|
Gan Chinese
Gan, Gann or Kan is a group of Sinitic languages spoken natively by many people in the Jiangxi province of China, as well as significant populations in surrounding regions such as Hunan, Hubei, Anhui, and Fujian. Gan is a member of the Sinitic languages of the Sino-Tibetan language family, and Hakka is the closest Chinese variety to Gan in terms of phonetics. There are different dialects of Gan; the Nanchang dialect is the prestige dialect. Classification Like all other varieties of Chinese, there is a large amount of mutual unintelligibility between Gan Chinese and other varieties. Within the variation of Chinese dialects, Gan has more similarities with Mandarin than with Yue or Min. However, Gan clusters more with Xiang than Mandarin. Gan and other Southern Chinese languages can be distinguished from Northern Chinese by their placement of direct objects before indirect objects. Gan's ditransitive verbs introduce the theme right after the verb, while Mandarin's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Character
Chinese characters are logographs used to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represent the only one that has remained in continuous use. Over a documented history spanning more than three millennia, the function, style, and means of writing characters have changed greatly. Unlike letters in alphabets that reflect the sounds of speech, Chinese characters generally represent morphemes, the units of meaning in a language. Writing all of the frequently used vocabulary in a language requires roughly 2000–3000 characters; , nearly have been identified and included in '' The Unicode Standard''. Characters are created according to several principles, where aspects of shape and pronunciation may be used to indicate the character's meaning. The first attested characters are oracle bone inscriptions made during the 13th century BCE in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
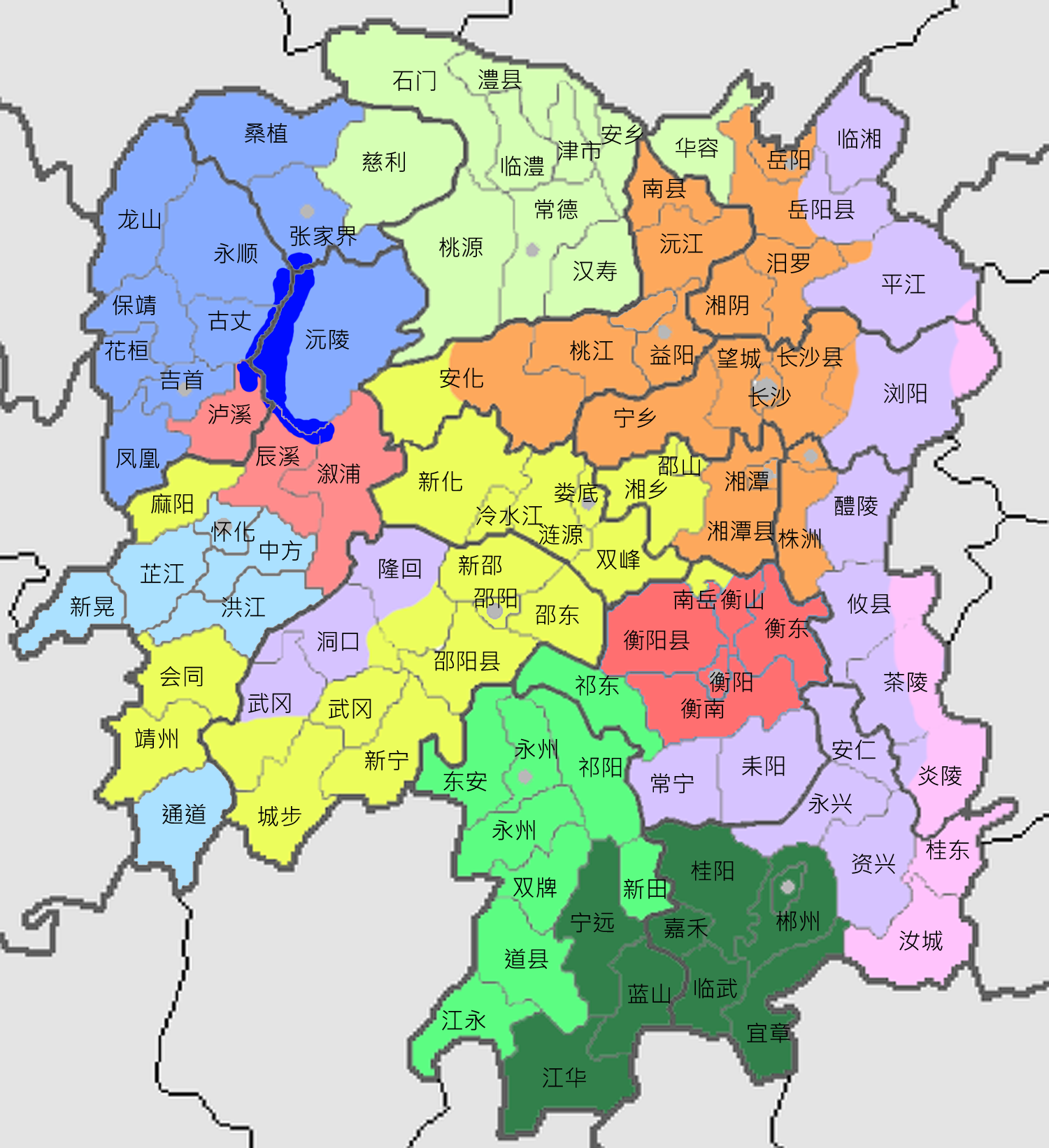
Chang–Du Gan
Chang–Du or Chang–Jing, sometimes called Nanchang or Nanchangese () after its principal dialect, is one of the Gan Chinese languages. It is named after Nanchang and Duchang County, and is spoken in those areas as well as in Xinjian, Anyi, Yongxiu, De'an, Xingzi, Hukou, and bordering regions in Jiangxi and in Pingjiang County, Hunan. Phonology The Nanchang dialect has 19 syllable onsets or initials (including the zero initial), 65 finals and 7 tones. Initials In each cell below, the first line indicates IPA transcription, the second indicates pinyin. Finals The finals of the Nanchang dialect are:Yan (2006), pp. 150–151, based on ''Hanyu Fangyin Zihui''. Consonantal codas * The codas in ''italic'' are at present only reserved in several Gan dialects. Tone Like other Chinese varieties, tones in Gan make phonemic distinctions. There are five phonemic tones in Gan, which are reduced to two 'entering tones' before stop consonants. In the traditional classification, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valency (linguistics)
In linguistics, valency or valence is the number and type of arguments and complements controlled by a predicate, content verbs being typical predicates. Valency is related, though not identical, to subcategorization and transitivity, which count only object arguments – valency counts all arguments, including the subject. The linguistic meaning of valency derives from the definition of valency in chemistry. Like valency found in chemistry, there is the binding of specific elements. In the grammatical theory of valency, the verbs organize sentences by binding the specific elements. Examples of elements that would be bound would be the complement and the actant. Although the term originates from valence in chemistry, linguistic valency has a close analogy in mathematics under the term arity. The valency metaphor appeared first in linguistics in Charles Sanders Peirce's essay "The Logic of Relatives" in 1897, and it then surfaced in the works of a number of linguists decade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Object
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term " agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Chinese
Xiang or Hsiang ( Chinese: 湘; Changsha Xiang: , Mandarin: ), also known as Hunanese, is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages, spoken mainly in Hunan province but also in northern Guangxi and parts of neighboring Guizhou, Guangdong, Sichuan, Jiangxi and Hubei provinces. Scholars divided Xiang into five subgroups: Lou–Shao (Old Xiang), Chang–Yi (New Xiang), Chen–Xu or Ji–Xu, Hengzhou, and Yong–Quan. Among those, Lou–Shao, or Old Xiang, still exhibits the three-way distinction of Middle Chinese obstruents, preserving the voiced stops, fricatives, and affricates. Xiang has also been heavily influenced by Mandarin, which adjoins three of the four sides of the Xiang-speaking territory, and Gan in Jiangxi Province, from where a large population immigrated to Hunan during the Ming dynasty. Xiang-speaking Hunanese people have played an important role in Modern Chinese history, especially in those reformatory and revolutionary m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min Chinese
Min ( zh, t=, s=闽语, p=Mǐnyǔ, poj=Bân-gú / Bân-gír / Bân-gí; Bàng-uâ-cê, BUC: ''Mìng-ngṳ̄'') is a broad group of Sinitic languages with about 75 million native speakers. These languages are spoken in Fujian province and Chaoshan, as well as by the descendants of Min-speaking colonists on the Leizhou Peninsula, Hainan, parts of Zhongshan, three counties in southern Wenzhou, the Zhoushan archipelago, Taiwan, and scattered in pockets or sporadically across Hong Kong, Macau, and several countries in Southeast Asia, particularly Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Brunei. The name is derived from the Min River (Fujian), Min River in Fujian, which is also the abbreviated name of Fujian Province. Min varieties are not mutually intelligible with one another nor with any other variety of Chinese (such as Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, Cantonese, Wu Chinese, Wu, Gan Chinese, Gan, Xiang Chinese, Xiang, or Hakka Chinese, Hak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yue Chinese
Yue () is a branch of the Sinitic languages primarily spoken in Northern and southern China, Southern China, particularly in the provinces of Guangdong and Guangxi (collectively known as Liangguang). The term Cantonese is often used to refer to the whole branch, but linguists prefer to reserve the name Cantonese for the variety used in Guangzhou (Canton), Wuzhou (Ngchow), Hong Kong and Macau, which is the Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige dialect of the group. Taishanese, from the coastal area of Jiangmen (Kongmoon) located southwest of Guangzhou, was the language of most of the 19th-century emigrants from Guangdong to Southeast Asia and North America. Most later migrants have been speakers of Cantonese. Yue languages are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible with each other or with other varieties of Chinese, Chinese languages outside the branch. They are among the most Linguistic conservatism, conservative varieties with regard to the final consonants and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in the northeast. Its spread is generally attributed to the greater ease of travel and communication in the North China Plain compared to the more mountainous south, combined with the relatively recent spread of Mandarin to frontier areas. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as Southwestern Mandarin, those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze Mandarin, Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the Beijing dialect (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Because Mandarin originated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanchang Dialect
Nanchang is the capital of Jiangxi, China. Located in the north-central part of the province and in the hinterland of Poyang Lake Plain, it is bounded on the west by the Jiuling Mountains, and on the east by Poyang Lake. Because of its strategic location connecting the prosperous East and South China, it has become a major railway hub in Southern China in recent decades. As the Nanchang Uprising in 1927 is distinctively recognized by the ruling Communist Party as "firing the first gunshot against the Nationalists", the current government has therefore named the city since 1949 "the place where the People's Liberation Army was born", and the most widely known "place where the military banner of the People's Liberation Army was first raised". Nanchang is also a major city, appearing among the top 100 cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index and home to Nanchang University. History Imperial era The territories encompassing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Tibetan Language Family
Sino-Tibetan (also referred to as Trans-Himalayan) is a language family, family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European languages, Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Sinitic languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese language, Burmese (33 million) and the Tibetic languages (6 million). Four United Nations member states (China, Singapore, Myanmar, and Bhutan) have a Sino-Tibetan language as a main native language. Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented. Several low-level subgroups have been securely linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed, but reconstruction of a proto-language for the family as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Language
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period hypothesis, critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers to the language of one's ethnic group rather than the individual's actual first language. Generally, to state a language as a mother tongue, one must have full native fluency in that language. The first language of a child is part of that child's personal, social and cultural identity. Another impact of the first language is that it brings about the reflection and learning of successful social patterns of acting and speaking. Research suggests that while a non-native speaker may develop fluency in a targeted language after about two years of immersion, it can take between five and seven years for that child to be on the same working level as their native speaking counterparts. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |