|
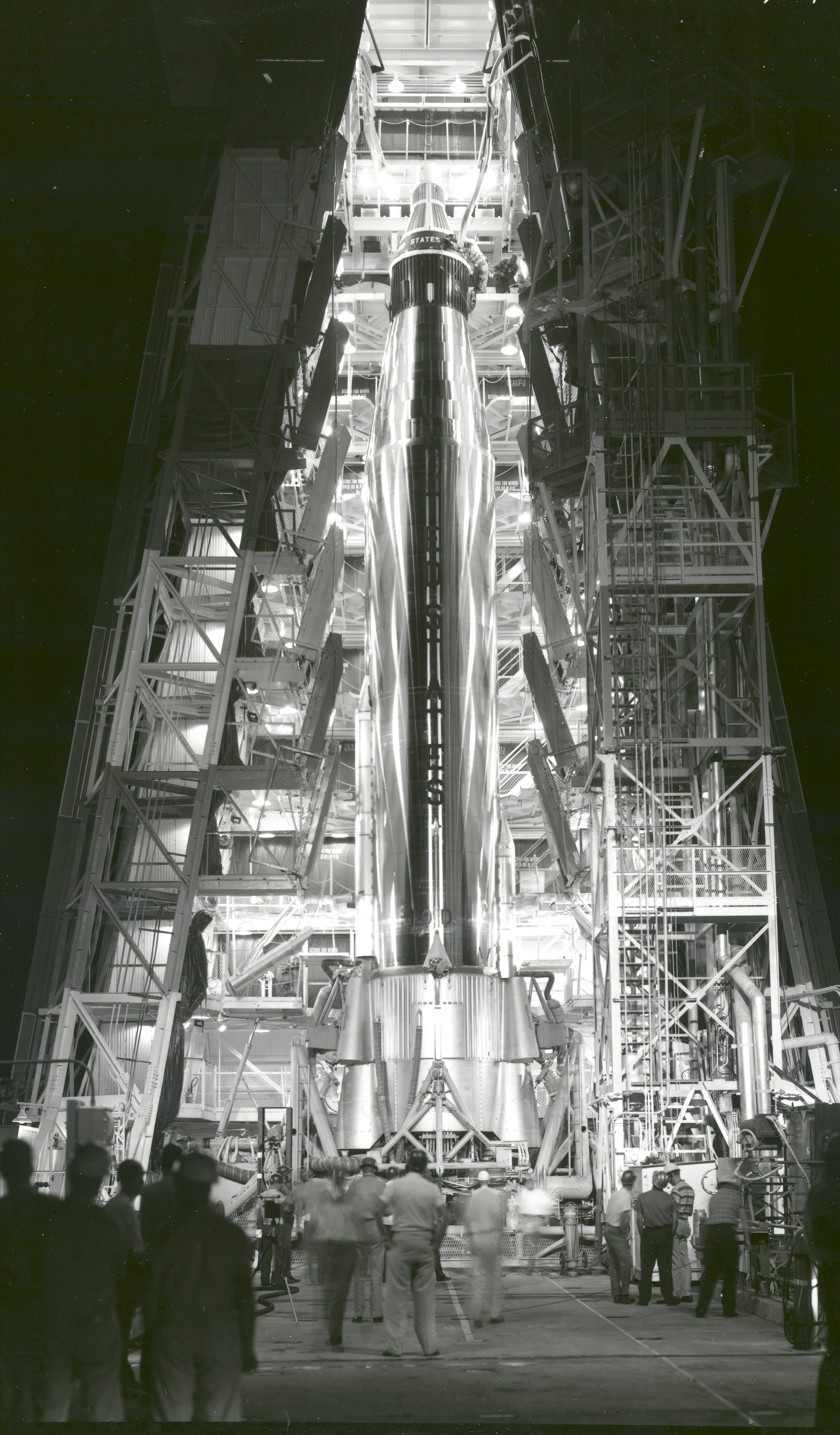
Gemini 1
Gemini 1 was the first mission in NASA's Gemini program. An uncrewed test flight of the Gemini spacecraft, its main objectives were to test the structural integrity of the new spacecraft and modified Titan II launch vehicle. It was also the first test of the new tracking and communication systems for the Gemini program and provided training for the ground support crews for the first crewed missions. Originally scheduled for launch in December 1963, difficulties in the development of both the spacecraft and its booster caused four months of delay. Gemini 1 was launched from Launch Complex 19 at Cape Kennedy (now Canaveral), Florida on April 8, 1964. The spacecraft stayed attached to the second stage of the rocket. The mission lasted for three orbits while test data were taken, but the spacecraft stayed in space for almost 64 orbits until its orbit decayed due to atmospheric drag. The spacecraft was not intended to be recovered, and holes were drilled through its heat shield to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Complex 19
Launch Complex 19 (LC-19) is a deactivated launch site on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. One of the eight pads considered part of Missile Row, it is most famous for being used as part of Project Gemini, being the launch site of all ten crewed missions in 1965 and 1966. Additionally, it was used for tests of the HGM-25A Titan I in the late 1950s and early 1960s. History Launch Complex 19 was originally built from 1957 to 1959 for the United States Air Force as part of the Titan I missile program, being used for test launches alongside LC-20 to the north and LC-15 and LC-16 to the south. The first launch out of the complex was made on August 14, 1959, when a Titan I exploded on the pad thanks to a premature engine shutdown after liftoff. This extensively damaged LC-19, which took a few months to repair before the first successful flight occurred on February 2, 1960. Going from 1959 to 1962, the complex saw a total of 15 launches of the Titan I, all of them be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas LV-3B
The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets. With the Atlas having been originally designed as a weapon system, testing and design changes were made to the missile to make it a safe and reliable launch vehicle. After the changes were made and approved, the US launched the LV-3B nine times, four of which had human spaceflight, crewed Mercury spacecraft. Design The Atlas LV-3B was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by American aircraft manufacturing company Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
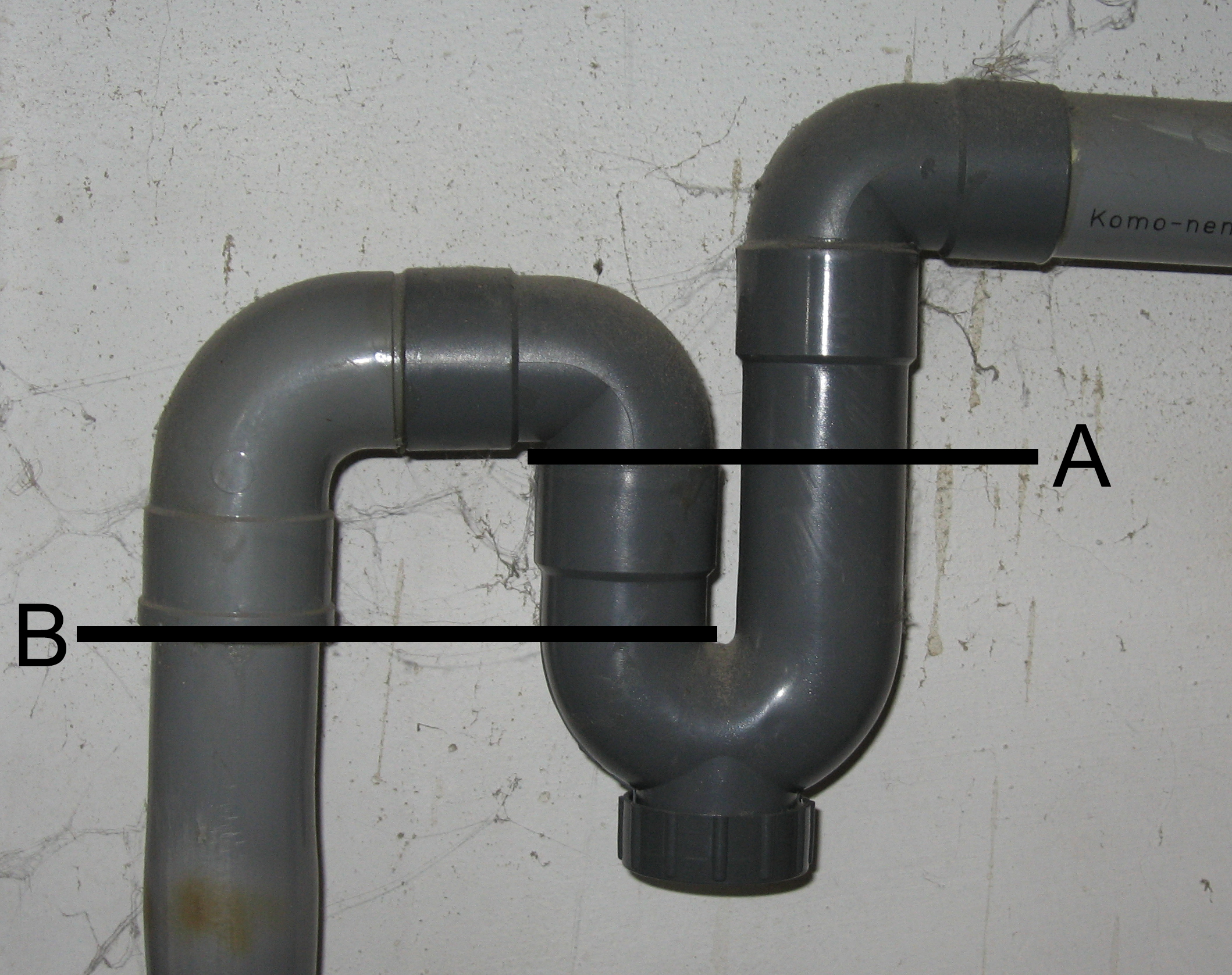
Standpipe (plumbing)
In plumbing, a trap is a U-shaped portion of pipe designed to trap liquid or gas to prevent unwanted flow; most notably sewer gases from entering buildings while allowing waste materials to pass through. In oil refineries, traps are used to prevent hydrocarbons and other dangerous gases and chemical fumes from escaping through drains. In heating systems, the same feature is used to prevent thermo-siphoning which would allow heat to escape to locations where it is not wanted. Similarly, some pressure gauges are connected to systems using U bends to maintain a local gas while the system uses liquid. For decorative effect, they can be disguised as complete loops of pipe, creating more than one U for added efficacy. General description In domestic applications, traps are typically U, S, Q, or J-shaped pipe (material), pipe located below or within a plumbing fixture. An S-shaped trap is also known as an S-bend. It was invented by Alexander Cumming in 1775 but became known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit Payload (air and space craft), payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) in 1958 by the newly formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion, launching the Pegasus satellite program, Pegasus satellites, and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift launch vehicle, heavy lift derivative Saturn IB, which used a larger, higher impulse (physics), total impulse second stage and an improved Saturn V instrument unit, guidance and control system. It also led the way to development of the super heavy-lift launch veh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pogo Oscillation
Pogo oscillation is a self-excited vibration in liquid-propellant rocket engines caused by Rocket engine#Combustion instabilities, combustion instability. The unstable combustion results in variations of engine thrust, causing variations of acceleration on the vehicle's flexible structure, which in turn cause variations in propellant pressure and flow rate, closing the self-excitation cycle. The name is a metaphor comparing the Flight control surfaces#Longitudinal axis, longitudinal vibration to the bouncing of a pogo stick. Pogo oscillation places stress on the frame of the vehicle, which in severe cases can be dangerous. Origin NASA Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight George Mueller (NASA), George Mueller explained Apollo 6's pogo oscillation to a congressional hearing: In general, pogo oscillation occurs when a surge in combustion chamber pressure increases back pressure against the fuel coming into the engine. This reduces fuel flow and thus chamber pressure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
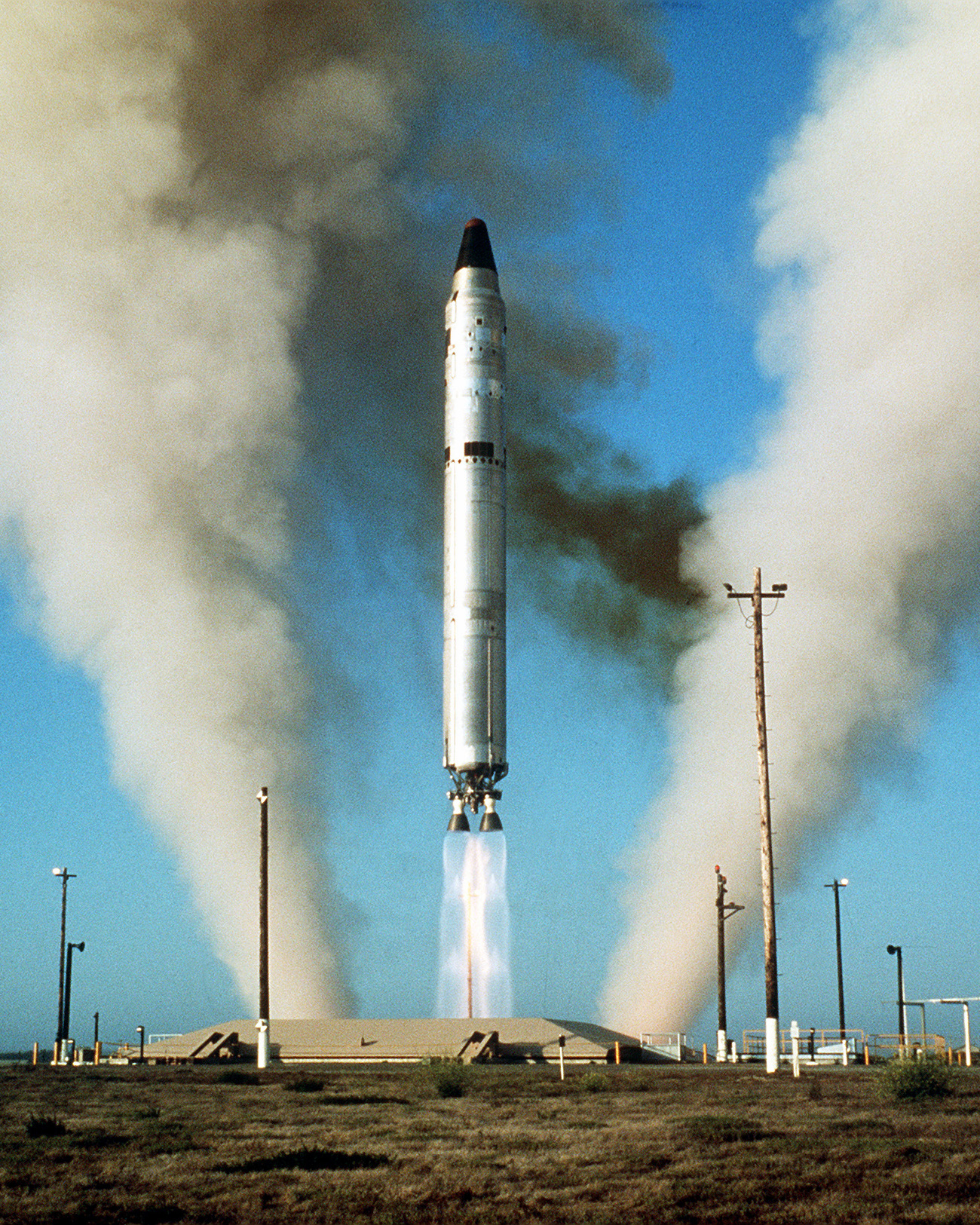
LGM-25C Titan II
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier HGM-25A Titan I, Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a Medium-lift launch vehicle, medium-lift space launch vehicle (these adaptations were designated Titan II GLV and Titan 23G) to carry payloads to Earth orbit for the United States Air Force (USAF), NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Those payloads included the USAF Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP), NOAA weather satellites, and NASA's Project Gemini, Gemini crewed space capsules. The modified Titan II SLVs (Space Launch Vehicles) were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, up until 2003. Titan II missile Part of the Titan (rocket family), Titan rocket family, the Titan II ICBM was the successor to the Titan I, with double the payload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablative Heat Shield
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass (ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector quantities (in that they have Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and Direction (geometry), direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's second law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is Direct proportionality, directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is Inverse proportionality, inversely proportional to the object's mass. The International System of Units, SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |