|
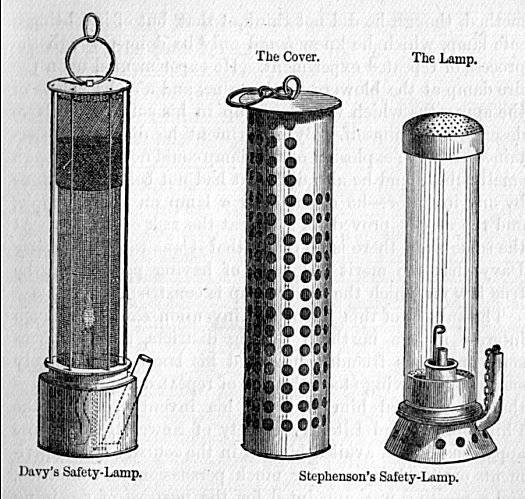
Geordie Lamp
The Geordie lamp was a safety lamp for use in flammable atmospheres, invented by George Stephenson in 1815 as a miner's lamp to prevent explosions due to firedamp in coal mines. Origin In 1815, Stephenson was the engine-wright at the Killingworth Colliery in Northumberland and had been experimenting for several years with candles close to firedamp emissions in the mine. In August, he ordered an oil lamp, which was delivered on 21 October and tested by him in the mine in the presence of explosive gases. He improved this over several weeks with the addition of capillary tubes at the base so that it gave more light, and tried new versions on 4 and 30 November. This was presented to the Literary and Philosophical Society of Newcastle upon Tyne (Lit & Phil) on 5 December 1815. Although controversy arose between Stephenson's design and the Davy lamp (invented by Humphry Davy in the same year), Stephenson's original design worked on significantly different principles from Davy's fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnsley
Barnsley () is a market town in South Yorkshire, England. It is the main settlement of the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley and the fourth largest settlement in South Yorkshire. The town's population was 71,422 in 2021, while the wider borough had a population of 244,600 in the 2021 census. Historic counties of England, Historically in the West Riding of Yorkshire, Barnsley is located on the M1 motorway, M1 corridor between the cities of Sheffield to the south and Wakefield to the north. Doncaster is to the east, Huddersfield to the north-west, and Manchester lies west across the Peak District to which it is connected to via the A628 road. Barnsley's former industries include linen, coal mining, glass making and textiles. Barnsley's culture is rooted in its industrial heritage and it has a tradition of brass bands, originally created as social clubs by its mining communities. History Following the Norman invasion of 1066, many abbeys and priories were built in Yorkshire. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Lamp
An oil lamp is a lamp used to produce light continuously for a period of time using an oil-based fuel source. The use of oil lamps began thousands of years ago and continues to this day, although their use is less common in modern times. They work in the same way as a candle but with fuel that is liquid at room temperature, so that a container for the oil is required. A textile wick drops down into the oil, and is lit at the end, burning the oil as it is drawn up the wick. Oil lamps are a form of lighting, and were used as an alternative to candles before the use of electric lights. Starting in 1780, the Argand lamp quickly replaced other oil lamps still in their basic ancient form. These in turn were replaced by the kerosene lamp in about 1850. In small towns and rural areas the latter continued in use well into the 20th century, until such areas were finally Electrification, electrified and light bulbs could be used. Sources of fuel for oil lamps include a wide variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Coal Mining
The history of coal mining goes back thousands of years, with early mines documented in ancient China, the Roman Empire and other early historical economies. It became important in the Industrial Revolution of the 19th and 20th centuries, when it was primarily used to power steam engines, heat buildings and generate electricity. Coal mining continues as an important economic activity today, but has begun to decline due to coal's strong contribution to global warming and environmental issues, which result in decreasing demand and in some geographies, peak coal. Compared to wood fuels, coal yields a higher amount of energy per unit mass, specific energy or massic energy, and can often be obtained in areas where wood is not readily available. Though it was used historically as a domestic fuel, coal is now used mostly in industry, especially in smelting and alloy production, as well as electricity generation. Large-scale coal mining developed during the Industrial Revolution, and coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Inventions
English inventions and discoveries are objects, processes or techniques invented, innovated or discovered, partially or entirely, in England by a person from England. Often, things discovered for the first time are also called inventions and in many cases, there is no clear line between the two. Nonetheless, science and technology in England continued to develop rapidly in absolute terms. Furthermore, according to a Japanese research firm, over 40% of the world's inventions and discoveries were made in the UK, followed by France with 24% of the world's inventions and discoveries made in France and followed by the US with 20%. The following is a list of inventions, innovations or discoveries known or generally recognised to be English. Agriculture * 1701: Seed drill improved by Jethro Tull (1674–1741). *18th century: of the horse-drawn hoe and scarifier by Jethro Tull * 1780s: Selective breeding and artificial selection pioneered by Robert Bakewell (1725–1795). * 1842: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheat Lamp
A wheat lamp is a type of incandescent light designed for use in underground mining, named for inventor Grant Wheat and manufactured by Koehler Lighting Products in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, United States, a region known for extensive mining activity. A safety lamp designed for use in potentially hazardous atmospheres such as firedamp and coal dust, the lamp is mounted on the front of the miner's helmet and powered by a wet cell battery worn on the miner's belt. The average wheat lamp uses a three to five watt bulb which will typically operate for five to 16 hours depending on the amp-hour capacity of the battery and the current draw of the bulb being used.L. C. Isley, A. B. Hooker, ''Permissible Electric Mine Lamps'', US Department of Commerce Bulletin No. 332, 1930, pp. 32-34 A grain-of-wheat lamp is an unrelated, very small incandescent lamp An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp that provides illumination in places such as coal mines where the air may carry coal dust or a build-up of flammable gases, which may explode if ignited, possibly by an electric spark. Until the development of effective electric lamps in the early 1900s, miners used flame lamps to provide illumination. Open flame lamps could ignite flammable gases which collected in mines, causing explosions; safety lamps were developed to enclose the flame to prevent it from igniting the explosive gases. Flame safety lamps have been replaced for lighting in mining with sealed explosion-proof electric lights, but continue to be used to detect gases. Background Damps or gases Miners have traditionally referred to the various gases encountered during mining as damps, from the Middle Low German word ''dampf'' (meaning "vapour"). Damps are variable mixtures and are historic terms. * '' Firedamp'' Naturally occurring flammable mixtures, principally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Light Sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic energy, and include light bulbs and stars like the Sun. Reflectors (such as the moon, cat's eyes, and mirrors) do not actually produce the light that comes from them. Incandescence Incandescence is the emission of light from a hot body as a result of its temperature. * * Combustion Lamps * (obsolete) * * * (error) * * * * * *s * (obsolete) * * Other * - shock wave * * * * * * * * * * * * * Nuclear and high-energy particle * * ** ** * * * * * Celestial and atmospheric * Astronomical objects ** Sun (sunlight, solar radiation) *** *** **Star ( Starlight) *** Nova / supernova / hypernova *** **** *** ** *** *** *** *** *** * ** Meteor *** ** *** *Lightning ( Plasma) ** ** ** ** * Luminescence Luminesce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracts Vol 19 P35 George Stephenson's Safety Lamp
Tract may refer to: Geography and real estate * Housing tract, an area of land that is subdivided into smaller individual lots * Land lot or tract, a section of land * Census tract, a geographic region defined for the purpose of taking a census Writings * Tract (literature), a short written work, usually of a political or religious nature * Tract (liturgy), a component of Roman Catholic liturgy * Treatise Biology * Nerve tract, a bundle of fibers that connects different parts of the central nervous system - analogous to a nerve in the peripheral nervous system * A genetic tract, a sequence of repeating nucleotides or amino acids, such as a polyglutamine tract * A collection of related anatomic structures, such as: ** Gastrointestinal tract ** Genitourinary tract ** Reproductive tract ** A grouping of feathers, e.g. primaries, auricular, scapular Businesses * Tract (imprint), an imprint of the German group VDM Publishing devoted to the reproduction of Wikipedia content See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Glass
Safety glass is glass with additional safety features that make it less likely to break, or less likely to pose a threat when broken. Common designs include toughened glass (also known as tempered glass), laminated glass, and wire mesh glass (also known as wired glass). Toughened glass was invented in 1874 by Francois Barthelemy Alfred Royer de la Bastie. Wire mesh glass was invented in 1892 by Frank Shuman. Laminated glass was invented in 1903 by the French chemist :fr:Édouard_Bénédictus, Édouard Bénédictus (1878–1930). These three approaches can easily be combined, allowing for the creation of glass that is at the same time toughened, laminated, and contains a wire mesh. However, combination of a wire mesh with other techniques is unusual, as it typically betrays their individual qualities. In many developed countries safety glass is part of the building code, building regulations making properties safer. Toughened glass Toughened glass is processed by controlled he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oaks Explosion
The Oaks explosion, which happened at a coal mine in West Riding of Yorkshire on 12 December 1866, remains the worst mining disaster in England. A series of explosions caused by firedamp ripped through the underground workings at the Oaks Colliery at Hoyle Mill near Stairfoot in Barnsley killing 361 miners and rescuers. It was the worst mining disaster in the United Kingdom until the 1913 Senghenydd explosion in Wales. Oaks Colliery The first shaft at the Oaks Colliery was sunk in the early 1830s. In 1845 two separate explosions occurred at the colliery. On both occasions few men were below ground and no more than three or four workers died. Two years later a more serious incident occurred after firedamp, which had accumulated in old workings, was ignited and exploded. Of the men underground, 73 were killed and 26 were rescued. Changes were then made to the colliery's ventilation. The downcast shaft was converted to upcast with a furnace at its foot. Two abandoned shafts w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |