|
Gael Brian
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx, and Scottish Gaelic. Gaelic language and culture originated in Ireland, extending to Dál Riata in western Scotland. In antiquity, the Gaels traded with the Roman Empire and also raided Roman Britain. In the Middle Ages, Gaelic culture became dominant throughout the rest of Scotland and the Isle of Man. There was also some Gaelic settlement in Wales, as well as cultural influence through Celtic Christianity. In the Viking Age, small numbers of Vikings raided and settled in Gaelic lands, becoming the Norse-Gaels. In the 9th century, Dál Riata and Pictland merged to form the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba. Meanwhile, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King often claiming lordship over them. In the 12th century, Anglo-Normans conquered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnolinguistic Group
An ethnolinguistic group (or ethno-linguistic group) is a group that is unified by both a common ethnicity and language. Most ethnic groups share a first language. However, "ethnolinguistic" is often used to emphasise that language is a major basis for the ethnic group, especially in regard to its neighbours. A central concept in the linguistic study of ethnolinguistic groups is ethnolinguistic vitality, the ability of the group's language and ethnicity to sustain themselves. An ethnolinguistic group that lacks such vitality is unlikely to survive as a distinct entity. Factors that influence the ethnolinguistic vitality are demographics, institutional control and status (including language planning factors). See also *First language *Ethnolinguistics *Ethnoreligious group *Nation state *Race (human classification) *Regionalism (politics) References Further reading *Bourhis, Richard Y. "Language in ethnic interaction: A social psychological approach." Language and ethnic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
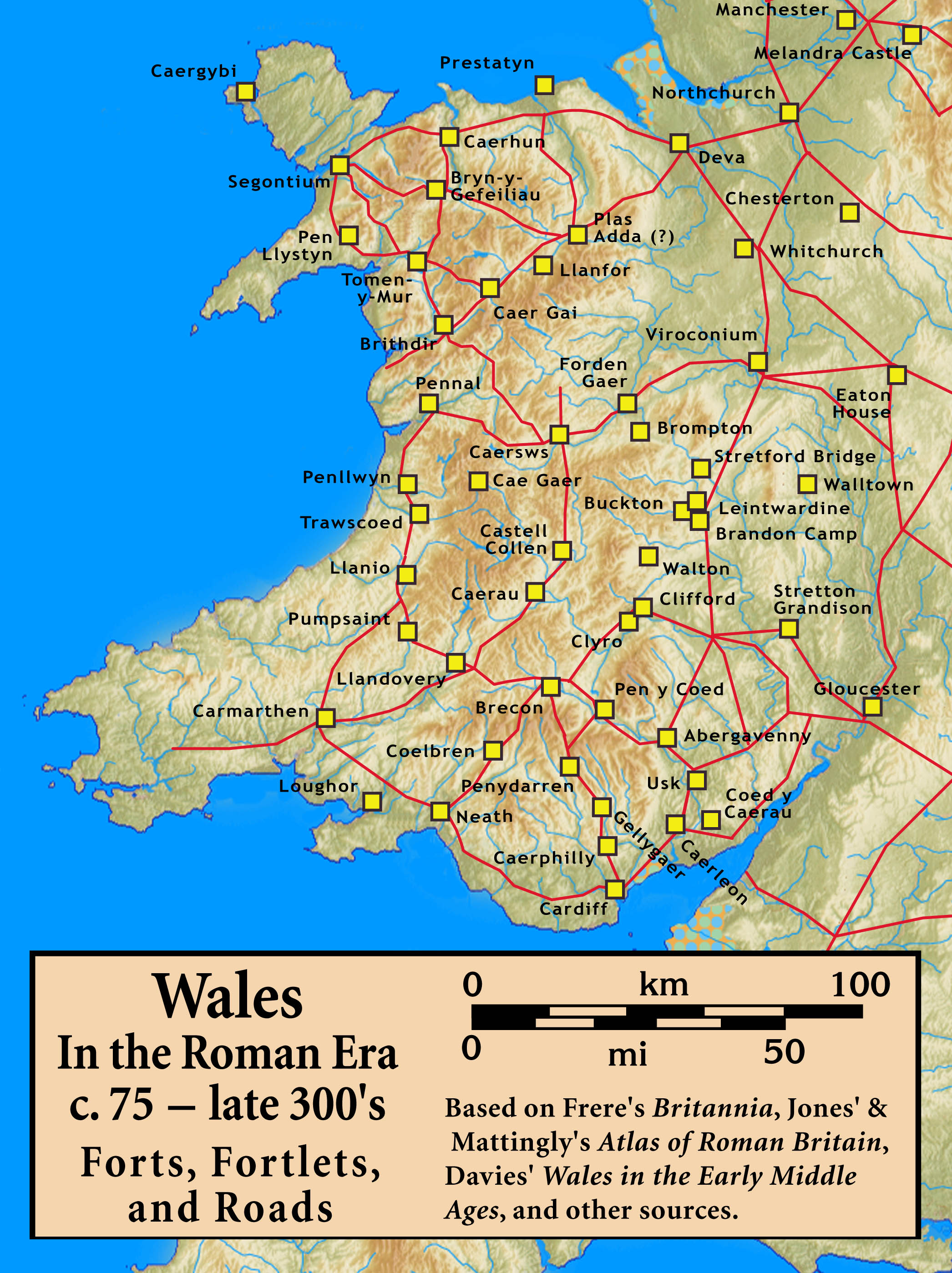
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the Roman governor, imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the End of Roman rule in Britain, region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanization (cultural), Romanisation #Romanisation, in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae, Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of #Mining, mineral wealth, and the Romans used Roman engineering, their engineering Roman technology, technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman #Roman invasion and conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Of Roman Rule In Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain occurred as the military forces of Roman Britain withdrew to defend or seize the Western Roman Empire's continental core, leaving behind an autonomous post-Roman Britain. In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew troops from northern and western Britain, probably leaving local warlords in charge. In 407, the usurper Constantine III took the remaining mobile Roman soldiers to Gaul in response to the crossing of the Rhine, and external attacks surged. The Romano-British deposed Roman officials around 410, and government largely reverted to city level. That year Emperor Honorius refused an appeal from Britain for military assistance. The following decades saw the collapse of urban life and the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Chronology 383–388 In 383, the Roman general then assigned to Britain, Magnus Maximus, launched his successful bid for imperial power, crossing to Gaul with his troops. He killed the Western Roman Emperor Gratian an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiberno-Roman Relations
Hiberno-Roman relations refers to the relationships (mainly commercial and cultural) which existed between Ireland (Hibernia) and the ancient Roman Empire, which lasted from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD in Western Europe. Ireland was one of the few areas of western Europe not conquered by Ancient Rome. Characteristics Rome never annexed Hibernia (the Latin name for Ireland) into the Roman Empire, but did exert influence on the island, although only a small amount of evidence of this has survived. This influence was expressed in three characteristic ways: commercial; cultural and religious; and military. Commercial The relationship between Rome and Hibernia was mostly commercial. In 1995, scholar Richard Warner wrote that after emperor Claudius' invasion of southern Britannia, the trade routes between the Mediterranean Sea and Roman Britannia encompassed even Hibernia. The geographer Ptolemy, in his map of the 1st century AD, pinpointed the coastal settlements and tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
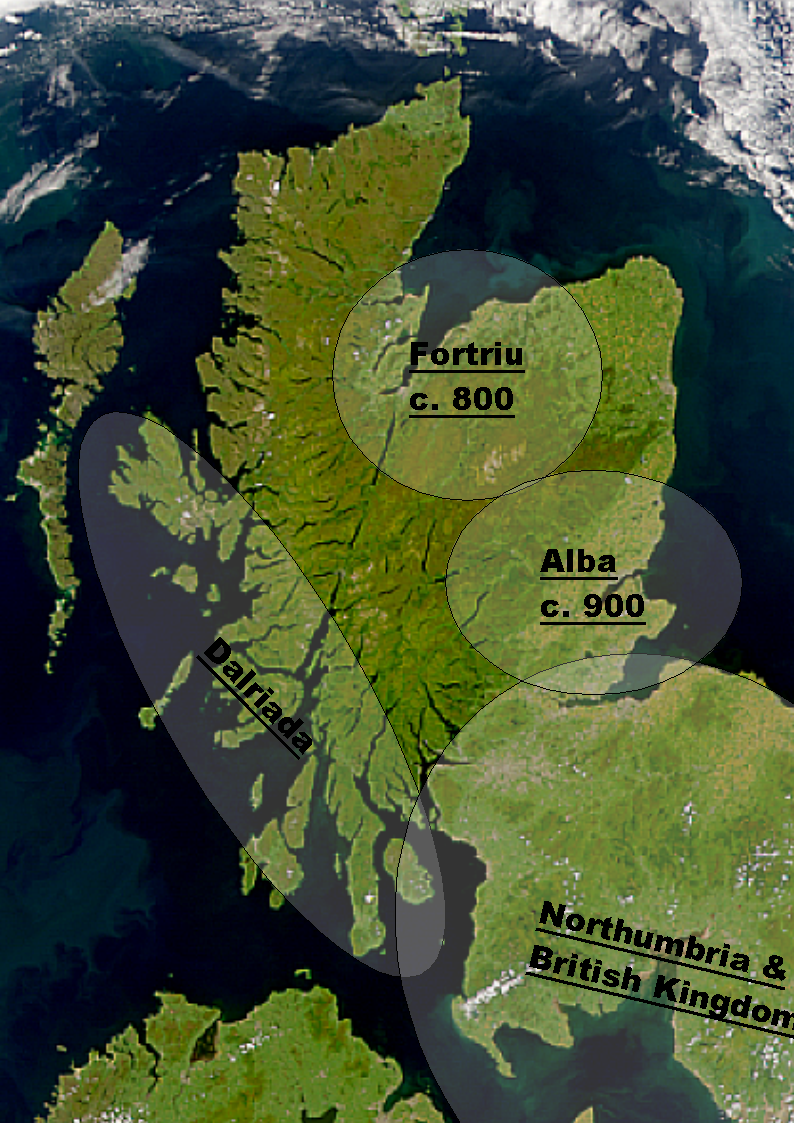
Scotland In The Middle Ages
Scotland in the Middle Ages concerns the history of Scotland from the departure of the Romans to the adoption of major aspects of the Renaissance in the early sixteenth century. From the fifth century northern Britain was divided into a series of kingdoms. Of these the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Strathclyde and the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Bernicia, later taken over by Northumbria. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late eighth century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established along parts of the coasts and in the islands. In the ninth century the Scots and Picts combined under the House of Alpin to form a single Kingdom of Alba, with a Pictish base and dominated by Gaelic culture. After the reign of King David I in the twelfth century, the Scottish monarchs are best described as Scoto-Norman, preferring French culture to native Scottish culture. Alexander II and his son Alexander III, were able to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is now Argyll ("Coast of the Gaels") in Scotland and part of County Antrim in Northern Ireland.Clancy, Thomas Owen, "Philosopher King: Nechtan mac Der Ilei," SHR 83 (2004): 135–149 After a period of expansion, Dál Riata eventually became associated with the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba.''Oxford Companion to Scottish History'' pp. 161–162, edited by Michael Lynch, Oxford University Press. . In Argyll, it consisted of four main clan, kindreds or tribes, each with their own chief: the Cenél nGabráin (based in Kintyre), the Cenél nÓengusa (based on Islay), the Loarn mac Eirc, Cenél Loairn (who gave their name to the district of Lorne, Scotland, Lorn) and the Cenél Comgai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Gaelic warfare, Warfare between List of Irish kingdoms, these territories was common. Traditionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of Irish clans, clans and, like the rest of History of Europe, Europe, was structured hierarchically according to Social class, class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly Pastoralism, pastoral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Languages
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves Pezron, who made the explicit link between the Celts described by classical writers and the Welsh and Breton languages. During the first millennium BC, Celtic languages were spoken across much of Europe and central Anatolia. Today, they are restricted to the northwestern fringe of Europe and a few diaspora communities. There are six living languages: the four continuously living languages Breton, Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh, and the two revived languages Cornish and Manx. All are minority languages in their respective countries, though there are continuing efforts at revitalisation. Welsh is an official language in Wales and Irish is an official language across the island of Ireland and of the European Union. Welsh is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goidelic Languages
The Goidelic ( ) or Gaelic languages (; ; ) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages. Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from Ireland through the Isle of Man to Scotland. There are three modern Goidelic languages: Irish ('), Scottish Gaelic ('), and Manx ('). Manx died out as a first language in the 20th century but has since been revived to some degree. Nomenclature ''Gaelic'', by itself, is sometimes used to refer to Scottish Gaelic, especially in Scotland, and therefore is ambiguous. Irish and Manx are sometimes referred to as Irish Gaelic and Manx Gaelic (as they are Goidelic or Gaelic languages), but the use of the word ''Gaelic'' is unnecessary because the terms Irish and Manx, when used to denote languages, always refer to those languages. This is in contrast to Scottish Gaelic, for which "Gaelic" distinguishes the language from the Germanic language known as Scots. In Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonization
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence. Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples for the purpose of cultivation, exploitation, trade and possibly settlement, setting up coloniality and often colonies. Colonization is commonly pursued and maintained by, but distinct from, imperialism, mercantilism, or colonialism. The term "colonization" is sometimes used synonymously with the word "settling", as with colonisation in biology. Settler colonialism is a type of colonization structured and enforced by the settlers directly, while their or their ancestors' metropolitan country ('' metropole'') maintains a connection or control through the settler's activities. In settler colonization, a minority group rules either through the assimilation or oppression of the existing inhabitants, or by establishing itself as the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |