|
GYKI-52466
GYKI 52466 is a 2,3-benzodiazepine that acts as an ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist, which is a non-competitive AMPA receptor antagonist (IC50 values are 10-20, ~ 450 and >> 50 μM for AMPA-, kainate- and NMDA-induced responses respectively), orally-active anticonvulsant, and skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ... relaxant. Unlike conventional 1,4-benzodiazepines, GYKI 52466 and related 2,3-benzodiazepines do not act on GABAA receptors. Like other AMPA receptor antagonists, GYKI 52466 has anticonvulsant and neuroprotective properties. CNS review: See also * GYKI 52895, another 2,3-benzodiazepine with other than GABAergic function * Tifluadom * Lufuradom References {{Benzodiazepines AMPA receptor antagonists Anticonvulsants Muscle relaxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMPA Receptor
The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPA receptor, AMPAR, or quisqualate receptor) is an ionotropic receptor, ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) and predominantly sodium ion channel that mediates fast excitatory neurotransmission in the Central nervous system, central nervous system (CNS). Its activation by the neurotransmitter Glutamate (neurotransmitter), glutamate facilitates rapid neuronal communication, essential for various brain functions, including learning and memory. Its name is derived from the ability to be activated by the artificial glutamate analog AMPA. The receptor was initially named the "Quisqualic acid, quisqualate receptor" by Watkins and colleagues after the naturally occurring agonist quisqualic acid, quisqualate. Later, the receptor was designated as the "AMPA receptor" following the development of the selective agonist AMPA by Tage Honore and colleagues at the Royal Danish School of Pharmacy in Copenhagen. The ''GRIA2''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955, and was made available in 1960 by Roche, Hoffmann–La Roche, which followed with the development of diazepam (Valium) three years later, in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, GABAA receptor, resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in two optically isomeric forms; the optical rotation, dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxylic acid, carboxyl groups −COOH and one amine, amino group � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and Signal_transduction, transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses, such as a change in the electrophysiology, electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptor, GABA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand (biochemistry), ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Cell surface receptors, also known as transmembrane receptors, include ligand-gated ion channels, G prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the uncontrolled and excessive firing of neurons during seizures and in doing so can also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs have diverse mechanisms of action but many block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GABA transporter type 1, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
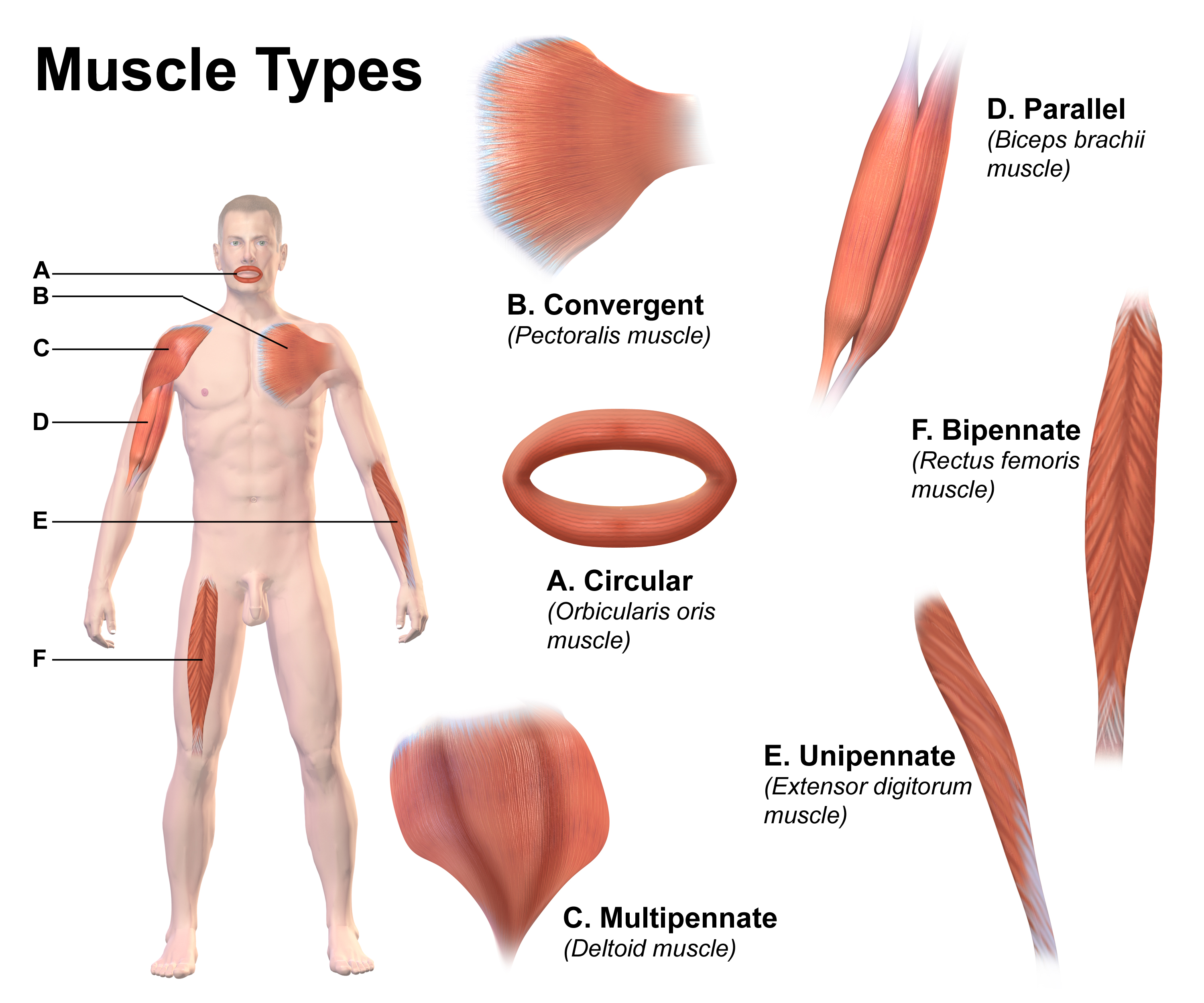
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, neuromuscular blockers and Antispasmodic, spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous Ligand (biochemistry), ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the Chemical synapse, postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to Chloride, chloride ions () and, to a lesser extent, Bicarbonate, bicarbonate ions (). GABAAR are members of the ligand-gated ion channel receptor superfamily, which is a chloride channel family with a dozen or more heterotetrametric subtypes and 19 distinct subunits. These subtypes have distinct brain regional and subcellular localization, age-dependent expression, and the ability to undergo plastic alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroprotective
Neuroprotection refers to the relative preservation of neuronal structure and/or function. In the case of an ongoing insult (a neurodegenerative insult) the relative preservation of neuronal integrity implies a reduction in the rate of neuronal loss over time, which can be expressed as a differential equation. Mechanisms in neurodegeneration, and associated treatments It is a widely explored treatment option for many central nervous system disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, and acute management of neurotoxin consumption (i.e. methamphetamine overdoses). Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Despite differences in symptoms or injuries associated with CNS disorders, many of the mechanisms behind neurodegeneration are the same. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GYKI 52895
GYKI 52895 is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative that also shares the 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine pharmacophore. Unlike other similar drugs, GYKI 52895 is a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DARI), which appears to have an atypical mode of action compared to other DARIs. Its DRI activity is shared by numerous addictive drugs including amphetamine and its derivatives (e.g. dextromethamphetamine), cocaine, and methylphenidate and its derivatives (e.g. ethylphenidate). However, dopaminergic drugs are also prone to producing emetic effects such as in the case of apomorphine. Egis Pharmaceuticals began clinical development of the drug in 1997 for major depressive disorder and Parkinson's disease, but it was discontinued in 2001. See also * GYKI 52466, another 2,3-benzodiazepine with other than GABAergic function * Tifluadom * Lufuradom * Benzodiazepine * Substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine The substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines (abbreviated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tifluadom
Tifluadom is a benzodiazepine derivative with an unusual activity profile. Unlike most benzodiazepines, tifluadom has no activity at the GABAA receptor, but instead is a selective agonist for the κ-opioid receptor. It has potent analgesic and diuretic effects in animals, and also has sedative effects and stimulates appetite. While tifluadom has several effects which might have potential uses in medicine, such as analgesia and appetite stimulation, κ-opioid agonists tend to produce undesirable effects in humans such as dysphoria and hallucinations, and so these drugs tend to only be used in scientific research. Dysphoric effects are similar to those seen when using other κ-opioid receptor agonists like pentazocine and salvinorin A Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in '' Salvia divinorum''. Salvinorin A is considered an atypical dissociative hallucinogen. It is structurally distinct from other naturally occurring hallucinogens (such as DMT, psil . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |