|
Garanganze
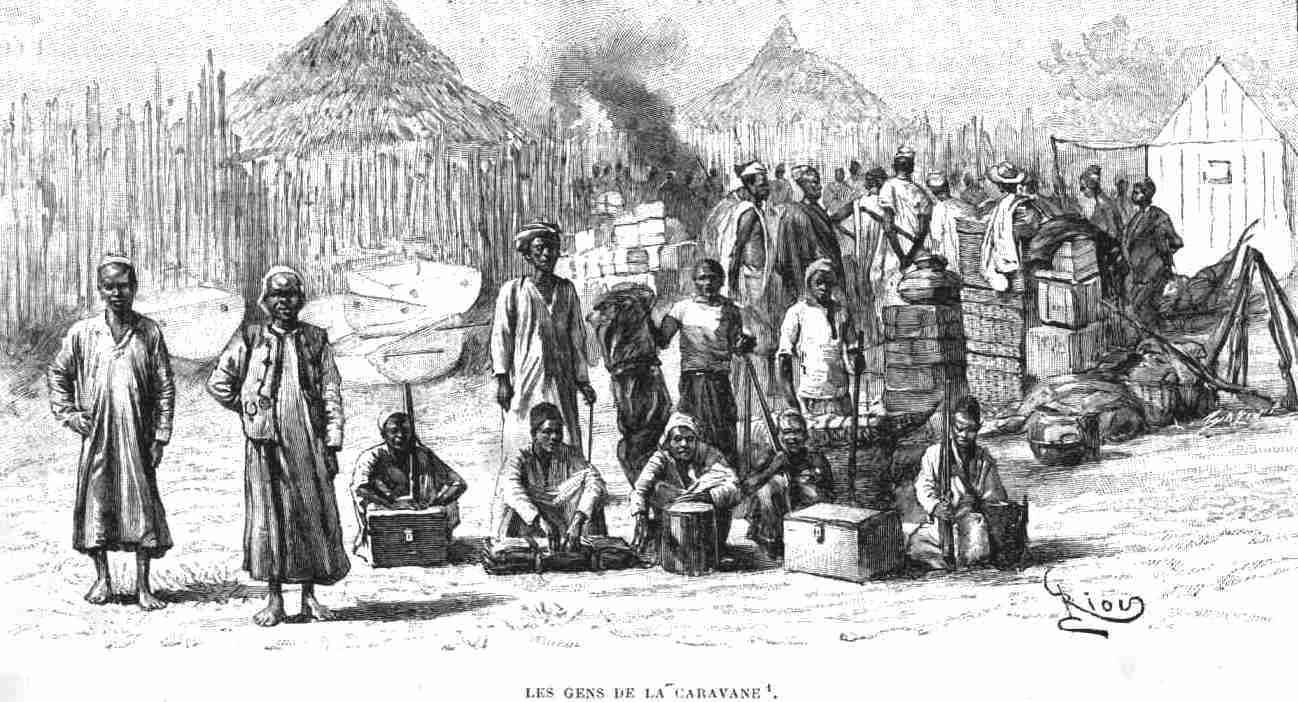
The Garanganze, Yeke or Bayeke are a people of Katanga Province, Katanga, in the Democratic Republic of Congo. They established the Yeke Kingdom under the warrior-king Msiri, who dominated the southern part of Central Africa from 1850 to 1891 and controlled the trade route between Angola and Zanzibar from his capital, at Bunkeya. Msiri and his people were originally Nyamwezi people, Nyamwezi traders from around Tabora who migrated to Katanga to reach the source of copper, ivory trade, ivory and slaves to trade. They took over and merged with a Wasanga chieftainship and established a powerful base by conquering neighbouring tribes. In 1891, Msiri was killed by the Stairs Expedition sent by King Leopold II of Belgium to take possession of Katanga for his Congo Free State. Many of the Yeke dispersed, with some settling in the Luapula River, Luapula Valley and the western shores of Lake Mweru around the Garanganze Missions of the Plymouth Brethren, led by Dan Crawford (missionary), Dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Msiri
Msiri (c. 1830 – December 20, 1891) founded and ruled the Yeke Kingdom (also called the Garanganze or Garenganze kingdom) in south-east Katanga (now in DR Congo) from about 1856 to 1891. His name is sometimes spelled 'M'Siri' in articles in French. Other variants are "Mziri", "Msidi", and "Mushidi"; and his full name was Mwenda Msiri Ngelengwa Shitambi.''Mwami Msiri, King of Garanganze''. Retrieved 8 February 2007. Msiri's origins and rise to power From Tabora to Katanga Msiri was a Nyamwezi from Tabora in modern-day |
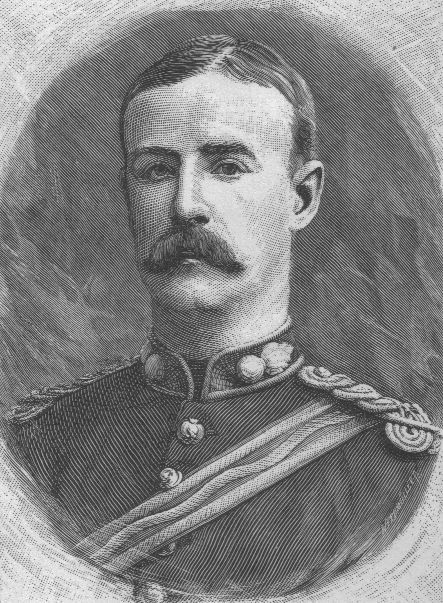
Stairs Expedition
The Stairs Expedition to Katanga (1891−92), led by Captain William Stairs, was the winner in a race between two imperial powers, the British South Africa Company BSAC and the Congo Free State, to claim Katanga, a vast mineral-rich territory in Central Africa for colonization. The mission became notable when a local chief, ( Mwenda Msiri), was killed, and also for the fact that Stairs, the leader of one side, actually held a commission in the army of the other. This "scramble for Katanga" was a prime example of the colonial Scramble for Africa, and one of the most dramatic incidents of that period. Historical background On one side of the race was the Congo Free State, Belgian King Leopold II's instrument for private colonisation in Central Africa. On the other was the company chartered by the British government to make treaties with African chiefs, the BSAC of Cecil Rhodes, who mixed a determined approach to gaining mineral concessions with a vision for British imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeke Kingdom
The Yeke Kingdom (also called the ''Garanganze'' or ''Garenganze'' kingdom) of the Garanganze people in Katanga, DR Congo, was short-lived, existing from about 1856 to 1891 under one king, Msiri, but it became for a while the most powerful state in south-central Africa, controlling a territory of about half a million square kilometres. The Yeke Kingdom also controlled the only trade route across the continent from east to west, since the Kalahari Desert and Lozi Kingdom in the south and the Congo rainforest in the north blocked alternative routes. It achieved this control through natural resources and force of arms—Msiri traded Katanga's copper principally, but also slaves and ivory, for gunpowder and firearms—and by alliances through marriage. The most important alliances were with Portuguese–Angolans in the Benguela area, with Tippu Tip in the north and with Nyamwezi and Swahili traders in the east, and indirectly with the Sultan of Zanzibar who controlled the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luapula River
The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu (Zambia), which are fed by the Chambeshi River. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo before emptying into Lake Mweru. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province.Terracarta/International Travel Maps, Vancouver Canada: "Zambia, 2nd edition", 2000 Source and upper Luapula The Luapula drains Lake Bangweulu and its swamps into which flows the Chambeshi River, the source of the Congo. There is no single clear channel connecting the two rivers and the lake, but a mass of shifting channels, lagoons and swamps, as the explorer David Livingstone found to his cost. (He died exploring the area, and one of his last acts was to question Chief Chitambo about the course of the Luapula.)Blaikie, William Garden (1880): ''The Personal Life Of David Livingstone''Project Gutenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunkeya
Bunkeya is a community in the Lualaba Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is located on a huge plain near the Lufira River. Before the Belgian colonial conquest, Bunkeya was the center of a major trading state under the ruler Msiri. Early history In the later 19th-century, Bunkeya was the capital of Msiri, the son of an East African trader. Msiri's father had been in the business of buying copper ore in Katanga and transporting it to the east coast of Africa for resale. As a young man Msiri remained behind in the region as his father's agent. He became leader of a group of Bayeke people, and established a state that extended from the Luapula River south to the Congo-Zambezi watershed, and from Lake Mweru in the east to the Lualaba River in the west. Based on Bunkeya, the state controlled a huge central-African trading network, mostly dealing in slaves but also in ivory, salt, copper and iron ore. Traders came to Bunkeya from the Zambezi and Congo basins, from Angol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is a rich mining region which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered from the south by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Katanga Province
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
demography, Demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo include Ethnic group, ethnicity, education level, health, Socioeconomic status, economic status, Religion in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. As many as 250 ethnic groups have been distinguished and named. The most numerous people are the Luba people, Luba, Mongo people, Mongo, and Bakongo, Kongo. Although 700 local languages and dialects are spoken, the linguistic variety is bridged both by the use of French language, French, and the intermediary languages Kituba language, Kikongo ya leta, Luba-Kasai language, Tshiluba, Swahili language, Swahili, and Lingala language, Lingala. Population The The World Factbook, CIA World Factbook estimated the population to be over 105 million as of 2022 (the exact number being 108,407,721), now exceeding that of Vietnam (with 98,721,275 inhabitants as of 2020) and ascending the country to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobutu
Mobutu Sese Seko Kuku Ngbendu wa za Banga ( ; born Joseph-Désiré Mobutu; 14 October 1930 – 7 September 1997), often shortened to Mobutu Sese Seko or Mobutu and also known by his initials MSS, was a Congolese politician and military officer who was the first and only president of Zaire from 1971 to 1997. Previously, Mobutu served as the second president of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1965 to 1971. He also served as the fifth chairperson of the Organisation of African Unity from 1967 to 1968. During the Congo Crisis, Mobutu, serving as Chief of Staff of the Army and supported by Belgium and the United States, deposed the democratically elected government of left-wing nationalist Patrice Lumumba in 1960. Mobutu installed a government that arranged for Lumumba's execution in 1961, and continued to lead the country's armed forces until he took power directly in a second coup in 1965. To consolidate his power, he established the Popular Movement of the Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godefroid Munongo
Godefroid Munongo Mwenda M'Siri (20 November 1925 – 28 May 1992) was a Congolese politician. He was a minister and briefly interim president, in 1961. It has been claimed he was involved in ethnic cleansing and in the assassination of Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, during the Congo Crisis. Early life Munongo was born on 20 November 1925 in Bunkeya (now in Lualaba Province). He was a descendant of King Msiri Msiri (c. 1830 – December 20, 1891) founded and ruled the Yeke Kingdom (also called the Garanganze or Garenganze kingdom) in south-east Katanga (now in DR Congo) from about 1856 to 1891. His name is sometimes spelled 'M'Siri' in articles in F ... of the Nyamwezi, who founded the State of Garenganze in the latter half of the 19th century.Patrick Munongo , his son, accessed February 2009 He entered the major seminary in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Chief
A tribal chief, chieftain, or headman is a leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom. Tribal societies There is no definition for "tribe". The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in Cities of the Ancient Near East, cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified society, stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with Urban area, urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swahili Language
Swahili, also known as as it is referred to endonym and exonym, in the Swahili language, is a Bantu languages, Bantu language originally spoken by the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya, and Mozambique (along the East African coast and adjacent littoral islands). Estimates of the number of Swahili speakers, including both native and second-language speakers, vary widely. They generally range from 150 million to 200 million; with most of its native speakers residing in Tanzania and Kenya. Swahili has a significant number of loanwords from other languages, mainly Arabic, as well as from Portuguese language, Portuguese, English language, English and German language, German. Around 40% of Swahili vocabulary consists of Arabic loanwords, including the name of the language ( , a plural adjectival form of an Arabic word meaning 'of the coasts'). The loanwords date from the era of contact between Arab slave trade, Arab traders and the Northeast Bantu languages, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |