|
Gauge
Gauge ( ) may refer to: Measurement * Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments * Gauge (firearms) * Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire ** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, especially electrical ** Birmingham gauge, a measure of ferrous wire and hypodermic needle diameter ** Jewelry wire gauge, the size of wire used in jewelry making * Sheet metal gauge, thickness of metal in sheet form * Film gauge, a physical property of film stock which defines its size * The size of objects used in stretching (body piercing), especially earrings * Gauge block, a metal or ceramic block of precisely known dimension, used in measuring * Sight glass, also known as a water gauge, for measuring liquid level heights in storage tanks and pressure vessels * Boost gauge, a gauge used in conjunction with turbo-super-chargers * Pressure gauge or vacuum gauge, see pressure measurement * Gauge pressure, pressure above ambient pressure * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Gauge
Variable gauge systems allow railway vehicles to travel between two railways with different track gauges. Vehicles are equipped with variable gauge axles (VGA). The gauge is altered by driving the train through a gauge changer installed at the break of gauge which moves the wheels to the gauge desired. Variable gauge systems exist within the internal network of Spain, and are installed on international links between Spain/France (Spanish train), Sweden/Finland (Swedish train), Poland/Lithuania (Polish train) and Poland/Ukraine Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ... (Polish train). A system for changing gauge without the need to stop is in widespread use for passenger traffic in Spain, for services run on a mix of dedicated high-speed lines (using Standard gauge) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
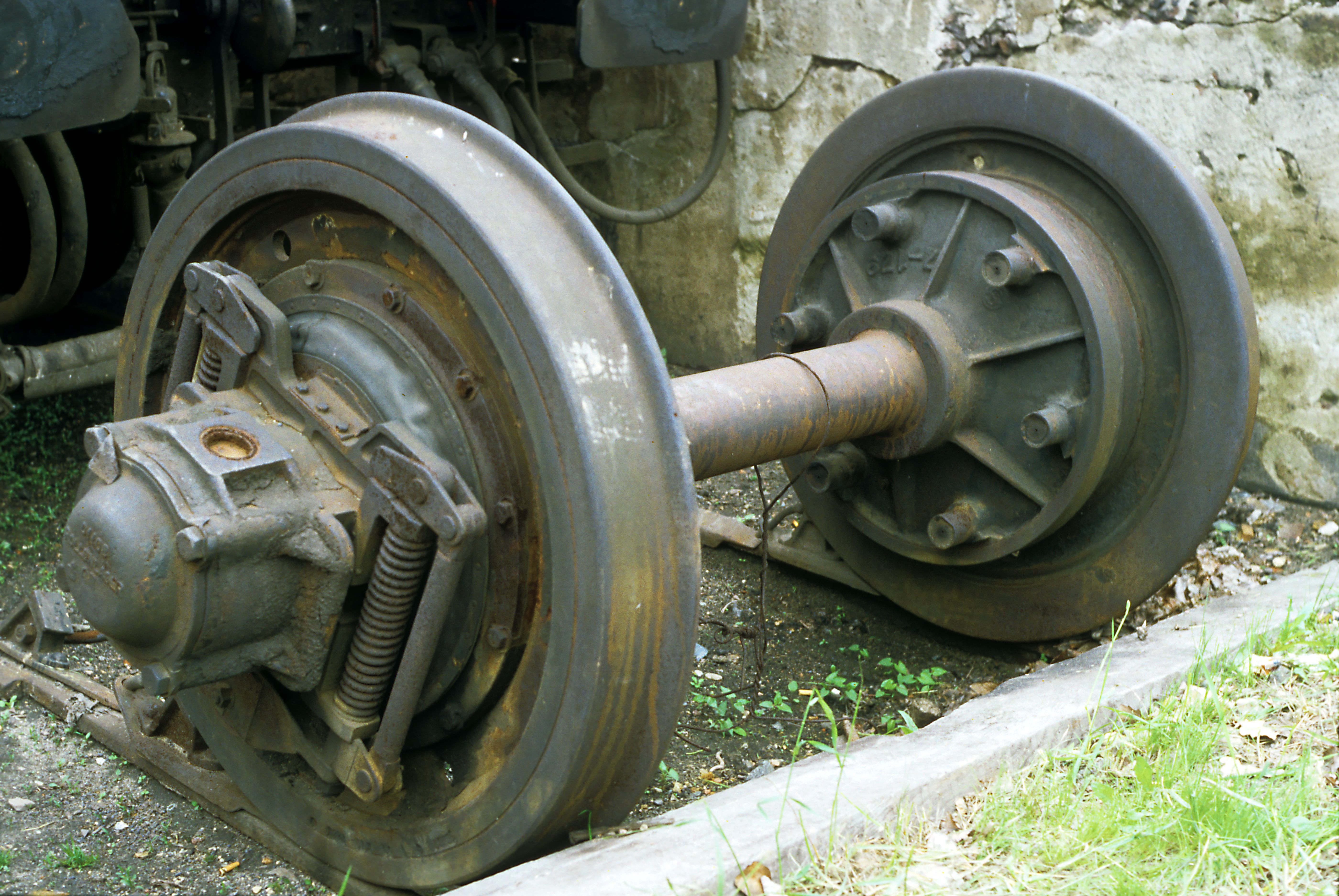
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the transverse distance be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Theory
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, does not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie groups). Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant under these transformations. The term "gauge" refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian of a physical system. The transformations between possible gauges, called gauge transformations, form a Lie group—referred to as the '' symmetry group'' or the gauge group of the theory. Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group generators. For each group generator there necessarily arises a corresponding field (usually a vector field) called the gauge field. Gauge fields are included in the Lagrangian to ensure its invariance under the local group transformations (called gauge invariance). When such a theory is quantized, the quanta of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and keep clear of platforms, trackside buildings and structures. Classification systems vary between different countries, and loading gauges may vary across a network, even if the track gauge is uniform. The term loading gauge can also be applied to the maximum size of road vehicles in relation to tunnels, overpasses and bridges, and doors into automobile repair shops, bus garages, filling stations, residential garages, multi-storey car parks and warehouses. A related but separate gauge is the structure gauge, which sets limits to the extent that bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure can encroach on rail vehicles. The difference between these two gauges is called the clearance. The specified amount of clearance makes allowance for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Block
Gauge blocks (also known as gage blocks, Johansson gauges, slip gauges, or Jo blocks) are a system for producing precision lengths. The individual gauge block is a metal or ceramic block that has been precision grinding (abrasive cutting), ground and Lapping, lapped to a specific thickness. Gauge blocks come in sets of blocks with a range of standard lengths. In use, the blocks are stacked to make up a desired length (or height). Gauge blocks were invented in 1896 by Swedish machinist Carl Edvard Johansson. They are used as a reference for the calibration of measuring equipment used in machine shops, such as micrometer (device), micrometers, sine bars, calipers, and dial gauge, dial indicators (when used in an Quality control, inspection role). Gauge blocks are the main means of length standardization used by industry. An important feature of gauge blocks is that they can be joined together with very little dimensional uncertainty. The blocks are joined by a sliding process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Metal Gauge
Sheet metal is metal formed into thin, flat pieces, usually by an industrial process. Thicknesses can vary significantly; extremely thin sheets are considered foil or leaf, and pieces thicker than 6 mm (0.25 in) are considered plate, such as plate steel, a class of structural steel. Sheet metal is available in flat pieces or coiled strips. The coils are formed by running a continuous sheet of metal through a roll slitter. In most of the world, sheet metal thickness is consistently specified in millimeters. In the U.S., the thickness of sheet metal is commonly specified by a traditional, non-linear measure known as its gauge. The larger the gauge number, the thinner the metal. Commonly used steel sheet metal ranges from 30 gauge (0.40 mm) to about 7 gauge (4.55 mm). Gauge differs between ferrous ( iron-based) metals and nonferrous metals such as aluminum or copper. Copper thickness, for example, is in the USA traditionally measured in ounces, representing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Integral
Gauge ( ) may refer to: Measurement * Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments * Gauge (firearms) * Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire ** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, especially electrical ** Birmingham gauge, a measure of ferrous wire and hypodermic needle diameter ** Jewelry wire gauge, the size of wire used in jewelry making * Sheet metal gauge, thickness of metal in sheet form * Film gauge, a physical property of film stock which defines its size * The size of objects used in stretching (body piercing), especially earrings * Gauge block, a metal or ceramic block of precisely known dimension, used in measuring * Sight glass, also known as a water gauge, for measuring liquid level heights in storage tanks and pressure vessels * Boost gauge, a gauge used in conjunction with turbo-super-chargers * Pressure gauge or vacuum gauge, see pressure measurement * Gauge pressure, pressure above ambient pressure * Stream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge (band)
Gauge is an American post-hardcore band from the northwest suburbs of Chicago, Illinois. History Gauge formed at the beginning of 1991. Members had previously been in the bands Ivy League and Target. Highly regarded in Chicago's northwest suburban punk scene, Gauge inspired and performed with other bands from the same area such as Cap'n Jazz, Friction, and Braid. Gauge released their first full-length, Soothe, by the end of 1992. After releasing their second album in 1994, entitled Fire Tongue Burning Stomach, they announced their break up. A posthumous 10" was released in 1995, making the band's final recordings available. During their career, Gauge played 150 shows. Their final show was on October 6, 1994, at The Moose Lodge in Mount Prospect, IL with Cap'n Jazz and Tetsuo. Members of Gauge went on to perform in the bands Sky Corvair, Euphone, 5ive Style, Sweater Weather, Haymarket Riot, Traluma, Radio Flyer, Heroic Doses, Ambulette and Rollo Tomasi, as well as working with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
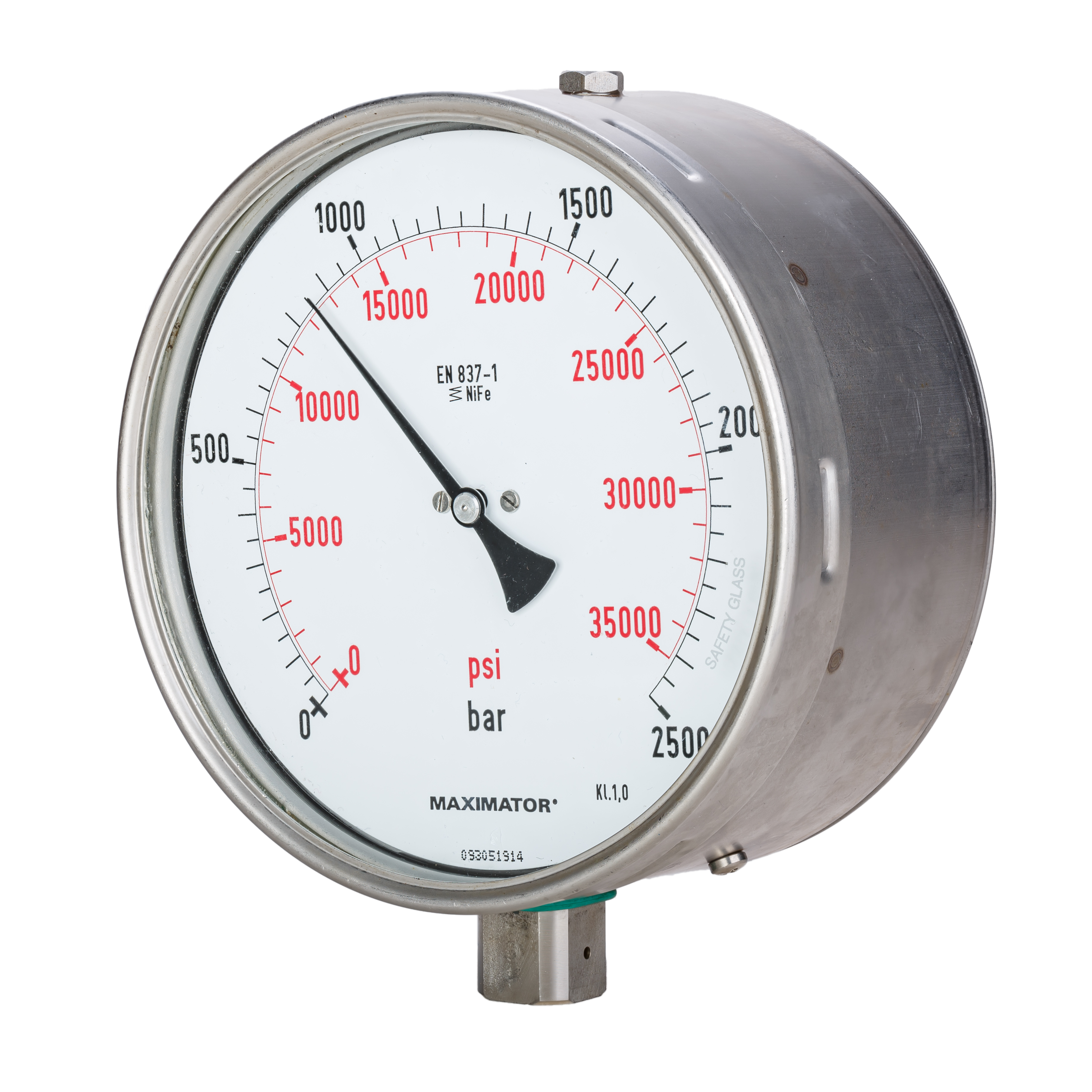
Gauge Pressure
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Measurement
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge (firearms)
The gauge (in American English or more commonly referred to as bore in British English) of a firearm is a unit of measurement used to express the inner diameter (bore diameter) and other necessary parameters to define in general a smoothbore Gun barrel, barrel (compare to caliber, which defines a barrel with rifling and its Cartridge (firearms), cartridge). The gauge of a shotgun is a list that includes all necessary data to define a functional barrel. For example, the dimension of the chamber, the shotgun bore dimension and the valid proof load and commercial ammunition, as defined globally by the Commission internationale permanente pour l'épreuve des armes à feu portatives, C.I.P.; defined in Great Britain by the ''Rules, regulations and scales applicable to the proof of small arms'' (2006) of Worshipful Company of Gunmakers, The London Proof House and Birmingham Proof House, The Birmingham Proof House, as referred in the Gun Barrel Proof Act 1978, Paragraph 6; and defined in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
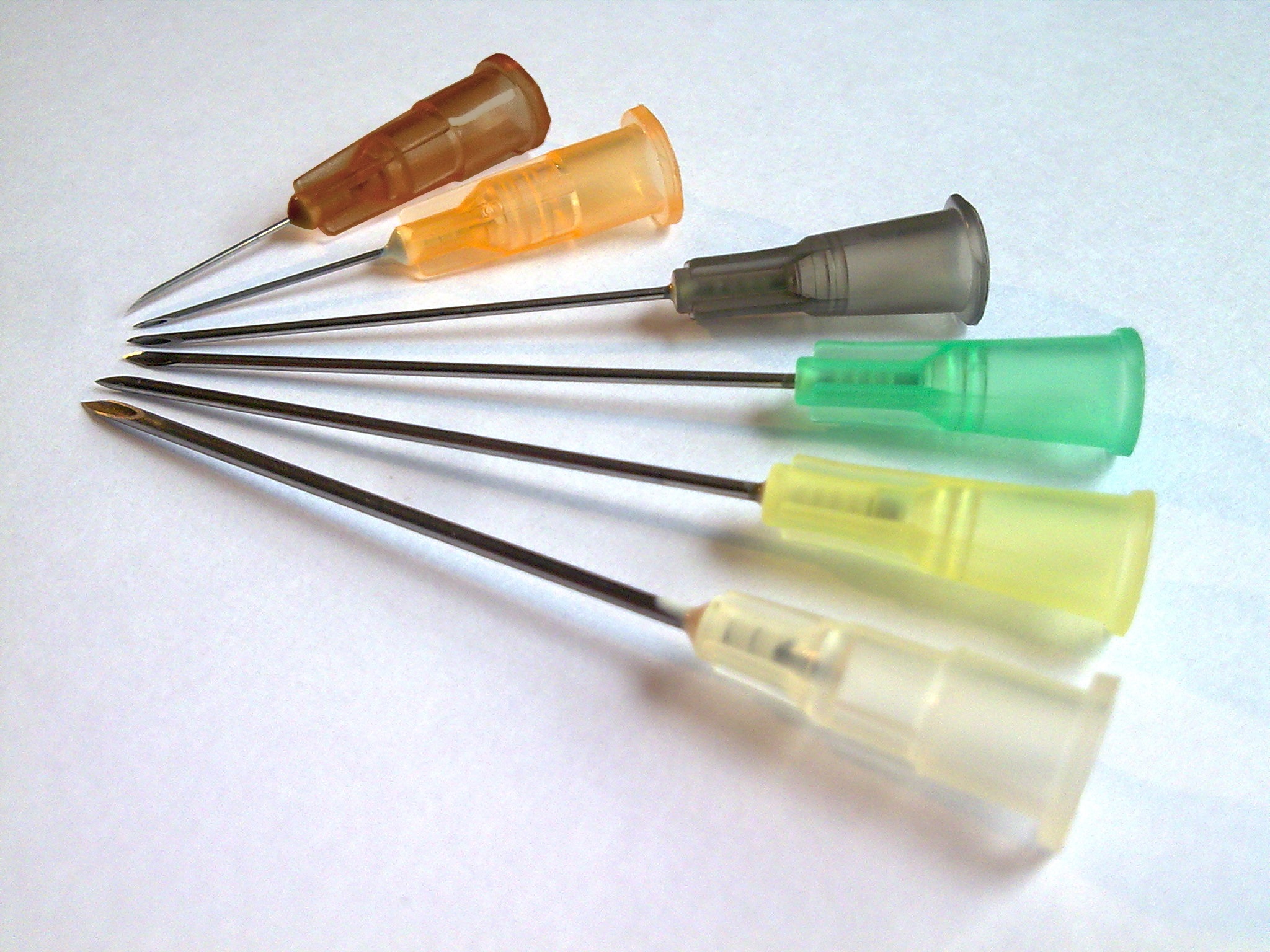
Birmingham Gauge
The Birmingham gauge, officially the Birmingham Wire Gauge and often abbreviated as ''G'' or ''ga'', is unit or wire gauge used to measure the thickness or diameter of wires and tubing, including hypodermic needles and other medical tube products. Terminology The Birmingham gauge is also known as the Stubs Iron Wire Gauge or Birmingham Wire Gauge and is distinct from the Stubs Steel Wire Gauge and the British Standard Wire Gauge. It is commonly referred to simply as ''gauge'' (abbreviated as ''G''), but this should not be confused with the French gauge, a separate system used for measuring the outer diameter of catheters. System The Birmingham gauge ranges from 5/0 or 00000, the lowest gauge number corresponding to the largest size of , to 36, the highest gauge number corresponding to the smallest size of . The increments between gauge sizes are not linear and vary. At higher gauge numbers, the increment between the two highest gauges is , while at lower gauge numbers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |