|
Gajar
Gajary (; ) is a village and municipality in western Slovakia close to the town of Malacky in the Bratislava region. It lies around 40 km (25 statute miles) north-west of Slovakia's capital Bratislava close to the Austrian border. The village has around 3500 inhabitants. The village is an important archaeological site: findings from the Neolithic period, Eneolithic period, Bronze Age, early Slavic period (several Slavic settlements) have been excavated there. Names and etymology The Slovak name ''Gajary'' (1460 ''Gayary'') comes from German personal name Geier (1337 ''Gaywar'', later German name was ''Gairing''). In the 14th century, the village had also the Hungarian name ''Öregház'' (''Old House'', 1377 ''Eureghaz''), but the name was forgotten and then they used the name of German origin ''Gajár''. Genealogical resources The records for genealogical research are available at the state archive "Statny Archiv in Bratislava, Slovakia" * Roman Catholic church re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities And Towns In Slovakia
This is an alphabetical list of the 2,891 (singular , "municipality") in Slovakia. They are grouped into 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts (, singular ), in turn grouped into 8 Regions of Slovakia, regions (, singular ); articles on individual districts and regions list their municipalities. The average area of Slovak municipalities is about and an average population of about 1,888 people. * Ábelová * Abovce * Abrahám * Abrahámovce, Bardejov District * Abrahámovce, Kežmarok District * Abramová * Abranovce * Adamovské Kochanovce * Adidovce * Alekšince * Andovce * Andrejová * Ardanovce * Ardovo * Arnutovce * Báb, Nitra District, Báb * Babie * Babín * Babiná * Babindol * Babinec, Slovakia, Babinec * Bacúch * Bacúrov * Báč * Bačka, Slovakia, Bačka * Bačkov, Trebišov District, Bačkov * Bačkovík * Baďan * Bádice * Badín * Báhoň * Bajany * Bajč * Bajerov * Bajerovce * Bajka * Bajtava * Baka, Slovakia, Baka * Balá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacky
Malacky ( German: ''Malatzka'', Hungarian: ''Malacka'') is a town and municipality in western Slovakia around north of Slovakia’s capital, Bratislava. From the second half of the 10th century until 1918, it was part of the Kingdom of Hungary. It is one of the key cities of the region " Záhorie", between the Little Carpathians in the east and Morava River in the west and a cultural and economic hub for nearby villages such as Gajary, Kostolište, Veľké Leváre and Jakubov. The town is located on the large Prague-Brno-Bratislava highway, and many residents commute daily to Bratislava. The Little Carpathians mountain range provides excellent opportunities for recreational activities like hiking or mountain biking, with its wide array of signposted trails. Etymology The origin of the name is uncertain. According to the first theory, the name refers to the Hungarian word ''malacka'' which means "piglet" in Hungarian and because the town seal features a pig. A drawback of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacky District
The Malacky District () is a district in the Bratislava Region of western Slovakia. It lies north from Bratislava on Záhorská nížina lowland. Its current borders have been established in 1996. The administrative seat is its largest town, Malacky Malacky ( German: ''Malatzka'', Hungarian: ''Malacka'') is a town and municipality in western Slovakia around north of Slovakia’s capital, Bratislava. From the second half of the 10th century until 1918, it was part of the Kingdom of Hungary. .... In the Malacky District the industrial park Eurovalley is located, on area of with several thousand employees. Second largest town is Stupava, which is located close to Bratislava. Demographics Municipalities References External links * Districts of Bratislava Region {{Bratislava-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geier (surname)
Geier is a common surname in Germany and somewhat less common among German-American people. It is also found as a French surname, and as Russian surname. The latter probably is associated with German emigration to Russia in the 17th and 18th centuries. The surname Geier is often considered to be interchangeable with Geyer, although some sources ascribe a different origin and meaning to the two surnames. German migrants to English-speaking countries often Anglicize Geier as Geyer, though this change has become less common in recent years. Similarly, Geier has often been mistakenly changed to Geyer, and vice versa in legal papers such as birth certificates and migration documents, especially in areas where the name is uncommon, or one version is vastly prevalent. Many using the surname ''Geier'' share an oral history attributing its origins to a heroic band of peasant villagers who climbed high to an aerie and clubbed to death a gigantic raptor (a ''geier'') which had been stealin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War II, defines a German as a German nationality law, German citizen. During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent, and history.. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity." Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary, though not exclusive, criterion of German identity. Estimates on the total number of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Language
Slovak ( ; endonym: or ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech-Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script and formerly in Cyrillic script. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech language, Czech, to the point of very high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish language, Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German language, German, as well as other Slavic languages. History The Czech–Slovak gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
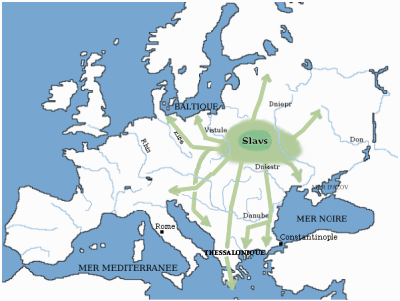
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). An asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in print and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten, though more complex forms exist. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk was already in use as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two-thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is known to have also used the asteriskos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, some sources estimate daily number of people moving around the city based on mobile phone SIM cards is more than 570,000. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the Danube and the left bank of the Morava (river), River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital to border two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Jews and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava Region
The Bratislava Region (, ; (until 1919); ) is one of the Regions of Slovakia, administrative regions of Slovakia. Its capital is Bratislava. The region was first established in 1923 and its present borders exist from 1996. It is the smallest of the eight regions of Slovakia as well as the most urbanized, most developed and most productive by GDP per capita. Geography The region is located in the south-western part of Slovakia and has an area of 2,053 km2 and a population of 622,706 (2009). The region is split by the Little Carpathians which start in Bratislava and continue north-eastwards; these mountains separate two lowlands, the Záhorie lowland in the west and the fertile Danubian Lowland in the east, which grows mainly wheat and maize. Major rivers in the region are the Morava (river), Morava River, the Danube and the Little Danube; the last of these, together with the Danube, encircle the Žitný ostrov in the south-east. There are three protected landscape areas in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |