|
Geocomposite
Geocomposites are combinations of two or more geosynthetic materials for civil engineering applications that perform multiple geosynthetic functions; the five basic functions are: separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and containment. Such composite materials may enhance technical properties of the soil or the geotechnical structure and minimize application costs. Geotextile-geonet composites When a geotextile is used on one or both sides of a geonet, the separation and filtration functions are always satisfied, but the drainage function is vastly improved in comparison to geotextiles by themselves. Such geocomposites are regularly used in intercepting and conveying leachate in landfill liner and cover systems and for conducting vapor or water beneath pond liners of various types. These drainage geocomposites also make effective drains to intercept water in a capillary zone where frost heave or salt migration is a problem. In all cases, the liquid enters through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynthetics
Geosynthetics are synthetic products used to stabilize terrain. They are generally polymeric products used to solve civil engineering problems. This includes eight main product categories: geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomembranes, geosynthetic clay liners, geofoam, geocells and geocomposites. The polymeric nature of the products makes them suitable for use in the ground where high levels of durability are required. They can also be used in exposed applications. Geosynthetics are available in a wide range of forms and materials. These products have a wide range of applications and are currently used in many civil, geotechnical, transportation, geoenvironmental, hydraulic, and private development applications including roads, airfields, railroads, embankments, retaining structures, reservoirs, canals, dams, erosion control, sediment control, landfill liners, landfill covers, mining, aquaculture and agriculture. History Inclusions of different sorts mixed with soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
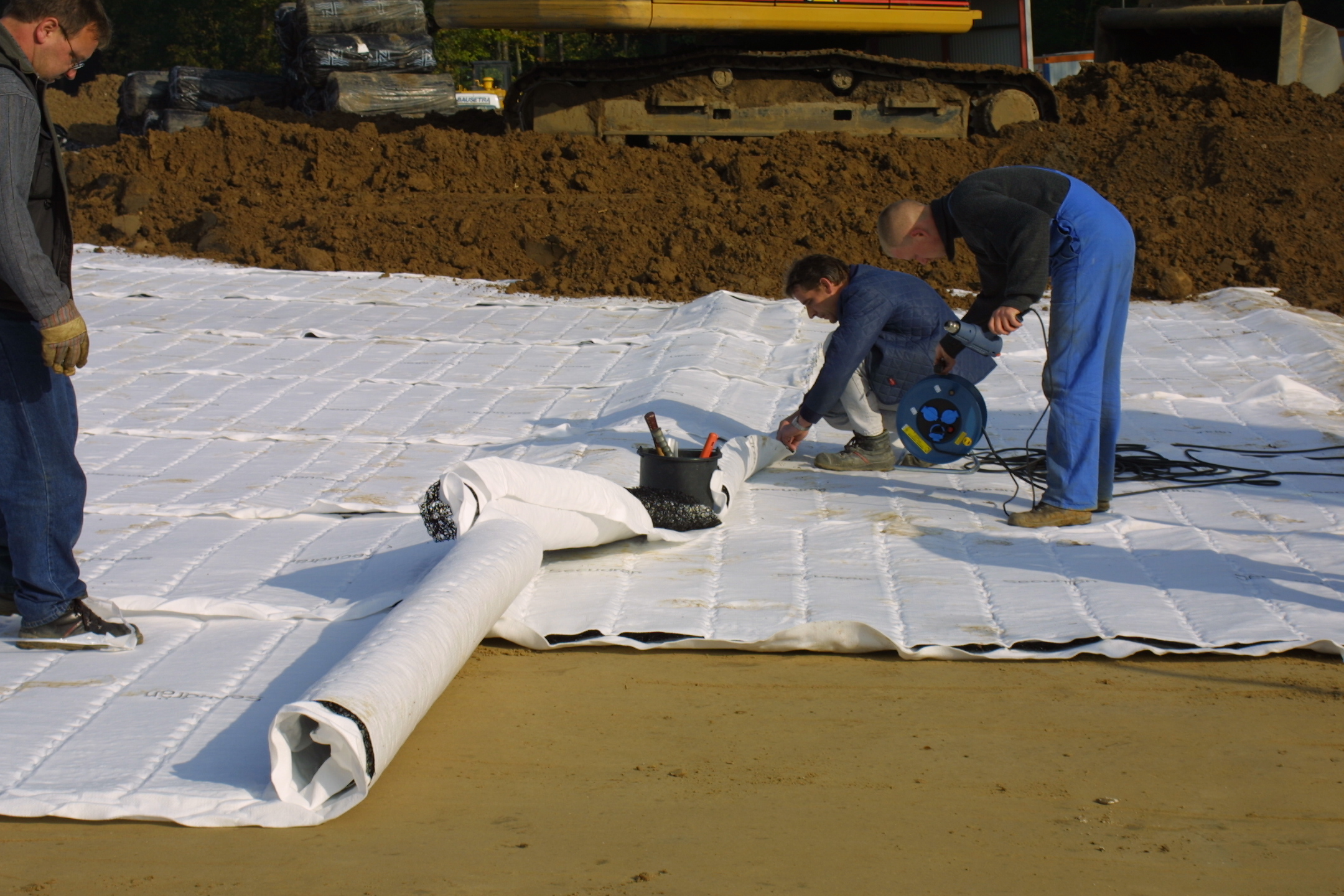
Geocomposite Drain Installation2
Geocomposites are combinations of two or more geosynthetic materials for civil engineering applications that perform multiple geosynthetic functions; the five basic functions are: separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and containment. Such composite materials may enhance technical properties of the soil or the geotechnical structure and minimize application costs. Geotextile-geonet composites When a geotextile is used on one or both sides of a geonet, the separation and filtration functions are always satisfied, but the drainage function is vastly improved in comparison to geotextiles by themselves. Such geocomposites are regularly used in intercepting and conveying leachate in landfill liner and cover systems and for conducting vapor or water beneath pond liners of various types. These drainage geocomposites also make effective drains to intercept water in a capillary zone where frost heave or salt migration is a problem. In all cases, the liquid enters through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geonets
A geonet is a geosynthetic material similar in structure to a geogrid, consisting of integrally connected parallel sets of ribs overlying similar sets at various angles for in-plane drainage of liquids or gases. Geonets are often laminated with geotextiles on one or both surfaces and are then referred to as drainage geocomposites. They are competitive with other drainage geocomposites having different core configurations. Manufacturing Geonets are formed by a continuous extrusion process into a netlike configuration of parallel sets of homogeneously interconnected ribs. There are three categories of geonets. The following are illustrated: * ''Biplanar geonets:'' These are the original and most common types and consist of two sets of intersecting ribs at different angles and spacings. The ribs themselves are of different sizes and shapes for different styles. * ''Triplanar geonets:'' These have parallel central ribs with smaller sets of ribs above and beneath mainly for geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leachate
A leachate is any liquid that, in the course of passing through matter, extracts soluble or suspended solids, or any other component of the material through which it has passed. Leachate is a widely used term in the environmental sciences where it has the specific meaning of a liquid that has dissolved or entrained environmentally harmful substances that may then enter the environment. It is most commonly used in the context of land-filling of putrescible or industrial waste. In the narrow environmental context leachate is therefore any liquid material that drains from land or stockpiled material and contains significantly elevated concentrations of undesirable material derived from the material that it has passed through. Landfill leachate Leachate from a landfill varies widely in composition depending on the age of the landfill and the type of waste that it contains. It usually contains both dissolved and suspended material. The generation of leachate is caused principall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste. In more mathematical or scientific terms, it signifies the level of performance that uses the least amount of inputs to achieve the highest amount of output. It often specifically comprises the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome with a minimum amount or quantity of waste, expense, or unnecessary effort.Sickles, R., and Zelenyuk, V. (2019).Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency: Theory and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . Efficiency refers to very different inputs and outputs in different fields and industries. In 2019, the European Commission said: "Resource efficiency means using the Earth's limited resources in a sustainable procent manner while minimising impacts on the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended function adequately for a specified period of time, OR will operate in a defined environment without failure. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The ''reliability function'' is theoretically defined as the probability of success. In practice, it is calculated using different techniques, and its value ranges between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates no probability of success while 1 indicates definite success. This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets, or through reliability testing and reliability modeling. Availability, testability, maintainability, and maintenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining Operations
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasibly created Chemical synthesis, artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include Metal#Extraction, metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk mining, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even fossil water, water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, and final mine reclamation, reclamation or restoration of the land after the mine is closed. Mining ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |