|
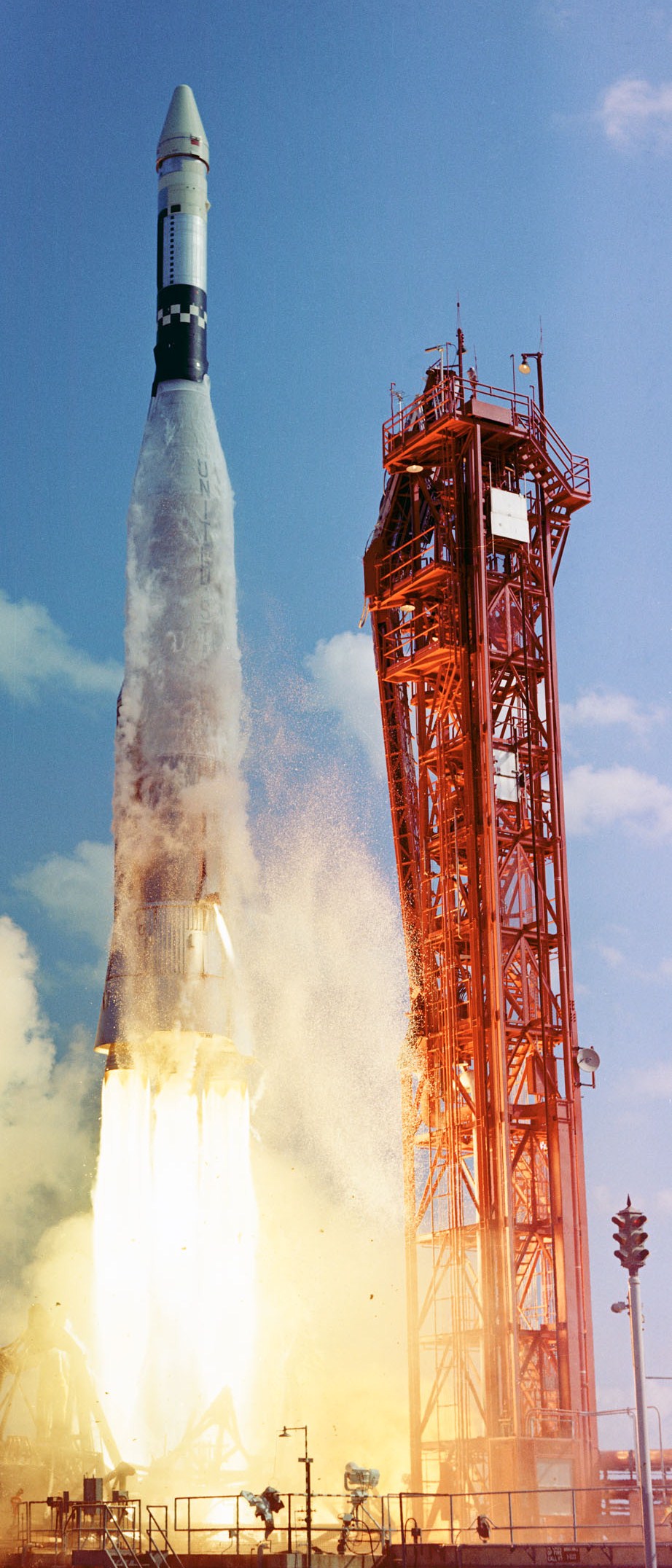
Gemini VII
Gemini 7 (officially Gemini VII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the fourth crewed Gemini flight, the twelfth crewed American spaceflight, and the twentieth crewed spaceflight including Soviet flights and X-15 flights above the Kármán line. The crew of Frank Borman and Jim Lovell spent nearly 14 days in space, making a total of 206 orbits. Their spacecraft was the passive target for the first crewed space rendezvous performed by the crew of Gemini 6A. Crew Backup crew Support crew * Charles Bassett (Houston CAPCOM) * Alan Bean (Cape CAPCOM) * Eugene Cernan (Houston CAPCOM) * Elliot See (Houston CAPCOM) Mission parameters * launch Mass: , landing mass: At December 9 epoch, five days after launch: * Perigee: * Apogee: * Inclination: 28.9° * Period: 90.54 min Stationkeeping with GT-6A * Start: December 15, 1965 19:33 UTC * End: December 16, 1965 00:52 UTC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini 6A
Gemini 6A (officially Gemini VI-A) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed United States spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. The mission, flown by Wally Schirra and Thomas P. Stafford, achieved the first crewed rendezvous with another spacecraft, its sister Gemini 7. Although the Soviet Union had twice previously launched simultaneous pairs of Vostok spacecraft, these established radio contact with each other, but they had no ability to adjust their orbits in order to rendezvous and came no closer than several kilometers of each other, while the Gemini 6 and 7 spacecraft came as close as one foot (30 cm) and could have docked had they been so equipped. Gemini 6A was the fifth crewed Gemini flight, the 13th crewed American flight, and the 21st crewed spaceflight of all time (including two X-15 flights over ). Crew Backup crew Support crew * Charles A. Bassett II (Houston CAPCOM) * Alan L. Bean (Cape CAPCO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ed White (astronaut)
Edward Higgins White II (November 14, 1930 – January 27, 1967) was an American aeronautical engineer, United States Air Force Officer (armed forces), officer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut. He was a member of the crews of Gemini 4 and Apollo 1. After graduating from United States Military Academy, West Point in 1952 with a Bachelor of Science degree, White was sent to flight training, and assigned to the 22nd Fighter Squadron, 22nd Fighter Day Squadron at Bitburg Airport, Bitburg Air Base, West Germany, where he flew the North American F-86 Sabre, F-86 Sabre and North American F-100 Super Sabre, F-100 Super Sabre fighters. In 1958, he enrolled in the University of Michigan to study Aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineering, receiving his Master of Science degree in 1959. White then received U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School, test pilot training at Edwards Air Force Base, California, before being assigned as a test pilot for the Aeronautical Systems Division at Wright-P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini 6
Gemini 6A (officially Gemini VI-A) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed United States spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. The mission, flown by Wally Schirra and Thomas P. Stafford, achieved the first crewed rendezvous with another spacecraft, its sister Gemini 7. Although the Soviet Union had twice previously launched simultaneous pairs of Vostok spacecraft, these established radio contact with each other, but they had no ability to adjust their orbits in order to rendezvous and came no closer than several kilometers of each other, while the Gemini 6 and 7 spacecraft came as close as one foot (30 cm) and could have docked had they been so equipped. Gemini 6A was the fifth crewed Gemini flight, the 13th crewed American flight, and the 21st crewed spaceflight of all time (including two X-15 flights over ). Crew Backup crew Support crew * Charles A. Bassett II (Houston CAPCOM) * Alan L. Bean (Cape CAPCOM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovell Pre-launch Gemini 7
Lovell may refer to: Places United States * Lovell, Maine, a town * Lovell, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Lovell, Oklahoma, a census-designated place * Lovell, Wyoming, a town * Chattanooga Metropolitan Airport (Lovell Field), Chattanooga, Tennessee Elsewhere * Minster Lovell, Oxfordshire, UK * Lovell (crater), a crater on the far side of the Moon Other uses * Lovell (surname) * Lovell Cook (born 1990), American professional basketball player * Lovell Pinkney (born 1972), American football player * Lovell Rousseau (1818 – 1869), a Union Army general during the American Civil War * Lovell Telescope The Lovell Telescope ( ) is a radio telescope at Jodrell Bank Observatory, near Goostrey, Cheshire, in the north-west of England. When construction was finished in 1957, the telescope was the largest steerable dish radio telescope in the world a ... at Jodrell Bank, UK See also * Lowell (other) * Lovells (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit. For celestial objects in general, the orbital period is determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, ''e.g.'' Earth around the Sun. Periods in astronomy are expressed in units of time, usually hours, days, or years. Its reciprocal is the orbital frequency, a kind of revolution frequency, in units of hertz. Small body orbiting a central body According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period ''T'' of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: :T = 2\pi\sqrt where: * ''a'' is the orbit's semi-major axis * ''G'' is the gravitationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliot See
Elliot McKay See Jr. (July 23, 1927 – February 28, 1966) was an American engineer, United States naval aviator, naval aviator, test pilot and NASA astronaut. See received an appointment to the United States Merchant Marine Academy in 1945. He graduated in 1949 with a Bachelor of Science degree in marine engineering and a United States Navy Reserve, United States Naval Reserve commission, and joined the Aircraft Gas Turbine Division of General Electric as an engineer. He was called to active duty as a naval aviator during the Korean War, and flew Grumman F9F Panther fighters with VA-52 (U.S. Navy), Fighter Squadron 144 (VF-144) from the aircraft carrier in the Mediterranean, and in the Western Pacific Ocean, Western Pacific. He married Marilyn Denahy in 1954, and they had three children. See rejoined General Electric (GE) in 1956 as a flight test engineer after his tour of duty, and became a group leader and experimental test pilot at Edwards Air Force Base, where he flew th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Cernan
Eugene Andrew Cernan (; March 14, 1934 – January 16, 2017) was an American astronaut, United States naval aviator, naval aviator, electrical engineer, aeronautical engineer, and fighter pilot. Cernan traveled into space three times and to the Moon twice: as pilot of Gemini 9A in June 1966, as lunar module pilot of Apollo 10 in May 1969, and as commander of Apollo 17 in December 1972, the final Apollo Moon landing, lunar landing. He was also a backup crew member of Gemini 12, Apollo 7, and Apollo 14. During the Apollo 17 mission, he became the 11th person to walk on the Moon as well as the astronaut with the longest time spent walking on the Moon; he is also the last person to walk on the Moon. Before becoming an astronaut, Cernan graduated with a bachelor of science degree in electrical engineering from Purdue University in Indiana, and joined the United States Navy, U.S. Navy through the Naval Reserve Officers Training Corps (NROTC). After flight training, he received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |