|
Gauge War
The Gauge War (or Gauge Wars) was a figurative war of intense competition to control new territory, waged between expanding railway companies in Great Britain in the nineteenth century. The contest for which track gauge should become the standard carried with it the greater struggle for which companies and stakeholders would win or lose in commerce, controlling or commercially dominating rights of way. The Gauge War was arguably the earliest format war between two similar but incompatible technologies. Origins The Great Western Railway adopted the broad gauge of at the outset, while competing railway companies adopted the gauge of , which later became standard gauge. As the railway companies sought to expand commercially and geographically, they wished to dominate areas of the country, hoping to exclude their competitors. The networks polarised into groups of ''broad gauge companies'' and of ''narrow gauge companies''. The term ''narrow gauge'' at the time referred to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figurative Analogy
A figurative analogy is a comparison about two things that are not alike but share only some common property. On the other hand, a literal analogy is about two things that are nearly exactly alike. The two things compared in a figurative analogy are not obviously comparable in most respects. Metaphors and similes are two types of figurative analogies. In the course of analogical reasoning, figurative analogies become weak if the disanalogies {{Short pages monitor [Baidu] |
Break Of Gauge
With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge (the distance between the rails, or between the wheels of trains designed to run on those rails) meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally cannot run through without some form of conversion between gauges, leading to passengers having to change trains and freight requiring transloading or transshipping; this can add delays, costs, and inconvenience to travel on such a route. History Break of gauge was a common issue in the early days of railways, as standards had not yet been set and different organizations each used their own favored gauge on the lines they controlled—sometimes for mechanical and engineering reasons (optimizing for geography or particular types of load and rolling stock), and sometimes for commercial and competitive reasons (interoperability and non-interoperability within and between companies and alliances were often key strategic moves). Various solutions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Of England
West of England is a combined authority area in South West England. It is made up of the Bristol, South Gloucestershire, and Bath and North East Somerset unitary authorities. The combined authority is led by the Mayor of the West of England Dan Norris. Background The term has been used in the Bristol and Bath area since at least the 18th century. The Royal Bath and West of England Society was named the Bath and West of England Society in 1790. The Royal West of England Academy received its present title in 1913. More recently the term has been used by organisations such as the West of England Partnership,West of England Partnership Accessed 6 March 2012 Connexions West of England, and the West of England Sport Trust, as a synonym for the former |
Regulating The Gauge Of Railways Act 1846
The Railway Regulation (Gauge) Act 1846 (9 & 10 Vic. c.57) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, that was designed to standardise railway tracks. It achieved royal assent on 18 August 1846, during the reign of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It mandated that the track gauge – which was the distance between the two running rails' inner faces – of 4 feet 8 inches to be the standard for Great Britain and 5 feet 3 inches to be the standard for Ireland.The metric equivalents of the dimensions specified are 1435 and 1600 millimetres respectively. The Act The Act stipulated that: Furthermore, it also provided that, following the Act's passing, it would be illegal to alter a railway gauge that was in use for the conveyance, i.e. transport, of passengers. Assessment The Act continued legislative approval of the broad-gauge railways constructed by the Great Western Railway engineer Isambard Kingdom B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Commission On Railway Gauges
The Royal Commission on Railway Gauges was held in the United Kingdom in 1845 to choose between the Broad Gauge of the Great Western Railway and its allies, and the so-called narrow gauge used by most of the rest of the country. The situation in Ireland where there were three gauges was also considered. Following the Royal Commission in August 1846 the Gauge Act was passed which mandated all new railways be constructed to in England, Scotland and Wales, and to in Ireland. The Great Western Railway was allowed to continue with . Narrow gauges Really narrow gauges such as of the Ffestiniog Railway appear to have been overlooked. in Unlike Italy and France, which regulated the choice of narrow gauge gauges, Britain did not, which resulted in a large number of narrow gauges, including: * – earliest use in 1836. * – 1879 * – 1859 * – 1884 * – 1873 * – 1863 * Several other rarely used gauges See also * Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Gauge
A variable gauge system allows railway vehicles in a train to travel across a break of gauge between two railway networks with different track gauges. For through operation, a train must be equipped with special bogies holding variable gauge wheelsets containing a variable gauge axle (VGA). The gauge is altered by driving the train through a gauge changer or gauge changing facility. In effect, the track widens or narrows. As the train passes through the gauge changer, the wheels are unlocked, are moved closer together, or further apart, and are then re-locked. Installed variable gauge systems exist within the internal network of Spain, and are installed on international links between Spain/France (Spanish train), Sweden/Finland (Swedish train), Poland/ Lithuania (Polish train) and Poland/Ukraine (Polish train). A system for changing gauge without the need to stop is in widespread use for passenger traffic in Spain, for services run on a mix of dedicated high-speed lines (using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers and ISO containers). Containerization is also referred as "Container Stuffing" or "Container Loading", which is the process of unitization of cargoes in exports. Containerization is the predominant form of unitization of export cargoes, as opposed to other systems such as the barge system or palletization. The containers have standardized dimensions. They can be loaded and unloaded, stacked, transported efficiently over long distances, and transferred from one mode of transport to another—container ships, rail transport flatcars, and semi-trailer trucks—without being opened. The handling system is completely mechanized so that all handling is done with cranes and special forklift trucks. All containers are numbered and tracked using computerized systems. Containerization originated several centuries ago but was not well developed or widely applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
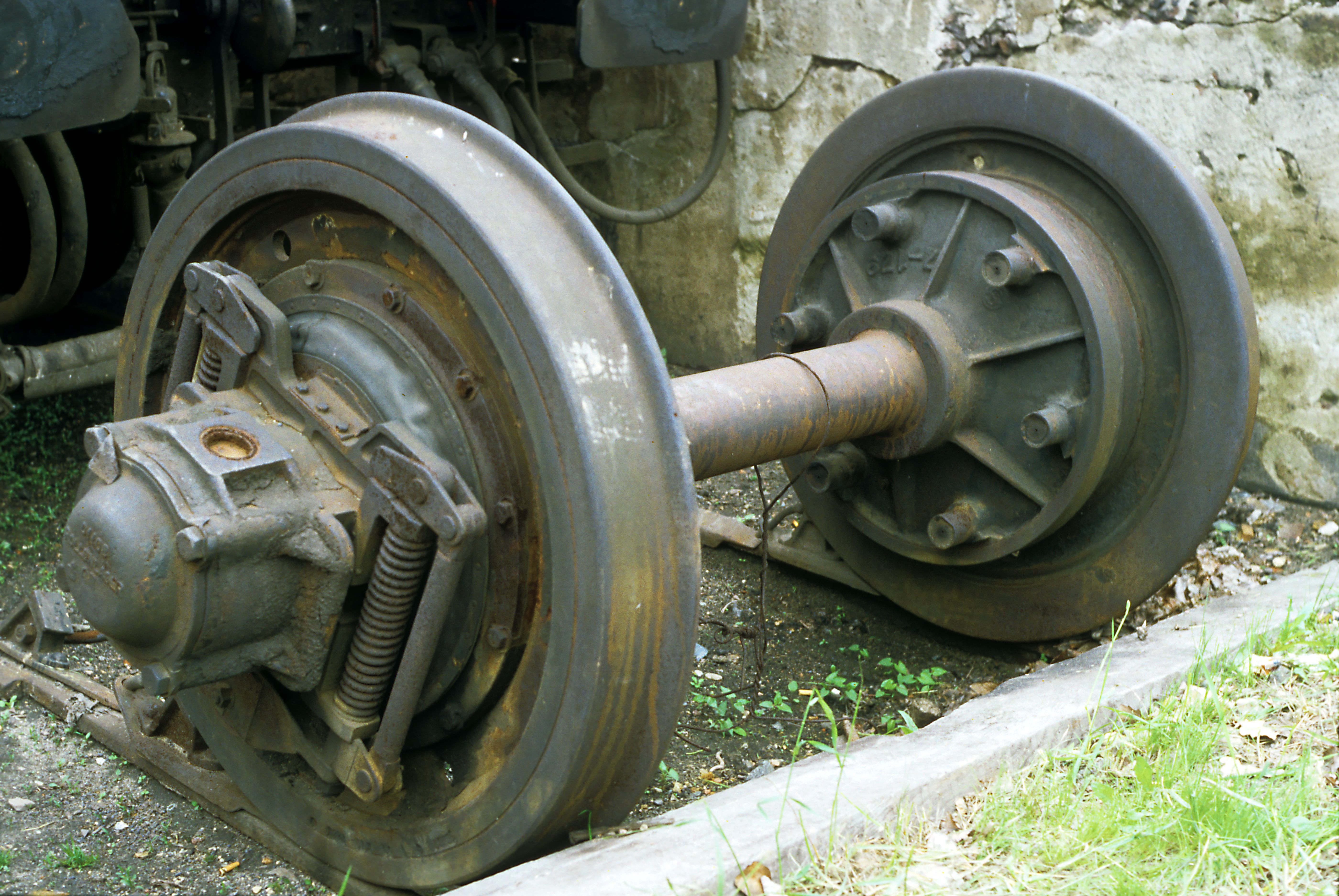
Dual Gauge
In railway engineering, " gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to carry railway vehicles with wheels matched to two different gauges. Such track is described as dual gauge – achieved either by addition of a third rail, if it will fit, or by two additional rails. Dual-gauge tracks are more expensive to configure with signals and sidings, and to maintain, than two separate single-gauge tracks. It is therefore usual to build dual-gauge or other multi-gauge tracks only when necessitated by lack of space or when tracks of two different gauges meet in marshalling yards or passenger stations. Dual-gauge tracks are by far the most common configuration, but triple-gauge tracks have been built in some situations. Background The rail gauge is the most fundamental specification of a railway. Rail tracks and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transporter Wagon
A transporter wagon, in railway terminology, is a wagon ( UIC) or railroad car (US) designed to carry other railway equipment. Normally, it is used to transport equipment of a different rail gauge. In most cases, a transporter wagon is a narrower gauge wagon for transporting a wider gauge equipment, allowing freight in a wider gauge wagons to reach destinations on the narrower gauge network without the expense and time of transshipment into a narrower gauge wagons. This is an attempt to overcome one of the primary problems with differing gauge systems—gauge incompatibility. However, it means that the narrower gauge network must be built to a structure gauge large enough to accommodate the loading gauge of the wider gauge equipment, negating one of the cost advantages of a narrower gauge construction. Additionally, a large wider gauge wagon balanced on a narrower gauge transporter wagon is not very stable, and is generally restricted to low speeds of or so. Transporter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rollbock
''Rollbocks'', sometimes called transporter trailers, are narrow gauge railway trucks or bogies that allow a standard gauge wagon to 'piggyback' on a narrow-gauge line. The Vevey system enables a coupled train of standard gauge wagons to be automatically loaded or rolled onto Rollbocks, so that the train can then continue through a change of gauge. The system uses a pair of narrow gauge (750 or 1,000 mm) rails laid in a pit that is built in the middle of a standard gauge track, which is elevated by about 30 cm. It allows the ''Rollbock'' bogies to sit underneath the standard gauge tracks and as the ''Rollbock'' train is pulled out of the ''Rollbock'' siding each bogie picks up one axle of a standard gauge wagon as it rises out of the ''Rollbock'' pit. Thus two ''Rollböcke'' are needed for a twin-axle wagon. They were a development of the transporter wagon (''Rollwagen''), designed to keep cost and weight down by avoiding the need for a complete wagon. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transloading
Transloading, also known as cross-docking, is the process of transferring a shipment from one mode of transportation to another. It is most commonly employed when one mode cannot be used for the entire trip, such as when goods must be shipped internationally from one inland point to another. Such a trip might require transport by truck to an airport, then by airplane overseas, and then by another truck to its destination; or it might involve bulk material (such as coal) loaded to rail at the mine and then transferred to a ship at a port. Transloading is also required at railroad break-of-gauge points, since the equipment can not pass from one track to another unless bogies are exchanged. Since transloading requires handling of the goods, it causes a higher risk of damage. Therefore, transloading facilities are designed with the intent of minimizing handling. Due to differing capacities of the different modes, the facilities typically require some storage facility, such as war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation Primary legislation and secondary legislation (the latter also called delegated legislation or subordinate legislation) are two forms of law, created respectively by the legislature, legislative and executive (government), executive branches of ..., are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_track%2C_South_Australian_Railways.jpg)
