|
General Intelligence Factor
The ''g'' factor is a construct developed in psychometric investigations of cognitive abilities and human intelligence. It is a variable that summarizes positive correlations among different cognitive tasks, reflecting the assertion that an individual's performance on one type of cognitive task tends to be comparable to that person's performance on other kinds of cognitive tasks. The ''g'' factor typically accounts for 40 to 50 percent of the between-individual performance differences on a given cognitive test, and composite scores ("IQ scores") based on many tests are frequently regarded as estimates of individuals' standing on the ''g'' factor.Kamphaus et al. 2005 The terms '' IQ, general intelligence, general cognitive ability, general mental ability'', and simply ''intelligence'' are often used interchangeably to refer to this common core shared by cognitive tests.Deary et al. 2010 However, the ''g'' factor itself is a mathematical construct indicating the level of observed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometric
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally covers specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of Latent variable, latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, Mental disorder, mental disorders, and Educational measurement, educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are Statistical inference, inferred through mathematical model, mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications, such as degrees or certifications, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritability Of IQ
Research on the heritability of intelligence quotient (IQ) inquires into the degree of variation in IQ within a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. There has been significant controversy in the academic community about the heritability of IQ since research on the issue began in the late nineteenth century. Intelligence in the normal range is a polygenic trait, meaning that it is influenced by more than one gene, and in the case of intelligence at least 500 genes. Further, explaining the similarity in IQ of closely related persons requires careful study because environmental factors may be correlated with genetic factors. Outside the normal range, certain single gene genetic disorders, such as phenylketonuria, can negatively affect intelligence. Early twin studies of adult individuals have found a heritability of IQ between 57% and 73%, with some recent studies showing heritability for IQ as high as 80%. IQ goes from being weakly corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rote Memory
Rote learning is a memorization technique based on repetition. The method rests on the premise that the recall of repeated material becomes faster the more one repeats it. Some of the alternatives to rote learning include meaningful learning, associative learning, spaced repetition and active learning. Versus critical thinking Rote learning is widely used in the mastery of foundational knowledge. Examples of school topics where rote learning is frequently used include phonics in reading, the periodic table in chemistry, multiplication tables in mathematics, anatomy in medicine, cases or statutes in law, basic formulae in any science, etc. By definition, rote learning eschews comprehension, so by itself it is an ineffective tool in mastering any complex subject at an advanced level. For instance, one illustration of rote learning can be observed in preparing quickly for exams, a technique which may be colloquially referred to as " cramming". Rote learning is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raven's Progressive Matrices
Raven's Progressive Matrices (often referred to simply as Raven's Matrices) or RPM is a non-verbal test typically used to measure general human intelligence and abstract reasoning and is regarded as a non-verbal estimate of fluid intelligence. It is one of the most common tests administered to both groups and individuals ranging from 5-year-olds to the elderly.Kaplan, R. M., & Saccuzzo, D. P. (2009). Standardized tests in education, civil service, and the military. Psychological testing: Principles, applications, and issues (7 ed. pp. 325–327). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. It comprises 60 multiple choice questions, listed in order of increasing difficulty. This format is designed to measure the test taker's reasoning ability, the eductive ("meaning-making") component of Spearman's ''g'' (''g'' is often referred to as general intelligence). The tests were originally developed by John C. Raven in 1936.Raven, J. C. (1936). ''Mental tests used in genetic studies: The performance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Wechsler
David "Weshy" Wechsler (; January 12, 1896 – May 2, 1981) was a Romanian-American psychologist. He developed well-known intelligence scales, such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) to get to know his patients at Bellevue Hospital. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Wechsler as the 51st most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Early life and education Wechsler was born in a Jewish family in Lespezi, Romania, and emigrated with his parents to the United States as a child. He studied at the City College of New York and Columbia University, where he earned his master's degree in 1917 and his Ph.D. in 1925 under the direction of Robert S. Woodworth. During World War I, he worked with the United States Army to develop psychological tests to screen new draftees while studying under Charles Spearman and Karl Pearson. Career Bellevue Hospital After short stints at various locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling Error
In statistics, sampling errors are incurred when the statistical characteristics of a population are estimated from a subset, or sample, of that population. Since the sample does not include all members of the population, statistics of the sample (often known as estimators), such as means and quartiles, generally differ from the statistics of the entire population (known as parameters). The difference between the sample statistic and population parameter is considered the sampling error.Sarndal, Swenson, and Wretman (1992), Model Assisted Survey Sampling, Springer-Verlag, For example, if one measures the height of a thousand individuals from a population of one million, the average height of the thousand is typically not the same as the average height of all one million people in the country. Since sampling is almost always done to estimate population parameters that are unknown, by definition exact measurement of the sampling errors will not be possible; however they can often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
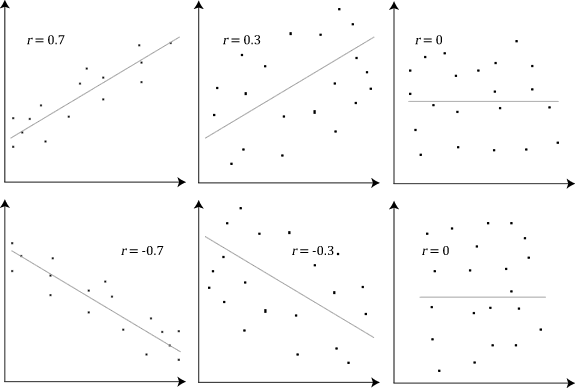
Correlation Matrix
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Visualization Ability
Spatial visualization ability or visual-spatial ability is the ability to mentally manipulate 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional figures. It is typically measured with simple cognitive tests and is predictive of user performance with some kinds of user interfaces. Measurement The cognitive tests used to measure spatial visualization ability including mental rotation tasks like the Mental Rotations Test or mental cutting tasks like the Mental Cutting Test; and cognitive tests like the VZ-1 (Form Board), VZ-2 (Paper Folding), and VZ-3 (Surface Development) tests from the Kit of Factor-Reference cognitive tests produced by Educational Testing Service. Though the descriptions of spatial visualization and mental rotation sound similar, mental rotation is a particular task that can be accomplished using spatial visualization. The Minnesota Paper Form Board Test involves giving participants a shape and a set of smaller shapes which they are then instructed to determine which co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Ability
Cognitive skills are skills of the mind, as opposed to other types of skills such as motor skills, social skills or life skills. Some examples of cognitive skills are literacy, self-reflection, logical reasoning, abstract thinking, critical thinking, introspection and mental arithmetic. Cognitive skills vary in processing complexity, and can range from more fundamental processes such as perception and various memory functions, to more sophisticated processes such as decision making, problem solving and metacognition. Specialisation of functions Cognitive science has provided theory , theories of how the brain works, and these have been of great interest to researchers who work in the Empirical research, empirical fields of brain science. A fundamental question is whether cognitive functions, for example visual processing and language, are autonomous modules, or to what extent the functions depend on each other. Research evidence points towards a middle position, and it is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlations Between Mental Tests
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
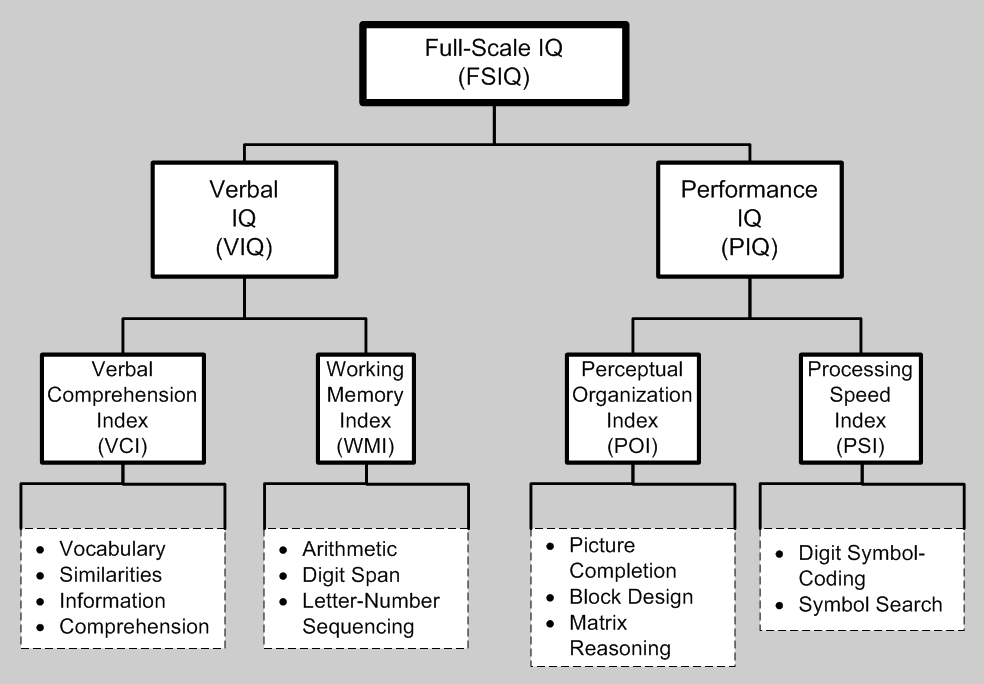
WAIS-R
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. For children between the ages of 6 and 16, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is commonly used. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, Chief Psychologist at Bellevue Hospital (1932–1967) in NYC, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale released in 1939. It is currently in its fifth edition (''WAIS-5''), released in 2024 by Pearson. It is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS was founded to get to know Wechsler's patients at Bellevue Hospital and on his definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construct Validity
Construct validity concerns how well a set of indicators represent or reflect a concept that is not directly measurable. ''Construct validation'' is the accumulation of evidence to support the interpretation of what a measure reflects.Polit DF Beck CT (2012). Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice, 9th ed. Philadelphia, USA: Wolters Klower Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Modern validity theory defines construct validity as the overarching concern of validity research, subsuming all other types of validity evidence such as content validity and criterion validity. Construct validity is the appropriateness of inferences made on the basis of observations or measurements (often test scores), specifically whether a test can reasonably be considered to reflect the intended construct. Constructs are abstractions that are deliberately created by researchers in order to conceptualize the latent variable, which is correlated with scores on a given me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |