|
Geography Of Ladakh
Ladakh is an administrative territory of India that has been under its control since 1947. The geographical region of Ladakh union territory is the highest altitude plateau region in India (much of it being over 3,000 m), incorporating parts of the Himalayan and Karakoram mountain ranges and the upper Indus River and valley. Political geography Historic Ladakh consists of a number of distinct areas (mainly under Indian rule), including the fairly populous main Indus valley, the more remote Zanskar (in the south) and Nubra valleys (to the north over Khardung La in the Ladakh mountain range, a high motorable pass at ), the almost deserted Aksai Chin (under Chinese rule) and the predominantly Shi'ite Muslim Kargil and Suru valley areas in the west (Kargil being the second most important town in Ladakh). Historically populated by the Ladakhi people, continued immigration and preferential treatment to Kashmiris by the J&K government have led to demographic changes in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kargil District
Kargil district is a district in Indian-administered Ladakh in the Kashmir#Dispute, disputed Kashmir-region,The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TERTIARY, tertiary sources (a) through (e), reflecting WP:DUE, due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (h) through (i) below, "held" is also considered politicised usage, as is the term "occupied," (see (j) below). (a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, the last two being part of a territory called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Springs, Changlung Valley
Gogra (also referred to as Nala Junction) is a pasture and campsite in the Ladakh union territory of India, near the Line of Actual Control with China. It is located in the Kugrang River valley, a branch valley of Chang Chenmo Valley, where the Changlung River flows into Kugrang. During the times of the British Raj, Gogra was a halting spot for travellers to Central Asia via the 'Chang Chenmo route', who proceeded through the Changlung river valley and the Aksai Chin plateau. In the late 1950s, China began to claim the Changlung river valley as its own territory. India established an outpost on a low pass overlooking the Nala Junction on 2 July 1962. Clashes occurred during the Sino-Indian War but the post held out. During the 2020–2022 skirmishes, the area around Gogra was again a scene of conflict, and continues to be a subject of active dispute between the two countries. Geography The Chang Chenmo ("Great Northern") Valley lies in a depression between the Karakora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Springs, Chang Chenmo Valley
__NOTOC__ Hot Springs (traditional name: Kyam) is a campsite and the location of an Indian border outpost in the Chang Chenmo River valley in Ladakh near the disputed border with China. It is so named because there is a hot spring at this location. The Line of Actual Control near Kongka Pass is only to the east. Name Historically, the name for the hot spring was ''Kyam'' (''Kiam'', ''Kayam''). The Chinese still refer to it by this name. Geography Geologist Frederic Drew states that the Chang Chenmo river flows on a barren gravel bed, with occasional alluvium, alluvial patches where vegetation is found. Hot Springs is one such location. In the vicinity are also other such patches, named Pamzal, Tsogtsalu (or ''Tsolu'') and Gogra, Ladakh, Gogra. They were historical halting places for travellers and trading caravans, with a supply of water, fuel and fodder. Nomadic Ladakhi graziers also used them for grazing cattle. A large tributary called Kugrang River, Kugrang joins t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsimik La
Marsimik La or Marsemik La, also called Lankar La, elevation is a high mountain pass in the Chang Chenmo Range in the Indian union territory of Ladakh, east of Leh as the crow flies. Ladakh's route to the Chang Chenmo Valley traverses the pass. Geography Marsimik La is located about northeast of Lukung at the tip of Pangong Lake, and southwest of Pamzal in the Chang Chenmo Valley. The ridge line of Marsimik La divides the basin of the Pangong Lake from the Chang Chenmo River. The description of Marsimik La in the ''Gazetteer of Kashmir and Ladak'' (1890) states:About 4 km to the east of Marsimik La is another ridge line which divides the western portion of the Pangong Lake basin with the central portion that drains into the lake via the Khurnak Plain. China's claimed border and the present Line of Actual Control runs through this ridge line. The passes Kiu La () and Ane La () lie on this ridge line. The river Kiu Chu flows down from Kiu La and joins Chume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakoram Pass
The Karakoram Pass () is a mountain pass between India and China in the Karakoram Range. It is the highest pass on the ancient caravan route between Leh in Ladakh and Yarkant County, Yarkand in the Tarim Basin. The name 'Karakoram' comes from a Turkic languages, Turkic language meaning 'Black Gravel'. Historically, the high altitude of the pass and the lack of fodder were responsible for the deaths of countless pack animals while the route was notorious for the trail of bones strewn along the way. There is an almost total absence of vegetation on the approaches to the pass. Travelling south from the pass involved three days' march across the barren Depsang Plains at about . To the north, the country was somewhat less desolate and involved travellers crossing the relatively easy and lower Suget Dawan (or Suget Pass) before reaching the lush grazing grounds around Shahidullah or Xaidulla in the upper valley of the Karakash River. The pass is in a col, saddle between two mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changchenmo Range
Chang Chenmo River or Changchenmo River is a tributary of the Shyok River, part of the Indus River system. It is at the southern edge of the disputed Aksai Chin region and north of the Pangong Lake basin in Ladakh. The source of Chang Chenmo is near the Lanak Pass in the Chinese-administered region of Jammu & Kashmir (as part of the Rutog County in Tibet). The river flows west from Lanak La. At the middle of its course lies the Kongka Pass, part of the Line of Actual Control between India and China passes. Continuing west, the river enters a deep gorge in the Karakoram Range until it joins the Shyok River in Ladakh. Name Chang Chenmo means "Great Northern" in Tibetic languages. It is primarily the name of the valley rather than the river. Geography The Chang Chenmo Valley lies in a depression between the Karakoram Range in the north and the Changchenmo Range in the south. The depression continues into Tibet, all the way to Yeshil Kul (Bangda Co) and Lake L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakoram Range
The Karakoram () is a mountain range in the Kashmir region spanning the border of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwestern extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range is within Pakistan's Gilgit-Baltistan region, the northern subdivision of Kashmir. Karakoram's highest and the world's second-highest peak, K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan. The mountain range begins in the Wakhan Corridor in Afghanistan in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, controlled by Pakistan and then extends into Ladakh, controlled by India and Aksai Chin, controlled by China. It is part of the larger Trans-Himalayan mountain ranges. The Karakoram is the second-highest mountain range on Earth and part of a complex of ranges that includes the Pamir Mountains, Hindu Kush, and the Indian Himalayas. The range contains 18 summits higher than in elevation, with four above : K2 ( AMSL) (the second-highest peak on Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh2
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India and China since 1959.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TERTIARY, tertiary sources (a) through (e), reflecting WP:DUE, due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (h) through (i) below, "held" is also considered politicised usage, as is the term "occupied", (see (j) below). (a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
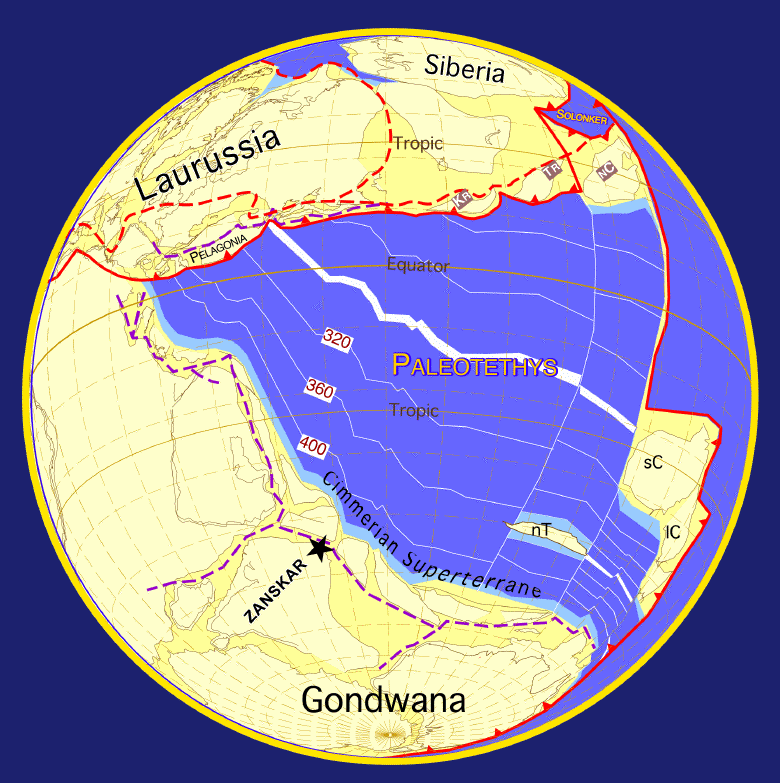
Geology Of The Himalaya
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift (nearly 10 mm/year at Nanga Parbat), the highest relief (8848 m at Mt. Everest Chomolangma), among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian plate (or India plate) is or was a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana and began moving north, carrying Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian plate to form a single Indo-Australian plate, but recent studies suggest that India and Australia may have been separate plates for at least 3 million years. The Indian plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China, western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan, and Balochistan in Pakistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian plate formed part of the supercontinent, Gondwana, together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana fragmented as these continents drifted apa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |