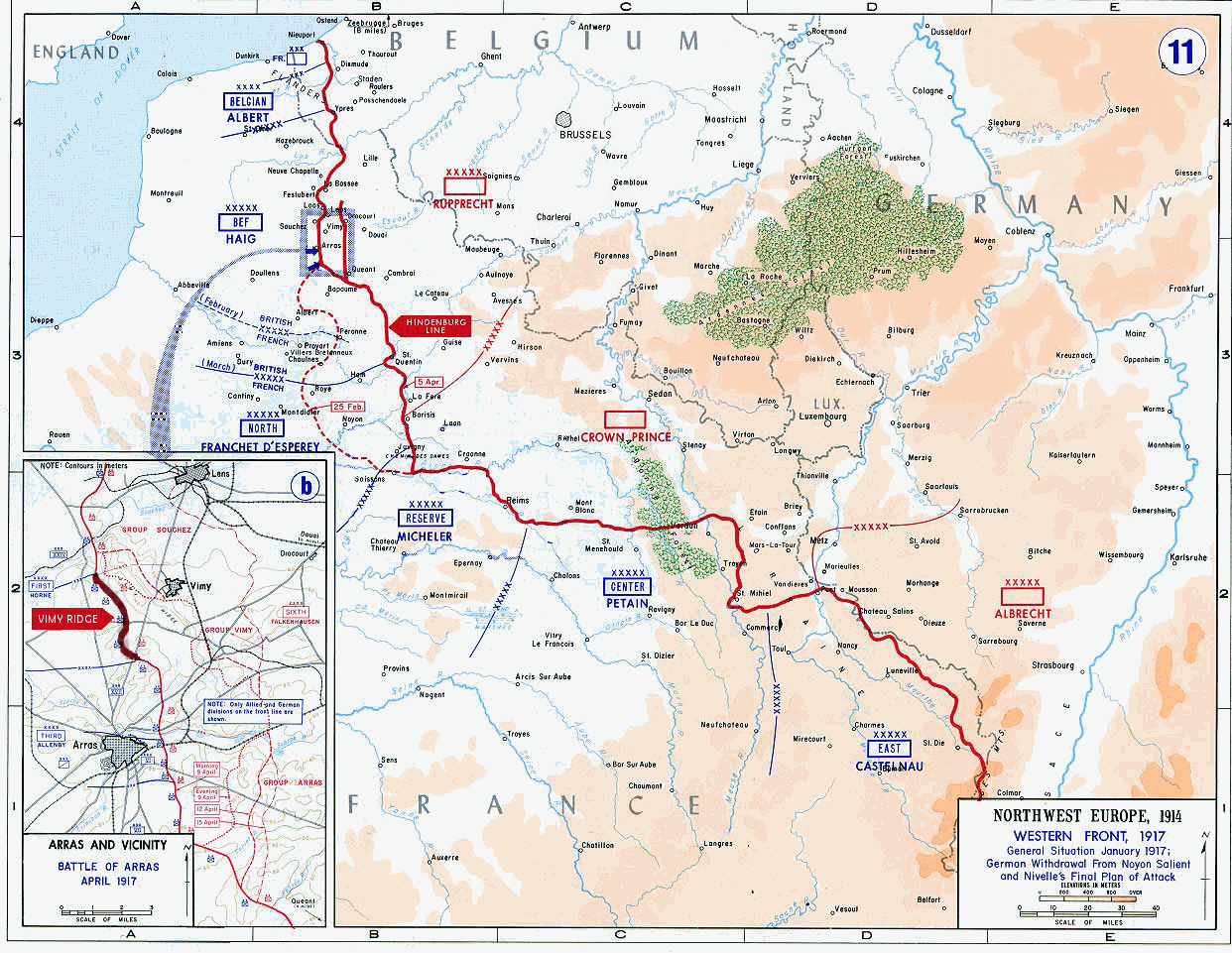
Battle Of Vimy Ridge
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was part of the Battle of Arras, in the Pas-de-Calais department of France, during the First World War. The main combatants were the four divisions of the Canadian Corps in the First Army, against three divisions of the German 6th Army. The battle occurred from 9 to 12 April 1917, marking the commencement of the Battle of Arras and serving as the inaugural assault of the Nivelle Offensive. The objective was to draw German reserves away from the French forces, preparing for a crucial offensive along the Aisne and the Chemin des Dames ridge several days later. The Canadian Corps was to capture the German-held high ground of Vimy Ridge, an escarpment on the northern flank of the Arras front. This would protect the First Army and the Third Army farther south from German enfilade fire. Supported by a creeping barrage, the Canadian Corps captured most of the ridge during the first day. The village of Thélus fell during the second day, as did the cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant (British Army And Royal Marines)
Lieutenant (; Lt) is a junior officer rank in the British Army and Royal Marines. It ranks above second lieutenant and below captain and has a NATO ranking code of OF-1 and it is the senior subaltern rank. Unlike some armed forces which use first lieutenant, the British rank is simply lieutenant, with no ordinal attached. The rank is equivalent to that of a flying officer in the Royal Air Force (RAF). Although formerly considered senior to a Royal Navy (RN) sub-lieutenant, the British Army and Royal Navy ranks of lieutenant and sub-lieutenant are now considered to be of equivalent status. The Army rank of lieutenant has always been junior to the Navy's rank of lieutenant. Usage In the 21st-century British Army, the rank is ordinarily held for up to three years. A typical appointment for a lieutenant might be the command of a platoon or troop of approximately thirty soldiers. Before 1871, when the whole British Army switched to using the current rank of "lieutenant", th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioned Officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service. Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent contextual qualification, the term typically refers only to a force's ''commissioned officers'', the more senior members who derive their authority from a commission from the head of state. Numbers The proportion of officers varies greatly. Commissioned officers typically make up between an eighth and a fifth of modern armed forces personnel. In 2013, officers were the senior 17% of the British armed forces, and the senior 13.7% of the French armed forces. In 2012, officers made up about 18% of the German armed forces, and about 17.2% of the United States armed forces. Historically armed forces have generally had much lower proportions of officers. During the First World War, fewer than 5% of British soldiers were officers (partly beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officers' Training Corps
The University Officers' Training Corps (UOTC), also known as the Officers' Training Corps (OTC), are British Army reserve units, under the command of the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst, which recruit exclusively from universities and focus on training and developing leadership. Their role is to allow university students the opportunity to undertake modules of Officer (armed forces), Reserve Officer training designed to fit around their degree and to develop the leadership abilities, skills and experience of their members, which could be useful in a future career in the British Army, or skills and training that can be utilised in a civilian career. While in the UOTC, Officer Cadets will undertake the Reserve Officer Training Modules (Selection and training in the British Army#Officers, Alpha & Bravo). University students serving with the UOTC are personnel of the Army Reserve (United Kingdom), Army Reserve, and are Oath of Allegiance (United Kingdom)#Armed forces, attested an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Souls College, Oxford
All Souls College (official name: The College of All Souls of the Faithful Departed, of Oxford) is a constituent college of the University of Oxford in England. Unique to All Souls, all of its members automatically become fellows (i.e., full members of the college's governing body). It has no student members, but each year, recent graduates are eligible to apply for a small number of examination fellowships through a competitive examination (once described as "the hardest exam in the world") and, for those shortlisted after the examinations, an interview.Is the All Souls College entrance exam easy now? , ''The Guardian'', 17 May 2010. The college entrance is on the north side of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Class Honours
The British undergraduate degree classification system is a grading structure used for undergraduate degrees or bachelor's degrees and integrated master's degrees in the United Kingdom. The system has been applied, sometimes with significant variation, in other countries and regions. The UK's university degree classification system, established in 1918, serves to recognize academic achievement beyond examination performance. Bachelor's degrees in the UK can either be honours or ordinary degrees, with honours degrees classified into First Class, Upper Second Class (2:1), Lower Second Class (2:2), and Third Class based on weighted averages of marks. The specific thresholds for these classifications can vary by institution. Integrated master's degrees follow a similar classification, and there is some room for discretion in awarding final classifications based on a student's overall performance and work quality. The honours degree system has been subject to scrutiny owing to signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackenbury Scholar
Hannah Brackenbury (1795–1873) was an English philanthropist. She was unmarried and had inherited wealth from James Brackenbury, a solicitor from Manchester, England, who had made money through involvement with the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway. Sources differ regarding whether James was her father or brother. Believing herself to be the last of the Brackenbury line, which she thought could be traced to Perse Brackenbury, who had married into the family of John Balliol around 1086 AD, she elected to engage in philanthropic endeavours in spheres that had connections to her relatives. Between 1865 and 1867, Brackenbury donated money to Balliol College at Oxford University to fund scholarships in history and natural sciences and to enable the construction of new buildings. The Brackenbury Scholarship at Balliol is funded to this day from her bequest and some of the buildings are named after the family. She had a brother, Ralph, who had been a doctor and scholarships in the Bracke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |