|
Gelbe Burg
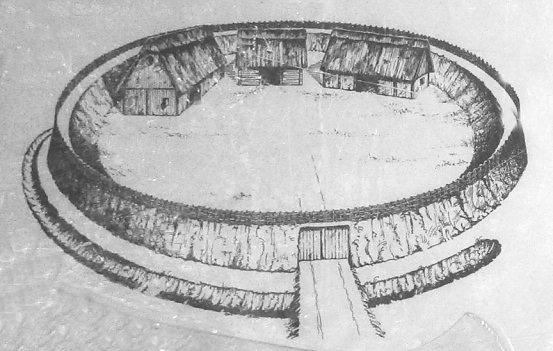
The Gelbe Burg ("Yellow Castle"), also called the ''Gelbe Bürg'', is the site of a hill castle on the Gelber Berg ("Yellow Mountain", ) northeast of the market village of Heidenheim in the Middle Franconian county of Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen in the German state of Bavaria. During the Migration Period there was a hilltop settlement on the Gelber Berg. Hardly anything is known of the founding of the medieval castle and the course of its history. Around 1180 the castle was owned by the bishops of Eichstätt: in a document the Eichstätt ''ministerialis'', Chono de Woluesprunnen, was appointed to a district office (''Amt'') there. On the eastern side of the mountain there are still clear traces of a long abandoned early medieval fortification of the circular rampart type. A neck ditch A neck ditch (), sometimes called a throat ditch, at www.roadstoruins.com. Accessed on 3 J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Castle
A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German ''Höhenburg'' used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles are thus distinguished from lowland castles (''Niederungsburgen''). Hill castles may be further subdivided depending on their situation into the following: * Hilltop castle (''Gipfelburg''), that stands on the summit of a hill with steep drops on all sides. A special type is the rock castle or ''Felsenburg''. * Ridge castle (''Kammburg''), that is built on the crest of a ridge. * Hillside castle (''Hangburg''), that is built on the side of a hill and thus is dominated by rising ground on one side. * Spur castle (''Spornburg''), that is built on a hill spur surrounded by steep terrain on three sides and thus only needs to be defended on the one remaining side. When in the 10th and 11th centuries castles lost their pure fortress character a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Bavaria
Numerous castles are found in the German state of Bavaria. These buildings, some of which have a history of over 1,000 years, were the setting for historical events, domains of famous personalities, and are still imposing structures to this day. This list encompasses castles described in German as ''Burg'' (castle), ''Festung'' (fort/fortress), ''Schloss'' (manor house) and ''Palais''/''Palast'' (palace). Many German castles after the Middle Ages were built mainly as royal or noble residences rather than as fortified buildings. Regierungsbezirk Oberbayern Altötting (district), Altötting # Burghausen Castle ('':de:Burg zu Burghausen, in German'') # Castle Tuessling ('':de:Schloss Tüßling, in German'') Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen # Seeburg (Münsing) # Schloss Hohenburg # Hohenburg (Lenggries) (ruin) Berchtesgadener Land # Berchtesgaden Castle ('':de:Königliches Schloss Berchtesgaden, de'') # Gruttenstein Castle ('':de:Burg Gruttenstein, de'') # Burgruine Karlstein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Castles
A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German ''Höhenburg'' used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles are thus distinguished from lowland castles (''Niederungsburgen''). Hill castles may be further subdivided depending on their situation into the following: * Hilltop castle (''Gipfelburg''), that stands on the summit of a hill with steep drops on all sides. A special type is the rock castle or ''Felsenburg''. * Ridge castle (''Kammburg''), that is built on the crest of a ridge. * Hillside castle (''Hangburg''), that is built on the side of a hill and thus is dominated by rising ground on one side. * Spur castle (''Spornburg''), that is built on a hill spur surrounded by steep terrain on three sides and thus only needs to be defended on the one remaining side. When in the 10th and 11th centuries castles lost their pure fortress characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidenheim Abbey (1757–1832), German exegete and grammarian
{{DEFAULTSORT:Heidenheim ...
Heidenheim may refer to: * Heidenheim an der Brenz, town in Baden-Württemberg, southern Germany **1. FC Heidenheim 1846, German football club from the city of Heidenheim **Heidenheim (district), district ''(Kreis)'' in the east of Baden-Württemberg * Heidenheim, Bavaria, municipality in the Hahnenkamm, Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen district, Bavaria, Germany People with the surname * Philipp Heidenheim (1814–1906), German rabbi and educator * Wolf Heidenheim Benjamin Wolf ben Samson Heidenheim (; 1757 – February 23, 1832) was a German Biblical exegesis, exegete and grammarian. Biography Early life Born at Heidenheim, Bavaria, Heidenheim, at an early age Heidenheim was sent to Fürth, where he stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Rampart
A circular rampart () is an embankment built in the shape of a circle that was used as part of the defences for a military fortification, hill fort or refuge, or was built for religious purposes or as a place of gathering. The period during which these structures were built ranged from the Neolithic to the Middle Ages. Construction The key feature of a circular Rampart (fortification), rampart is that the Earthworks (engineering)#Military use, embankment formed the primary element of the defensive fortification.Radig (1935), pp. 9–10. It can be constructed in various ways: as a simple earth embankment, as a wood and earth structure, or as a wall. Circular ramparts usually have a moat or Ditch (fortification), ditch in front of them; the embankment can be enhanced with a wooden palisade. They are mostly found on lowlands, but sometimes encircle the summit of a hill. Often several concentric rings were built, which produced a more effective defensive position against attackers. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministerialis
The ''ministeriales'' (singular: ''ministerialis'') were a legally unfree but socially elite class of knights, administrators, and officials in the High Middle Ages in the Holy Roman Empire, drawn from a mix of servile origins, free commoners, and even cadet sons of minor noble families, who served secular and ecclesiastical lords and often rose to hold hereditary land, noble titles, and political power indistinguishable from the free nobility. The word and its German translations, ''Ministeriale(n)'' and ''Dienstmann'', came to describe those unfree nobles who made up a large majority of what could be described as the German knighthood during that time. What began as an irregular arrangement of workers with a wide variety of duties and restrictions rose in status and wealth to become the power brokers of an empire. The ''ministeriales'' were not legally free people, but held social rank. Legally, their liege lord determined whom they could or could not marry, and they were not ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Eichstätt
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of post-Roman kingdoms there. The term refers to the important role played by the migration, invasion, and settlement of various tribes, notably the Burgundians, Vandals, Goths, Alemanni, Alans, Huns, early Slavs, Pannonian Avars, Bulgars and Magyars within or into the territories of Europe as a whole and of the Western Roman Empire in particular. Historiography traditionally takes the period as beginning in AD 375 (possibly as early as 300) and ending in 568. Various factors contributed to this phenomenon of migration and invasion, and their role and significance are still widely discussed. Historians differ as to the dates for the beginning and ending of the Migration Period. The beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgstall
A ''burgstall'' is a German term referring to a castle of which so little is left that its appearance cannot effectively be reconstructed.''Burgstall'' in the ''Adelung'' at lexika.digitale-sammlungen.de It has no direct equivalent in English, but may be loosely translated as "castle site". Variations in the literature include ''Burgstelle'', ''Altburgstelle'', ''die Burgställe'' (plural), ''Burgstähl'' (archaic) or ''abgegangene Burg'' ("lost castle"). In German castle studies, a ''burgstall'' is a castle that has effectively been levelled, whereas a "ruin" (''Ruine'') still has recognisable remnants of the original castle above the level of the ground. Definitions The word ''burgstall'' is of medieval origin and comes from ''Burg'' = "castle" and ''Stelle'' = "pla ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the list of German states by population, second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is list of German states by population density, below the German average. Major cities include Munich (its capital and List of cities in Bavaria by population, largest city, which is also the list of cities in Germany by population, third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celts, Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen
Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen () is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the west of Bavaria, Germany with a population of 95,000. Neighbouring districts are (from the north clockwise) Ansbach, Roth, Eichstätt and Donau-Ries. It is located in the south of Middle Franconia, 50 kilometres south of Nuremberg. Largest city and the administrative center is Weißenburg in Bayern. Geography The district is located on the Hahnenkamm and on the Franconian Alb in the North of the Altmühltal. In the north there are several lakes of the Franconian Lake District. The highest point of the district is the Dürrenberg. The Altmühl flows through the district. From here comes the Solnhofen limestone. Among its nature reserves is the Brombachmoor. History The district was formed in 1972 by a merger of the districts of Gunzenhausen, Weißenburg, and the previously independent urban district of Weißenburg. Coat of arms The coat of arms of the district is divided into three fields: left, right an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |