|
Garshunography
Garshunography is the use of "the script of one language to write utterances of another language which already has a script associated with it sociolinguistically". The phenomenon has also been called allography or heterography, although both these terms have other uses, the former to denote Allography, different shapes of the same grapheme and the latter to denote Heterography, different spellings of homophones. In French, the term has also been proposed.: "" [adoption of an alphabet of foreign origin by the speakers of a language already provided with a commonly accepted alphabet]. The term "garshunography" comes from Garshuni, a term of uncertain origin that refers to the writing of the Arabic language in the Syriac script. Concept George Kiraz identifies two sociolinguistic conditions for garshunography: "the source language is associated with a script that is perceived to be its own" and "there exists readership which is either unfamiliar with the script of the source langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garshuni
Garshuni or Karshuni (Syriac alphabet: , Arabic alphabet: ) are Arabic writings using the Syriac alphabet. The word "Garshuni", derived from the word "grasha" which literally translates as "pulling", was used by George Kiraz to coin the term " garshunography", denoting the writing of one language in the script of another. History Garshuni originated in the seventh century, when Arabic was becoming the dominant spoken language in the Fertile Crescent, but the Arabic alphabet was not yet fully developed. There is evidence that writing Arabic in Garshuni influenced the style of modern Arabic script. After this initial period, Garshuni writing has continued to the present day among some Syriac Christian communities in the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant and Mesopotamia, who commonly use the Sertâ script. Characteristics The Syriac alphabet has three principal varieties: * Estrangelâ (the Classical Syriac script), * Madnhâyâ (the Eastern Syriac script, often called "Assyria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allography
In graphemics and typography, the term allograph is used of a glyph that is a design variant of a letter or other grapheme, such as a letter, a number, an ideograph, a punctuation mark or other typographic symbol. In graphemics, an obvious example in Latin alphabet (and many other writing systems) is the distinction between uppercase and lowercase letters. Allographs can vary greatly, without affecting the underlying identity of the grapheme. Even if the word "cat" is rendered as "cAt", it remains recognizable as the sequence of the three graphemes , , . Letters and other graphemes can also have significant variations that may be missed by many readers. The letter g, for example, has two common forms in different typefaces, and a wide variety in people's handwriting. A positional example of allography is the long s , a symbol which was once a widely used as a non-final allograph for the lowercase letter s. A grapheme variant can acquire a separate meaning in a specialized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Orthography
English orthography comprises the set of rules used when writing the English language, allowing readers and writers to associate written graphemes with the sounds of spoken English, as well as other features of the language. English's orthography includes norms for spelling, hyphenation, capitalisation, word, word breaks, Emphasis (typography), emphasis, and punctuation. As with the orthographies of most other world languages, written English is broadly standardised. This standardisation began to develop when movable type spread to England in the late 15th century. However, unlike with most languages, there are multiple ways to spell every phoneme, and most grapheme, letters also represent multiple pronunciations depending on their position in a word and the context. This is partly due to the large number of words that have been Loanword, loaned from a large number of other languages throughout the history of English, without successful attempts at complete English-language spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
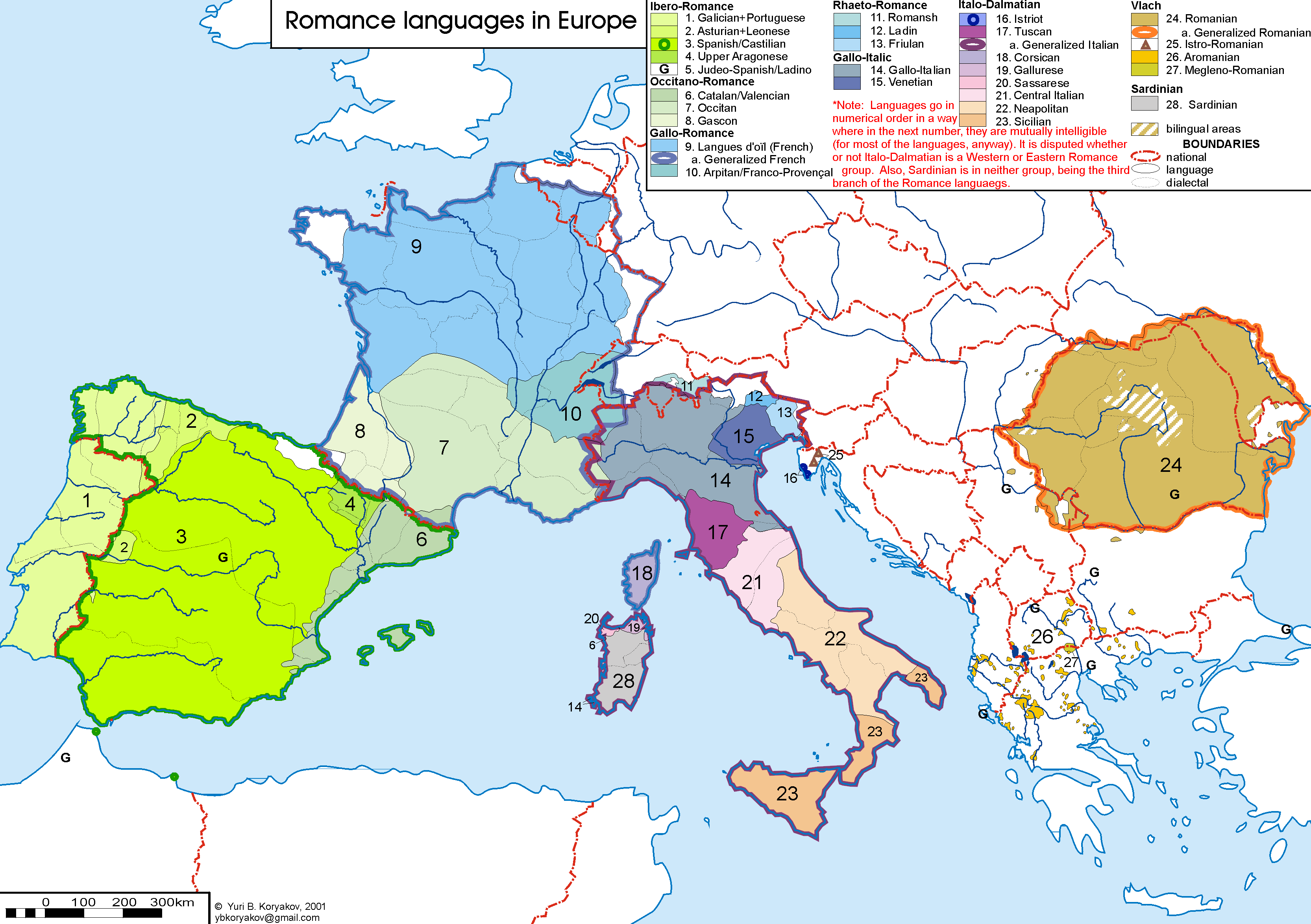
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widely used List of writing systems by adoption, writing system in the world by number of countries using it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese characters, Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With Spread of Islam, the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are Arabic language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian (Western Persian, Farsi and Dari), Urdu, Uyghur language, Uyghur, Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Pashto, Punjabi language, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi language, Sindhi, South Azerbaijani, Azerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aljamiado
'' Castillian translations in Aljamiado script above each line of Arabic Quranic text. file:Aljamiado.png">Aljamiado text by Mancebo de Arévalo. c. 16th century. ''Poema de Yuçuf'' ''Aljamiado'' (; ; trans. ''ʿajamiyah'' ) or ''Aljamía'' texts are manuscripts that use the Arabic script for transcribing European languages, especially Romance languages such as Old Spanish or Aragonese. This alphabet is also called the Morisco alphabet. According to Anwar G. Chejne, ''Aljamiado'' or ''Aljamía'' is "a corruption of the Arabic word ''ʿajamiyah'' (in this case it means foreign language) and, generally, the Arabic expression ''ʿajam'' and its derivative ''ʿajamiyah'' are applicable to peoples whose ancestry is not of Arabian origin". During the Arab conquest of Persia, the term became a pejorative. History The systematic writing of Romance-language texts in Arabic scripts appears to have begun in the fifteenth century, and the overwhelming majority of such texts th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogdian Language
The Sogdian language was an Eastern Iranian language spoken mainly in the Central Asian region of Sogdia (capital: Samarkand; other chief cities: Panjakent, Fergana, Khujand, and Bukhara), located in modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan; it was also spoken by some Sogdian immigrant communities in ancient China. Sogdian is one of the most important Middle Iranian languages, along with Bactrian, Khotanese Saka, Middle Persian, and Parthian. It possesses a large literary corpus. The Sogdian language is usually assigned to a Northeastern group of the Iranian languages. No direct evidence of an earlier version of the language ("Old Sogdian") has been found, although mention of the area in the Old Persian inscriptions means that a separate and recognisable Sogdia existed at least since the Achaemenid Empire (559–323 BCE). Like Khotanese, Sogdian may have possessed a more conservative grammar and morphology than Middle Persian. The modern Eastern Irania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suriyani Malayalam
Suriyani Malayalam (സുറിയാനി മലയാളം, ܣܘܪܝܢܝ ܡܠܝܠܡ), also known as Karshoni, Syro-Malabarica or Syriac Malayalam, is a dialect of Malayalam written in a variant form of the Syriac alphabet which was popular among the Saint Thomas Christians (also known as Syrian Christians or Nasranis) of Kerala in India. It uses Malayalam grammar, the Maḏnḥāyā or "Eastern" Syriac script with special orthographic features, and vocabulary from Malayalam and East Syriac. This originated in the South Indian region of the Malabar Coast (modern-day Kerala). Until the 19th century, the script was widely used by Syrian Christians in Kerala. Writing system There were numerous problems in writing Malayalam using the Syriac script, which was designed for a Semitic language. Only 22 letters were available from the East Syriac alphabet to render 53 or so phonemes of Malayalam. This problem were overcome by adopting letters from the Malayalam script. Basic Syria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Languages
Kurdish (, , ) is a Northwestern Iranian language or group of languages spoken by Kurds in the region of Kurdistan, namely in southeast Turkey, northern Iraq, northwest Iran, and northern Syria. It is also spoken in northeast Iran, as well as in certain areas of Armenia and Azerbaijan. Kurdish varieties constitute a dialect continuum, with some mutually unintelligible varieties, and collectively have 26 million native speakers. The main varieties of Kurdish are Kurmanji, Sorani, and Southern Kurdish (). The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script. A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the Zaza–Gorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds.Kaya, Mehmet. The Zaza Kurds of Turkey: A Middle Eastern Minority i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijani Language
Azerbaijani ( ; , , ) or Azeri ( ), also referred to as Azerbaijani Turkic or Azerbaijani Turkish (, , ), is a Turkic languages, Turkic language from the Oghuz languages, Oghuz sub-branch. It is spoken primarily by the Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan, where the North Azerbaijani Variety (linguistics), variety is spoken, while Iranian Azerbaijanis in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region of Iran, speak the South Azerbaijani Variety (linguistics), variety. Azerbaijani is the only official language in the Republic of Azerbaijan and one of the 14 official languages of Dagestan (a Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia), but it does not have official status in Iran, where the majority of Iranian Azerbaijanis, Iranian Azerbaijani people live. Azerbaijani is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Azerbaijani communities of Georgia (country), Georgia and Turkey and by Azerbaijani diaspora, diaspora communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian (endonym: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenians, Armenian people and the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian highlands, today Armenian is also widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by Saint Mesrop Mashtots. The estimated number of Armenian speakers worldwide is between five and seven million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits Centum and satem languages, more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |