|
Gayelord Hauser
Benjamin Gayelord Hauser (May 17, 1895 - December 26, 1984),Picart, C. (2000, February)''Hauser, Gayelord (1895-1984), nutritionist and author'' American National Biography. Ed. Retrieved 8 Feb. 2019. popularly known as Gayelord Hauser, was an American nutritionist and self-help writer, who promoted the 'natural way of eating' during the mid-20th century. He promoted foods rich in vitamin B and discouraged consumption of sugar and white flour. He rose to fame as a self-help author, popular on the lecture and social circuits, and was nutritional advisor to many celebrities. Hauser was supported by many film stars but was often in conflict with the medical community. He promised people they could add years to their life by eating five "wonder foods": blackstrap molasses, brewer's yeast, skimmed milk, wheat germ and yogurt. Barrett, Stephen, Jarvis, William T. (1993). ''The Health Robbers: A Close Look at Quackery in America''. Prometheus Books. p. 79. He was criticized as a " fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
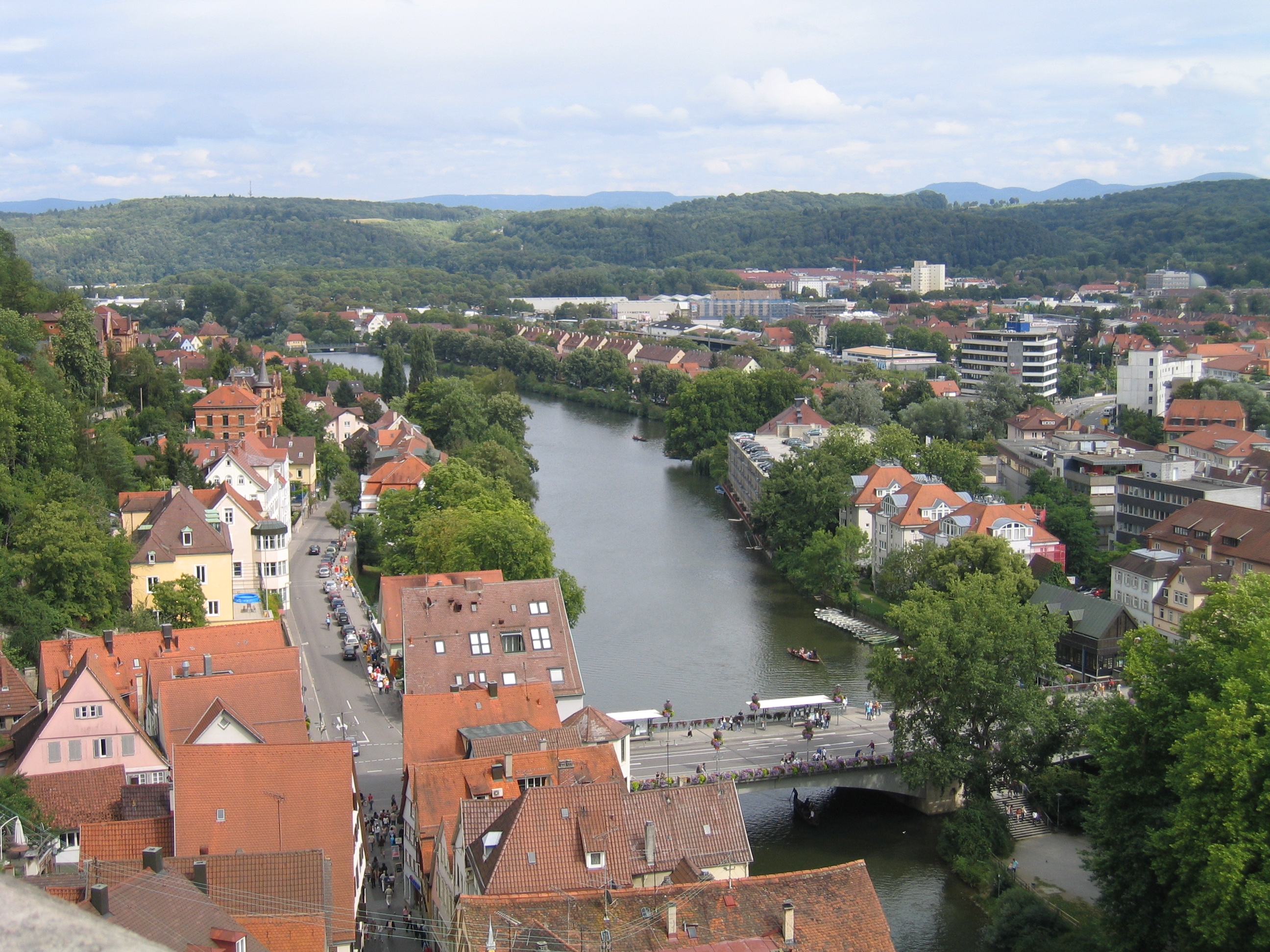
Tübingen
Tübingen (; ) is a traditional college town, university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer (Neckar), Ammer rivers. about one in three of the 90,000 people living in Tübingen is a student. As of the 2018/2019 winter semester, 27,665 students attend the University of Tübingen, Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen. The city has the lowest median age in Germany, in part due to its status as a university city. As of December 31, 2015, the average age of a citizen of Tübingen is 39.1 years. Immediately north of the city lies the Schönbuch, a densely wooded nature park. The Swabian Alb mountains rise about (beeline Tübingen City to Roßberg - 869 m) to the southeast of Tübingen. The Ammer and Steinlach rivers are Tributary, tributaries of the Neckar river, which flows in an easterly direction through the city, just south of the Middle Ages, medieval old town. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. It is not the same as junk science. The demarcation between science and pseudoscience has scientific, philosophical, and political implications. Philosophers debate the nature of science and the general criteria for drawing the line between scientific theories and pseudoscientific beliefs, but there is widespread agreement "that creationism, astrology, homeopathy, Kirlian photography, dowsing, ufology, ancient astronaut theory, Holocaust den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturopathy
Naturopathy, or naturopathic medicine, is a form of alternative medicine. A wide array of practices branded as "natural", "non-invasive", or promoting "self-healing" are employed by its practitioners, who are known as naturopaths. Difficult to generalize, these treatments range from the Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific and thoroughly discredited, like homeopathy, to the widely accepted, like certain forms of psychotherapy. The ideology and methods of naturopathy are based on vitalism and folk medicine rather than evidence-based medicine, although practitioners may use techniques supported by evidence. The ethics of naturopathy have been called into question by medical professionals and its practice has been characterized as quackery. Naturopathic practitioners commonly encourage alternative treatments that are rejected by conventional medicine, including resistance to surgery or vaccines for some patients. The diagnoses made by naturopaths often have no basis in science and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molasses
Molasses () is a viscous byproduct, principally obtained from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beet juice into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, the method of extraction, and the age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is usually used to sweeten and flavour foods. Molasses is a major constituent of fine commercial brown sugar. Molasses is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B6, iron, calcium, magnesium, and potassium. There are different types of molasses depending on the amount of time refined, including first molasses (highest sugar content), second molasses (slightly bitter), and blackstrap molasses (the darkest and most robust in flavor). Molasses was historically popular in the Americas before the 20th century as a sweetener. It is still commonly used in traditional cuisine, such as in Madeira Island's traditional dishes. In addition to culinary uses, molasses has industrial applications, such as in the distillation of rum, as an additiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skim Milk
Skimmed milk (British English), or skim milk (American English), is made when all the milkfat is removed from whole milk. It tends to contain around 0.1% to 0.3% fat. Background Historically, skimmed milk was used for fattening pigs, and was recommended as "not only the very best supplement for growing pigs, but is of almost equal value for fattening purposes" as it "furnishes a complete protein" and makes the feed "more palatable". Terminology In the United Kingdom, milk has been traditionally marketed and labelled as follows since being proposed by John Morris of the British Retail Consortium in 1998, which based the colours on Marks & Spencer cream packaging (blue for double cream, green for crème fraîche and red for single cream): * Whole milk (around 3–4% fat) – Plastic bottles marketed in blue packaging. * Semi-skimmed milk (around 1.8% fat) – Plastic bottles are marketed in green packaging. * Skimmed milk (around 0.1% fat) – Plastic bottles are marketed in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewers Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a multicellular cluster with specialised cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedict Lust
Benedict Lust (February 3, 1872 – September 5, 1945) was a German-American who was one of the founders of naturopathic medicine in the first decades of the twentieth century. Biography Lust was born in Michelbach, Baden, Germany.Anonymous. (1945)''The National Cyclopaedia of American Biography, Volume 32'' New York: James T. White & Company. pp. 505-506. As a youth, he became ill and was treated by Fr. Sebastian Kneipp, a famous advocate of the water cure system. In 1892, he moved to the United States as Kneipp's official water cure representative. Lust attended the New York Preparatory College. He graduated from the Universal Osteopathic College in 1897 and the Eclectic and Naturopathic College in 1904. He received an M.D. from the Eclectic Medical College of New York in 1914. In 1896, Lust began his career as a naturopath by opening a health center and health food store in New York City. He also opened the New York School of Massage in 1896 and the American School of Chir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturopath
Naturopathy, or naturopathic medicine, is a form of alternative medicine. A wide array of practices branded as "natural", "non-invasive", or promoting "self-healing" are employed by its practitioners, who are known as naturopaths. Difficult to generalize, these treatments range from the pseudoscientific and thoroughly discredited, like homeopathy, to the widely accepted, like certain forms of psychotherapy. The ideology and methods of naturopathy are based on vitalism and folk medicine rather than evidence-based medicine, although practitioners may use techniques supported by evidence. The ethics of naturopathy have been called into question by medical professionals and its practice has been characterized as quackery. Naturopathic practitioners commonly encourage alternative treatments that are rejected by conventional medicine, including resistance to surgery or vaccines for some patients. The diagnoses made by naturopaths often have no basis in science and are often not acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
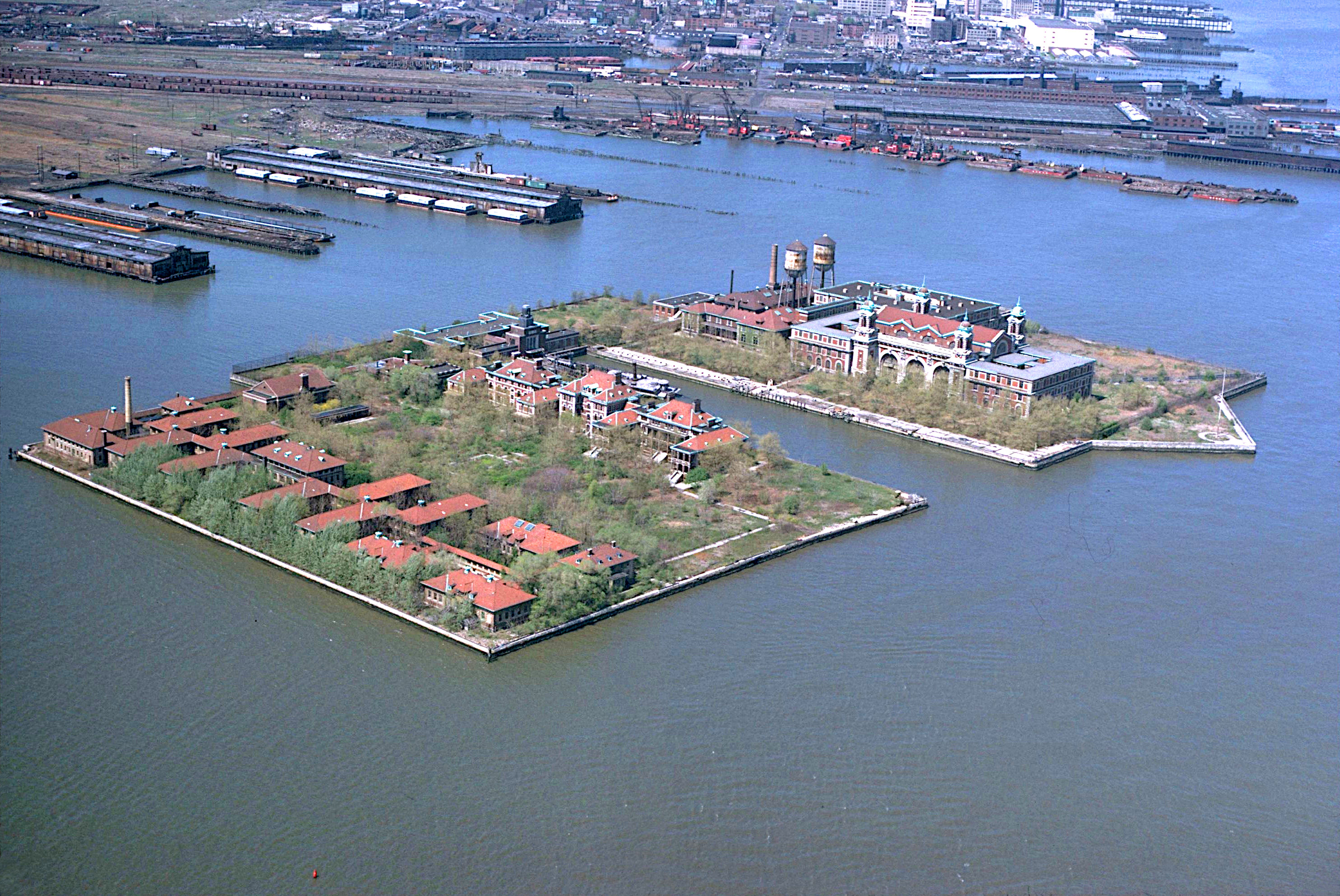
Ellis Island
Ellis Island is an island in New York Harbor, within the U.S. states of New Jersey and New York (state), New York. Owned by the U.S. government, Ellis Island was once the busiest immigrant inspection and processing station in the United States. From 1892 to 1954, nearly 12 million immigration to the United States, immigrants arriving at the Port of New York and New Jersey were processed there; approximately 40% of Americans may be descended from these immigrants. It has been part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument since 1965 and is accessible to the public only by ferry. The north side of the island is a national museum of immigration, while the south side of the island, including the Ellis Island Immigrant Hospital, is open to the public through guided tours. The name derives from Samuel Ellis, a Welshman who bought the island in 1774. In the 19th century, Ellis Island was the site of Fort Gibson and later became a Magazine (artillery)#Naval magazines, naval magazine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
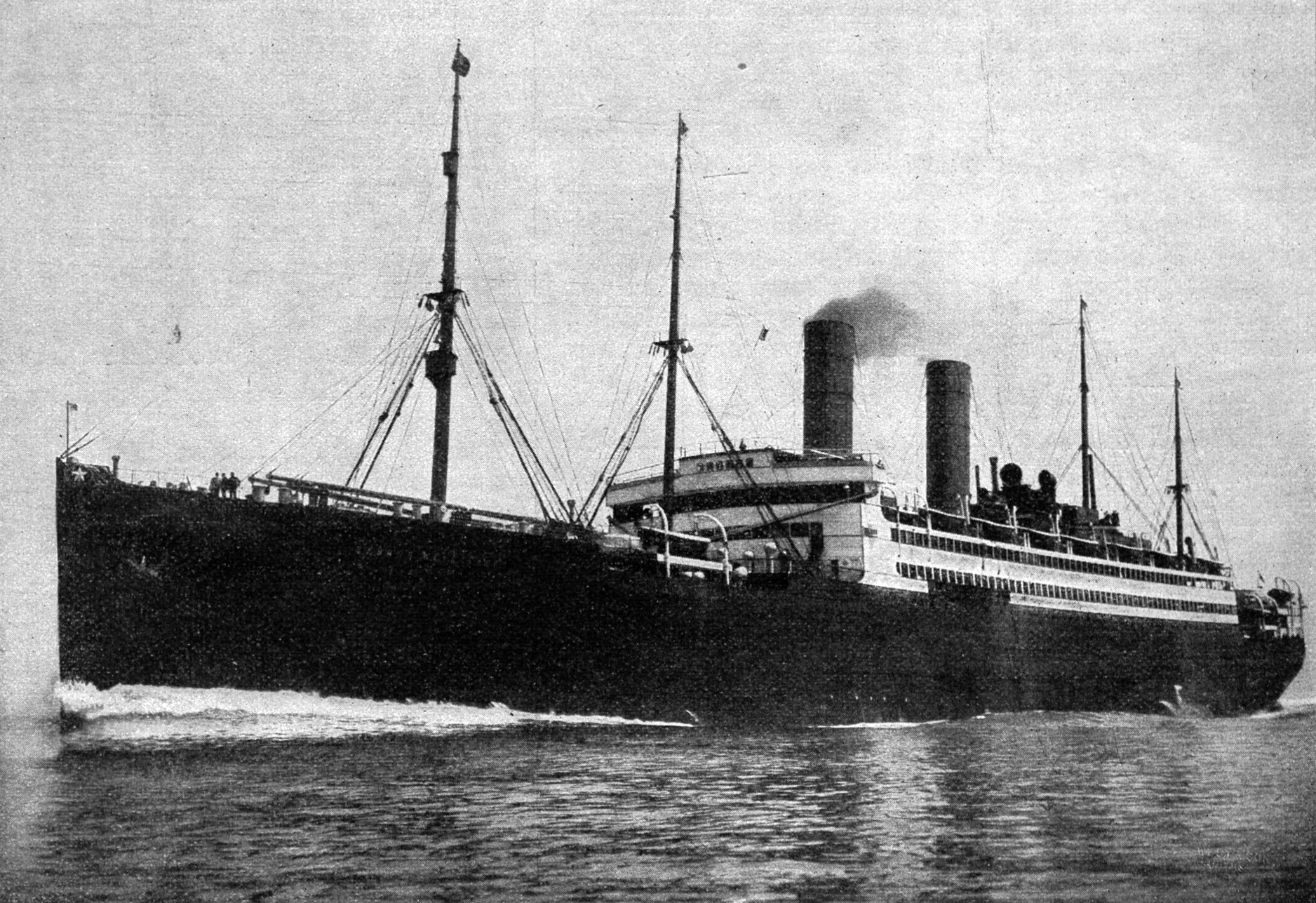
SS George Washington
SS ''George Washington'' was an ocean liner built in 1908 for the Bremen-based North German Lloyd and was named after George Washington, the first President of the United States. The ship was also known as USS ''George Washington'' (ID-3018) and USAT ''George Washington'' in service of the United States Navy and United States Army, respectively, in World War I. In the interwar period, she reverted to her original name of ''George Washington''. During World War II, the ship was known as both USAT ''George Washington'' and, briefly, as USS ''Catlin'' (AP-19), in a short, second stint in the US Navy. When ''George Washington'' was launched in 1908, she was the largest German Empire, German-built steamship and the third-largest ship in the world. ''George Washington'' was built to emphasize comfort over speed and was sumptuously appointed in her first-class passenger areas. The ship could carry a total of 2,900 passengers, and made her maiden voyage in January 1909 to New York. In Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |