|
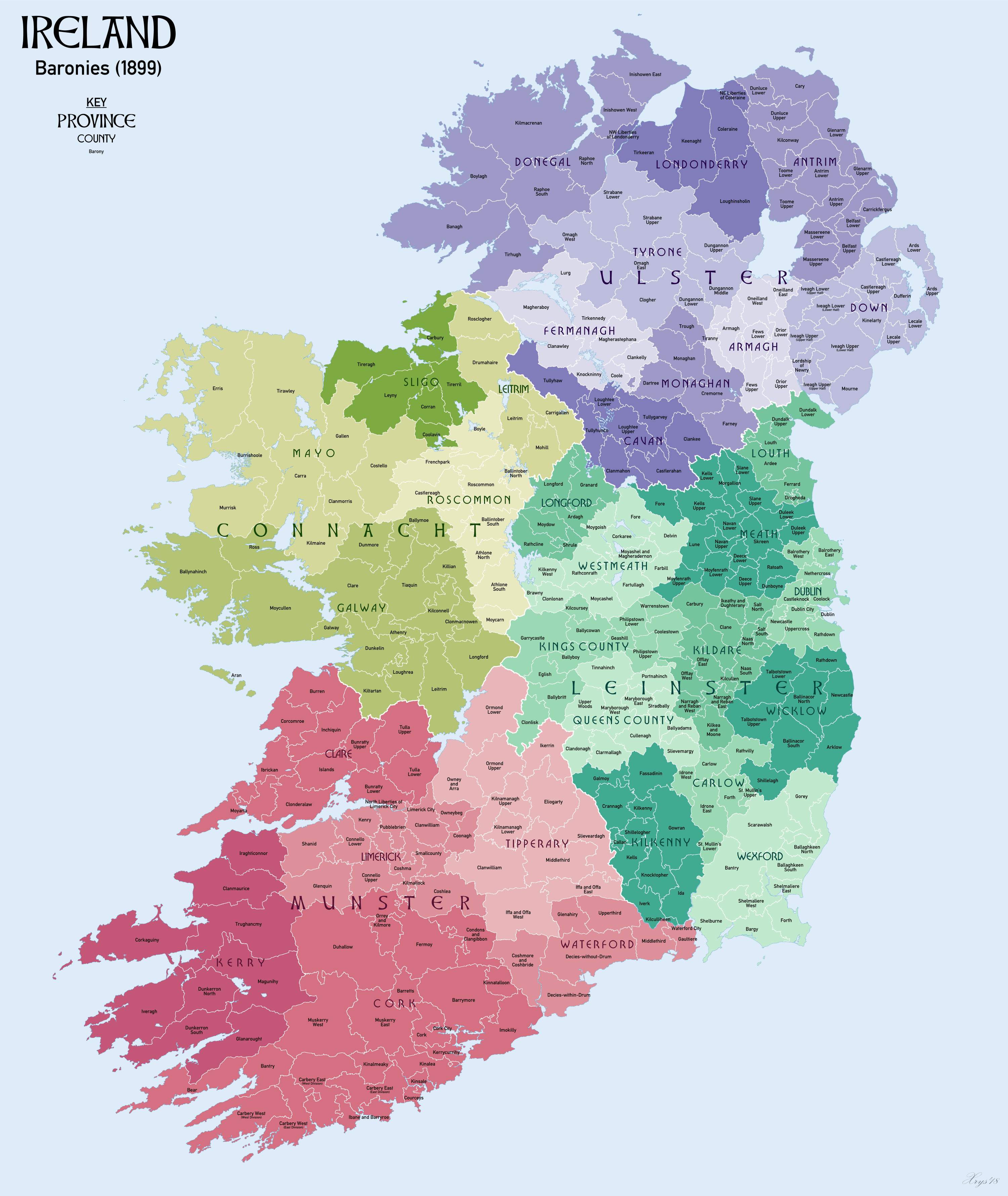
Geashill (barony)
Geashill (, ) is a barony in County Offaly (formerly King's County), Ireland. Etymology The name Geashill is from the village of Geashill (Irish ''Géisill'', "place of swans"). Location Geashill barony is located in central County Offaly, south of the Grand Canal. The Tullamore River and Clodiagh River flow through it, and it contains the Hawkswood Bog Natural Heritage Area. History Geashill is roughly formed from the ancient Túath Géisille of the Uí Failge septs of Leinster. As Viscount Clanmalier the Ó Diummasach (O'Dempsey) held part of this barony, where the main castle of the clan was located. The Ó hAimherigin (O'Bergin) sept are noted as chiefs in this barony in medieval times. List of settlements Below is a list of settlements in Geashill barony: *Ballinagar * Geashill *Killeigh Killeigh (, meaning "church of the field") is a village in County Offaly, Ireland. It is located around south of the county town of Tullamore, on the N80 national secondary ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (an Caighdeán Oifigiúil, Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous language, indigenous to the Ireland, island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became Linguistic imperialism, dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as County Cork, Cork, County Donegal, Donegal, County Galway, Galway, and County Kerry, Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties County Mayo, Mayo, County Meath, Meath, and County Waterford, Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second language, second-language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clodiagh River
The River Clodiagh () is a small river which rises in Lough Coumduala in the Comeragh Mountains in north County Waterford. (''It should not be confused with the River Clodiagh in County Kilkenny.'') It flows through the villages of Rathgormack, Clonea-Power and Portlaw before joining the River Suir just outside Portlaw. The river is fed by a number of smaller tributaries including Hunts stream and Aughtnawilliam stream. Kayak tragedy Two canoeists, one a sit-on kayak A kayak is a small, narrow watercraft which is typically propelled by means of a double-bladed paddle. The word kayak originates from the Greenlandic word ''qajaq'' (). The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each se ..., drowned after being stuck in a weir at Portlaw, in April 2010. References External links * Clodiagh {{Ireland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballinagar
Ballinagar (historically ''Bellanagar'', from ) is a village in County Offaly, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It lies on the R402 road (Ireland), R402 Regional road (Ireland), regional road, roughly midway between Daingean and Tullamore. The Church of St. Joseph, built in 1837, serves as the Roman Catholic parish church in the village. The local National school (Ireland), national school, also named St. Joseph's, originally opened in 1949 but moved to a new building in 2011/2012. The village has a pub named Tom and Jerry's bar. References See also * List of towns and villages in the Republic of Ireland Towns and villages in County Offaly {{Offaly-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscount Clanmalier
Viscount Clanmalier, in the King's and Queen's County, was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created on 22 December 1631 for Sir Terence O' Dempsey, Sheriff of Queen's County in 1591 who was knighted in 1599. He was made Baron of Phillipstown, in the Queen's County, at the same time, also in the Peerage of Ireland. His grandson, Lewis, the second Viscount, joined the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and was consequently attainted with his titles forfeited. However, in 1662 he was restored to a third of his former estates and presumably to his titles. His son, Maximilian, the third Viscount, was Governor of King's County. It is believed that Terence O'Dempsey, the youngest son of Maximilian fled Ireland with his cousin Sir John Byrne to England ( The Four Masters) . The actual velum title document still exists. Viscounts Clanmalier (1631) *Terence O'Dempsey, 1st Viscount Clanmalier (died ) **Hon. Owny O'Dempsey (died between 1637 and 1638) *Lewis O'Dempsey, 2nd Viscount Clanmalier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leinster
Leinster ( ; ga, Laighin or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, situated in the southeast and east of Ireland. The province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of Ireland, the historic "fifths" of Leinster and Meath gradually merged, mainly due to the impact of the Pale, which straddled both, thereby forming the present-day province of Leinster. The ancient kingdoms were shired into a number of counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has prompted further sub-division of the historic counties. Leinster has no official function for local-government purposes. However, it is an officially recognised subdivision of Ireland and is listed on ISO 3166-2 as one of the four provinces of Ireland. "IE-L" is attributed to Leinster as its ''country sub-division'' code. Leinster had a population of 2,858,501 according to the preliminary results of the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Túath
''Túath'' (plural ''túatha'') is the Old Irish term for the basic political and jurisdictional unit of Gaelic Ireland. ''Túath'' can refer to both a geographical territory as well the people who lived in that territory. Social structure In ancient Irish terms, a household was reckoned at about 30 people per dwelling. A '' trícha cét'' ("thirty hundreds"), was an area comprising 100 dwellings or, roughly, 3,000 people. A ''túath'' consisted of a number of allied ''trícha céta'', and therefore referred to no fewer than 6,000 people. Probably a more accurate number for a ''túath'' would be no fewer than 9,000 people. Each ''túath'' was a self-contained unit, with its own executive, assembly, courts system and defence force. ''Túatha'' were grouped together into confederations for mutual defence. There was a hierarchy of ''túatha'' statuses, depending on geographical position and connection to the ruling dynasties of the region. The organisation of ''túatha'' is cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Heritage Area
Natural Heritage Area () is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in Ireland. The Wildlife (Amendment) Act 2000 makes legal provision for the designation and protection of a national network of Natural Heritage Areas (NHAs). The designation is currently used by the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) to protect wildlife habitats, such as raised bogs. 75 raised bogs were designated for protection in 2004 under the Wildlife Act. Geological sites It is also intended that the designation be used to protect geosites (sites of geological and geomorphological interest). The Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) provides scientific appraisal and interpretative advice on such sites, while the NPWS have the responsibility of designation and management. In identifying important sites that are capable of being conserved as NHAs, the GSI groups them by geological themes. Karst (i.e. exposed limestone) was chosen as the first geological theme because of its vulnerability an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawkswood Bog
Hawkswood (English derived place name. The earliest known spelling is ''Hawswood'', meaning ''The Wood of the Hawthorns'' but the name seems to have been later corrupted to Hawkswood) is a townland in the civil parish of Kinawley, barony of Tullyhaw, County Cavan, Ireland. The original Irish place name was ''Cluain Caomh'' meaning 'The Beautiful Meadow'. The town of Swanlinbar is partially situated in Hawkswood. According to the 1938 Dúchas collection two sub-divisions are- ''The Cleity (Perhaps from the Gaelic 'Cleitigh' meaning feathers or plume or quill.)- A name given to a field in a farm owned by Mr. Patrick Maguire, Hawkswood, Swanlinbar, Co. Cavan. The Rhythars - a name given to a field in a farm owned by Mr Hugh McBrien, Hawkswood, Swanlinbar''. Geography Hawkswood is bounded on the north by Corranearty townland, on the south by Furnaceland townland, on the west by Gorteennaglogh and Monydoo (or Tonycrom) townlands and on the east by Cloghoge, Cornagran (Kinawl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullamore River
Tullamore (; ) is the county town of County Offaly in Ireland. It is on the Grand Canal, in the middle of the county, and is the fourth most populous town in the midlands region with 14,607 inhabitants at the 2016 census. The town retained Gold Medal status in the National Tidy Town Awards in 2015 and also played host to the World Sheep Dog Trials in 2005 which attracted international interest in the region. The Tullamore Show is held near the town every year. The town's most famous export is Tullamore Dew – an Irish whiskey distilled by Tullamore Distillery – that can be traced back to 1829. The original distillery was shut down in 1954, with the brand later being resurrected and produced at the Midleton Distillery, in Cork. However, the brand's new owners, William Grant & Sons, invested in a new distillery near Tullamore, bringing whiskey production back to the town in 2014. History In the Middle Ages, Tullamore was within the Gaelic territory of Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canal (Ireland)
The Grand Canal ( ga, An Chanáil Mhór) is the southernmost of a pair of canals that connect Dublin, in the east of Ireland, with the River Shannon in the west, via Tullamore and a number of other villages and towns, the two canals nearly encircling Dublin's inner city. Its sister canal on the Northside of Dublin is the Royal Canal. The last working cargo barge passed through the Grand Canal in 1960. Branches * Main line from Grand Canal Harbour near St. James's Gate to Shannon Harbour in Co. Offaly. ** Most of the Dublin City section of the route is now used by the Luas. While this section was in use, the canal from Crumlin to the Liffey in Ringsend Basin, which forms part of the current main line, was considered to be a branch. It was a later add-on and was known as the Circular Line. * Naas/Corbally ** Navigable to Naas, but a low bridge prevents access to Corbally * Barrow, joining the River Barrow at Athy * Milltown feeder * The Mountmellick Line, which left the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |