|
Geological Event
A geological event is a temporary and spatially heterogeneous and dynamic (diachronous) happening in Earth history that contributes to the transformation of Earth system and the formation of geological strata. Event stratigraphy was first proposed as a system for the recognition, study and correlation of the effects of important physical or biological events on the broader stratigraphical record. Geological events range in time span by orders of magnitude, from seconds to millions of years, and in spatial scale from local to regional and, ultimately, global. In contrast to chronostratigraphic or geochronological units, that define the boundaries between periods, epochs and other units of the geologic time scale, complex dynamic diachronous changes are inherent to the event-stratigraphy paradigm. The lithostratigraphic or biostratigraphic boundaries that mark the onset and termination of geological events in the stratigraphic record may be diachronous, whereas those of form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dansgaard–Oeschger Event
A Dansgaard–Oeschger event (often abbreviated D–O event), is a rapid climate fluctuation; such events occurred 25 times during the last glacial period. Some scientists say that the events occur quasi-periodically with a recurrence time being a multiple of 1,470 years, but this is debated. The comparable climate cyclicity during the Holocene is referred to as Bond events. ''Dansgaard–Oeschger'' refers to palaeoclimatologists Willi Dansgaard and Hans Oeschger. Evidence The best evidence for Dansgaard–Oeschger events remains in the Greenland ice cores, which only go back to the end of the last interglacial, the Eemian interglacial (about 115,000 years ago). Ice core evidence from Antarctic cores suggests that the Dansgaard–Oeschger events are related to the so-called Antarctic Isotope Maxima by means of a coupling of the climate of the two hemispheres, the Polar see-saw. If this relationship holds also for the previous glacials, Antarctic data suggest that D-O events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
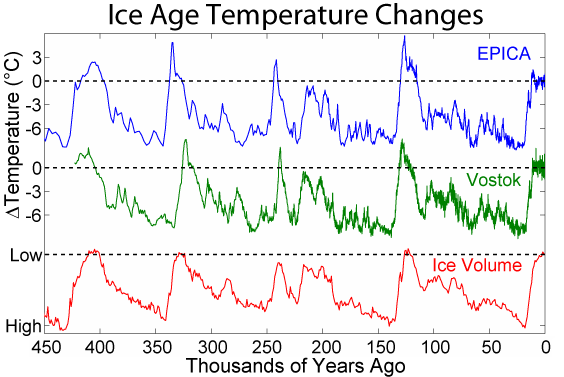
Glacial Cycle
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and greenhouse periods during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the ice age called Quaternary glaciation. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed ''glacial periods'' (''glacials, glaciations, glacial stages, stadials, stades'', or colloquially, ''ice ages''), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called ''interglacials'' or ''interstadials''. In glaciology, the term ''ice age'' is defined by the presence of extensive ice sheets in the northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, the current Holocene epoch is an interglacial period of an ice age. The accumulation of anthropogenic greenhouse gases is projected to delay the next glacial period. History of research In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires .... Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ice formed over a range of years. Cores are Ice drilling, drilled with hand Auger (drill), augers (for shallow holes) or powered drills; they can reach depths of over two miles (3.2 km), and contain ice up to 800,000 years old. The physical properties of the ice and of material trapped in it can be used to reconstruct the climate over the age range of the core. The proportions of different oxygen and hydrogen isotopes provide information about Paleothermometer, ancient temperatures, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstadial
Stadials and interstadials are phases dividing the Quaternary period, or the last 2.6 million years. Stadials are periods of colder climate, and interstadials are periods of warmer climate. Each Quaternary climate phase has been assigned with a marine isotope stage (MIS) number, which describes the alternation between warmer and cooler temperatures, as measured by oxygen isotope data. Stadials have even MIS numbers, and interstadials have odd MIS numbers. The current Holocene interstadial is MIS 1, and the Last Glacial Maximum stadial is MIS 2. Marine isotope stages are sometimes subdivided into stadials and interstadials by minor climate fluctuations within the overall stadial or interstadial, which are indicated by letters. The odd-numbered interstadial MIS 5, also known as the Sangamonian interglacial, contains two periods of relative cooling, and so is subdivided into three interstadials (5a, 5c, 5e) and two stadials (5b, 5d). A stadial isotope stage like MIS 6 wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the Phanerozoic eon. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a proposed third epoch, the Anthropocene, was rejected in 2024 by IUGS, the governing body of the ICS. The Quaternary is typically defined by the Quaternary glaciation, the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event
The Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event (GOBE) was an evolutionary radiation of animal life throughout the Ordovician period, 40 million years after the Cambrian explosion, whereby the distinctive Cambrian fauna fizzled out to be replaced with a Paleozoic fauna rich in suspension feeder and pelagic animals. It followed a series of Cambrian–Ordovician extinction events, and the resulting fauna went on to dominate the Palaeozoic relatively unchanged. Marine diversity increased to levels typical of the Palaeozoic, and morphological disparity was similar to today's. The diversity increase was neither global nor instantaneous; it happened at different times in different places. Consequently, there is unlikely to be a simple or straightforward explanation for the event; the interplay of many geological and ecological factors likely produced the diversification. Duration According to a comprehensive study of biodiversity throughout the Palaeozoic, GOBE began 497.05 Ma and ende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |