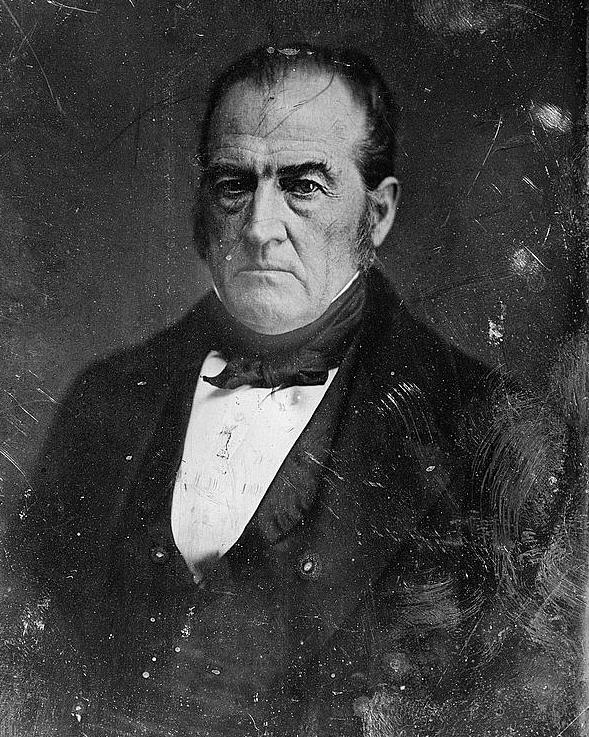|
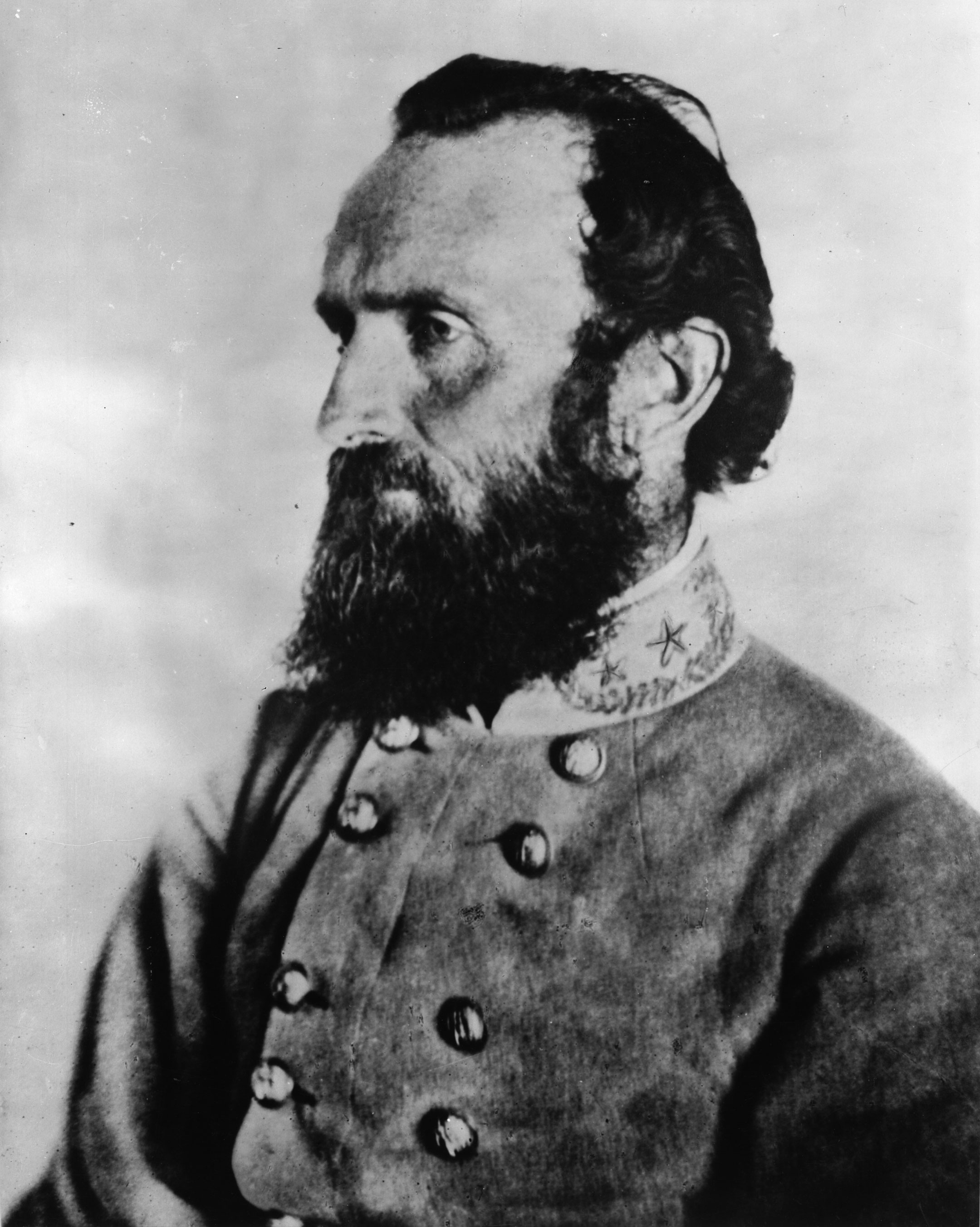
Gabriel C. Wharton
Gabriel Colvin Wharton (July 23, 1824 – May 12, 1906) was an American civil engineer and soldier who served as a general in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War. After the war he was a politician and later resumed his engineering work. Early life and career Wharton was born in Culpeper County, Virginia, in the summer of 1824. He entered Virginia Military Institute in Lexington on September 1, 1845. Wharton graduated on July 5, 1847, finishing second out of 12 cadets as a "distinguished graduate." After leaving Virginia Military Institute Wharton became a civil engineer. Later moving to the Arizona Territory to take up work as a mining engineer.Eicher, p. 562. Civil War service At the start of the American Civil War in 1861, Wharton chose to follow his home state of Virginia and the Confederate cause, and entered the Confederate Army. He was appointed a major in the 45th Virginia Infantry on July 1, and soon afterward was given command of the 51st Virginia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culpeper County, Virginia
Culpeper County is a county located along the borderlands of the northern and central region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 52,552. Its county seat and only incorporated community is Culpeper. Culpeper County is included in the Washington–Baltimore–Arlington, DC–MD–VA–WV–PA Combined Statistical Area. History At the time of European encounter, the inhabitants of future Culpeper County were a Siouan-speaking sub-group of the Manahoac tribe called the Tegninateo. Culpeper County was established in 1749, with territory partitioned from Orange County. The county is named for Thomas Colepeper, 2nd Baron Colepeper, colonial governor of Virginia from 1677 to 1683. In May 1749, the first Culpeper Court convened in the home of Robert Tureman, near the present location of the Town of Culpeper. In July 1749, Tureman commissioned 17-year-old George Washington as the first County surveyor. One of his first duties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major General (CSA)
The general officers of the Confederate States Army (CSA) were the senior military leaders of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War of 1861–1865. They were often former officers from the United States Army (the regular army) before the Civil War, while others were given the rank based on merit or when necessity demanded. Most Confederate generals needed confirmation from the Confederate States Congress, much like prospective generals in the modern U.S. armed forces. Like all of the Confederacy's military forces, these generals answered to their civilian leadership, in particular Jefferson Davis, the president of the Confederate States of America and therefore commander-in-chief of the military forces of the Confederate States. History Much of the design of the Confederate States Army was based on the structure and customs of the United States Army when the Confederate States Congress established the Confederate States War Department on February 21, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Corps, Army Of Northern Virginia
The Second Corps of the Army of Northern Virginia was a military organization within the Confederate States Army, Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during much of the American Civil War. It was officially created and named following the Battle of Sharpsburg in 1862, but comprised units in a corps organization for quite some time prior to that. The Second Corps developed a reputation for hard fighting under famed early commander Stonewall Jackson, Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson. Background The troops comprising the Second Corps originally were known as the Second Corps of the Army of the Potomac (Confederate), Army of the Potomac, under the command of Major general (United States), Major General Gustavus W. Smith. This unit was also known as the Second Division and was eventually subsumed into General officer, General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia as a reserve in Maj. Gen. D. H. Hill's Division. When Lee was able to reorganize his army after finishing battles with Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or Formation (military), formation, usually consisting of between 10,000 and 25,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades; in turn, several divisions typically make up a corps. Historically, the division has been the default combined arms unit capable of independent Military tactics, operations. Smaller combined arms units, such as the American regimental combat team (RCT) during World War II, were used when conditions favored them. In recent times, modern Western militaries have begun adopting the smaller brigade combat team (similar to the RCT) as the default combined arms unit, with the division to which they belong being less important. A similar word, ''Divizion, //'', is also used in Slavic languages (such as Russian, Serbo-Croatian, and Polish) for a battalion-size artillery or cavalry unit. In naval usage "division (naval), division" has a completely different range of meanings. Aboard ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennessee In The American Civil War
The American Civil War significantly affected Tennessee, with every county witnessing combat. During the War, Tennessee was a Confederate state, and the last state to officially secede from the Union to join the Confederacy. Tennessee had been threatening to secede since before the Confederacy was even formed, but didn’t officially do so until after the fall of Fort Sumter when public opinion throughout the state drastically shifted. Tennessee seceded in protest to President Lincoln's April 15 Proclamation calling forth 75,000 members of state militias to suppress the rebellion. Tennessee provided the second largest number of troops for the Confederacy, and would also provide more southern unionist soldiers for the Union Army than any other state within the Confederacy. In February 1862, some of the war's first serious fighting took place along the Tennessee and Cumberland rivers, recognized as major military highways, and mountain passes such as Cumberland Gap were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Longstreet
James Longstreet (January 8, 1821January 2, 1904) was a General officers in the Confederate States Army, Confederate general during the American Civil War and was the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his "Old War Horse". He served under Lee as a Corps#United States, corps commander for most of the battles fought by the Army of Northern Virginia in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, Eastern Theater, and briefly with Braxton Bragg in the Army of Tennessee in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, Western Theater. After graduating from the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York, West Point, Longstreet served in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War. He was wounded at the Battle of Chapultepec, and during recovery married his first wife, Louise Garland. Throughout the 1850s, he served on frontier duty in the American Southwest. In June 1861, Longstreet resigned his U.S. Army commission and joined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General (CSA)
The general officers of the Confederate States Army (CSA) were the senior military leaders of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War of 1861–1865. They were often former officers from the United States Army (the regular army) before the Civil War, while others were given the rank based on merit or when necessity demanded. Most Confederate generals needed confirmation from the Confederate States Congress, much like prospective generals in the modern U.S. armed forces. Like all of the Confederacy's military forces, these generals answered to their civilian leadership, in particular Jefferson Davis, the president of the Confederate States of America and therefore commander-in-chief of the military forces of the Confederate States. History Much of the design of the Confederate States Army was based on the structure and customs of the United States Army when the Confederate States Congress established the Confederate States War Department on February 21, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square rig, square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by Fore-and-aft rig, fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as Schooner, schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships. Brigs were prominent in the coastal coal trade of British waters. 4,395 voyages to London with coal were recorded in 1795. With an average of eight or nine trips per year for one vessel, that is a fleet of over 500 Collier (ship), colliers trading to London alone. Other ports and coastal communities were also served by colliers trading to Britain's coal ports. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military unit, military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a Division (military), division. Brigades formed into divisions are usually infantry or armored (sometimes referred to as combined arms brigades). In addition to combat units, they may include combat support units or sub-units, such as artillery and engineers, and logistic units. Historically, such brigades have been called brigade-groups. On operations, a brigade may comprise both organic elements and attached elements, including some temporarily attached for a specific task. Brigades may also be specialized and comprise battalions of a single branch, for example cavalry, mechanized, armored, artillery, air defence, aviation, engineers, signals or logistic. Some brigades are classified as independent or separate and operate independentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |