|
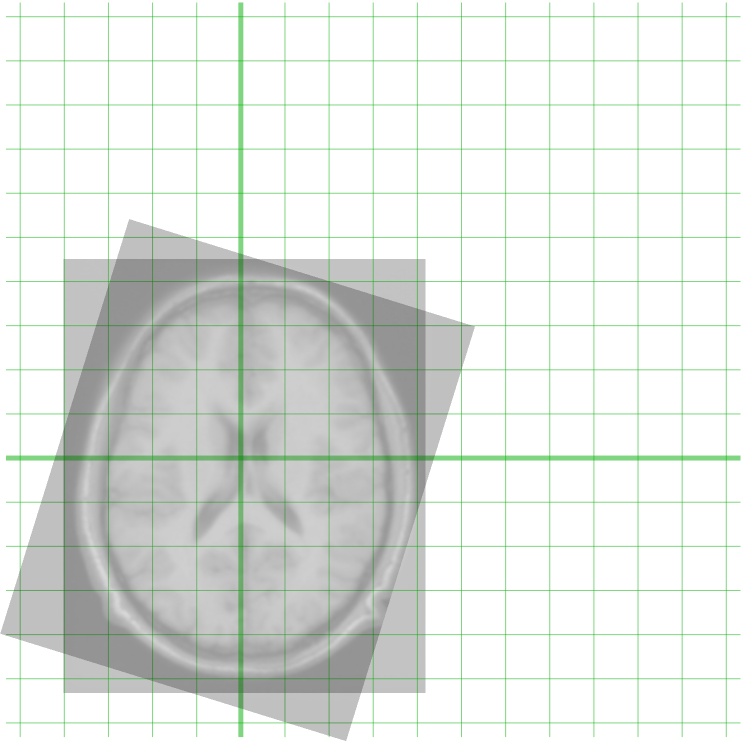
Georeferencing
Georeferencing or georegistration is a type of coordinate transformation that binds a digital raster image or vector database that represents a geographic space (usually a scanned map or aerial photograph) to a spatial reference system, thus locating the digital data in the real world. It is thus the geographic form of image registration or image rectification. The term can refer to the mathematical formulas used to perform the transformation, the metadata stored alongside or within the image file to specify the transformation, or the process of manually or automatically aligning the image to the real world to create such metadata. The most common result is that the image can be visually and analytically integrated with other geographic data in geographic information systems and remote sensing software. A number of mathematical methods are available, but the process typically involves identifying a sample of several ground control points (GCPs) with known locations on the image a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GIS File Format
A GIS file format or geospatial file format is a standard for encoding geographical information into a computer file. It is a specialized type of file format for use in geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing image processing tools, and other geospatial applications. Since the 1970s, dozens of formats have been created based on various data models for various purposes. They have been created by government mapping agencies (such as the USGS or National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency), GIS software vendors, standards bodies such as the Open Geospatial Consortium, informal user communities, and even individual developers. History The first GIS installations of the 1960s, such as the Canada Geographic Information System were based on bespoke software and stored data in bespoke file structures designed for the needs of the particular project. As more of these appeared, they could be compared to find best practices and common structures. When general-purpose GIS software w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Rectification
Image rectification is a transformation process used to project images onto a common image plane. This process has several degrees of freedom and there are many strategies for transforming images to the common plane. Image rectification is used in computer stereo vision to simplify the problem of finding matching points between images (i.e. the correspondence problem), and in geographic information systems (GIS) to merge images taken from multiple perspectives into a common map coordinate system. In computer vision Computer stereo vision takes two or more images with known relative camera positions that show an object from different viewpoints. For each pixel it then determines the corresponding scene point's depth (i.e. distance from the camera) by first finding matching pixels (i.e. pixels showing the same scene point) in the other image(s) and then applying triangulation (computer vision), triangulation to the found matches to determine their depth. Finding matches in stereo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubbersheeting
In cartography and geographic information systems, rubbersheeting is a form of coordinate transformation that warps a vector dataset to match a known geographic space. This is most commonly needed when a dataset has systematic positional error, such as one digitized from a historical map of low accuracy. The mathematics and procedure are very similar to the georeferencing of raster images, and this term is occasionally used for that process as well, but ''image georegistration'' is an unambiguous term for the raster process. Applications in history and historical geography Rubbersheeting is a useful technique in HGIS, where it is used to digitize and add old maps as feature layers in a modern GIS. Before aerial photography arrived, most maps were highly inaccurate by modern standards. Rubbersheeting may improve the value of such sources and make them easier to compare to modern maps. Software * ESRI's ArcGIS 8.3+ has the capability of rubbersheeting vector data, and Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocoding
Address geocoding, or simply geocoding, is the process of taking a text-based description of a location, such as an address or the name of a place, and returning geographic coordinates, frequently latitude/longitude pair, to identify a location on the Earth's surface. Reverse geocoding, on the other hand, converts geographic coordinates to a description of a location, usually the name of a place or an addressable location. Geocoding relies on a computer representation of address points, the street / road network, together with postal and administrative boundaries. * Geocode (''verb''): provide geographical coordinates corresponding to (a location). * Geocode (''noun''): is a code that represents a geographic entity ( location or object).In general is a human-readable and short identifier; like a nominal-geocode as ISO 3166-1 alpha-2, or a grid-geocode, as Geohash geocode. * Geocoder (''noun''): a piece of software or a (web) service that implements a geocoding process i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Reference System
A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS) is a framework used to precisely measure locations on the surface of Earth as coordinates. It is thus the application of the abstract mathematics of coordinate systems and analytic geometry to geographic space. A particular SRS specification (for example, "Universal Transverse Mercator WGS 84 Zone 16N") comprises a choice of Earth ellipsoid, Geodetic datum, horizontal datum, map projection (except in the geographic coordinate system), origin point, and unit of measure. Thousands of coordinate systems have been specified for use around the world or in specific regions and for various purposes, necessitating geographic coordinate conversion, transformations between different SRS. Although they date to the Hellenistic period, spatial reference systems are now a crucial basis for the sciences and technologies of Geoinformatics, including cartography, geographic information systems, surveying, remote sensing, and civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Registration
Image registration is the process of transforming different sets of data into one coordinate system. Data may be multiple photographs, data from different sensors, times, depths, or viewpoints. It is used in computer vision, medical imaging, military automatic target recognition, and compiling and analyzing images and data from satellites. Registration is necessary in order to be able to compare or integrate the data obtained from these different measurements. Algorithm classification Intensity-based vs feature-based Image registration or image alignment algorithms can be classified into intensity-based and feature-based.A. Ardeshir Goshtasby2-D and 3-D Image Registration for Medical, Remote Sensing, and Industrial Applications Wiley Press, 2005. One of the images is referred to as the ''target'', ''fixed'' or ''sensed'' image and the others are referred to as the ''moving'' or ''source'' images. Image registration involves spatially transforming the source/moving image(s) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Model (GIS)
A geographic data model, geospatial geographical measurements, or simply data from modules in the context of geographic information systems (GIS), is a mathematical and digital structure for representing phenomena over the Earth. Generally, such data modules represent various aspects of these phenomena by means of statistical data measurement, including locations, change over time. For example, the vector graphic data model represents geography as collections of points, lines, and arrays, and the elimination data model represent geography as space matrices that store numeric values. Data models are implemented throughout the GIS ecosystem, including the software tools for data management and spatial analysis, data stored in very specific languages of GIS file formats specifications and standards, and specific designs for GIS installations. While the unique nature of spatial information has led to its own set of model structures, much of the process of data modeling is similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinate System
A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical coordinate system, spherical or geodetic coordinates, geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating position (geometry), positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest, and most widely used type of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG Geodetic Parameter Dataset, EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Imagery
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs or "drones"), balloons, blimps and dirigibles, rockets, pigeons, kites, or using action cameras while skydiving or wingsuiting. Handheld cameras may be manually operated by the photographer, while mounted cameras are usually remotely operated or triggered automatically. Aerial photography typically refers specifically to bird's-eye view images that focus on landscapes and surface objects, and should not be confused with air-to-air photography, where one or more aircraft are used as chase planes that "chase" and photograph other aircraft in flight. Elevated photography can also produce bird's-eye images closely resembling aerial photography (despite not actually being aerial shots) when te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell images by licensing them to governments and businesses such as Apple Maps and Google Maps. History The first images from space were taken on Sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital flights. The US-launched V-2 flight on October 24, 1946, took one image every 1.5 seconds. With an Apsis, apogee of 65 miles (105 km), these photos were from five times higher than the previous record, the 13.7 miles (22 km) by the Explorer II balloon mission in 1935. The first satellite (orbital) photographs of Earth were made on August 14, 1959, by the U.S. Explorer 6. The first satellite photographs of the Moon might have been made on October 6, 1959, by the Soviet satellite Luna 3, on a mission to photograph the far side of the Moon. The Blue Marble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate Transformation
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are not interchangeable; they are commonly distinguished by their position in an ordered tuple, or by a label, such as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |