|
GSAT-10
GSAT-10 is an Indian communication satellite which was launched by Ariane-5ECA carrier rocket in September 2012. It has 12 Ku band, 12 C-band and 6 lower extended C-band transponders, and included a navigation payload to augment GAGAN capacity. Following its launch and on-orbit testing, it was placed in Geosynchronous orbit at 83.0° East, from where it will provide communication services in India. Payload *12 high power KU-band transponders employing 140 W TWTA. It is being used by Tata Sky *12 C-band Transponders employing 32 W TWTA. *6 extended C-band Transponders each having a bandwidth of 36 MHz employing 32 W TWTA. * GAGAN navigation payload operating in L1 and L5 bands. Satellite GSAT-10, with a design life of 15 years was operational by November 2012 and will augment telecommunication, Direct-To-Home and radio navigation services. At 3,400 kg at lift-off, at the time, it was the heaviest satellite built by the Bengaluru-headquartered Indian Space Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tata Sky
Tata Play is an Indian subscription-based satellite television (DTH) service provider owned by Tata Group. it was using MPEG-4 digital compression technology, transmitting using INSAT-4A GSAT-10 and GSAT-24 satellites. Incorporated in 2005, it currently offers 690+ channels, 579+ SD channels, 110+ HD channels and 1 UHD channel, along with 50+ other value added services in Standard definition and High definition, free SD+1 and HD+1 services with some channels and many internet based channels. Tata Play is the largest DTH service provider in India. As of March 2023, according to TRAI Tata Play serves 21.3 million subscribers which is 32.65% of total DTH users in India. Tata Play entered into an agreement with French firm Vantiva to supply 4K set top boxes from early 2015. The company was formerly known as Tata Sky. History Tata Sky was a joint venture between the Tata Group and News Corporation, which owned 80% and 20% stakes respectively until 2008, when Singapore-base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation
The GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation (GAGAN) is an implementation of a regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) by the Government of India. It is a system to improve the accuracy of a GNSS receiver by providing reference signals. The Airports Authority of India (AAI)'s efforts towards implementation of operational SBAS can be viewed as the first step towards introduction of modern communication, navigation and surveillance / air traffic management system over the Indian airspace. The project has established 15 Indian Reference Stations (INRES), 2 Indian Master Control Centre (INMCC) and 3 Indian Land Uplink Station (INLUS) and installation of all associated software and communication links. It will be able to help pilots to navigate in the Indian airspace by an accuracy of and will be helpful for landing aircraft in marginal weather and difficult approaches like Mangalore International and Kushok Bakula Rimpochee airports. Implementation The project was deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELA-3
ELA-3 () is a launch complex at the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana. The complex was first used in June 1996 in support of the now retired Ariane 5 Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationar ... rocket. It is currently being refurbished to support Vega E launches. The complex is in size. Launch history Launch graph Launch chart References {{Ariane Guiana Space Centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I-3K
I-3K or the INSAT 3000 is a satellite bus developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), and marketed by Antrix Corporation and New Space India Ltd. It is the standard bus for 3,000-kg class satellites; the 'I' in I-3K stands for INSAT The Indian National Satellite System or INSAT, is a series of multipurpose geostationary satellites launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to satisfy telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue ope ..., a group of communication satellites developed and launched by ISRO. The I-3K bus can supply DC power up to 6500 watts, and is suitable for satellites with lift-off mass in range of 3,000-3,400 kg. List of satellites launched using I-3K bus * Eutelsat W2M (Now Afghansat 1) * INSAT series ( 4A 4B) * GSAT series ( 8 10 16 15 18 19 17 24 29 30) * Chandrayaan-3 (Propulsion module) See also * Comparison of satellite buses References External links I-3K ISRO bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSAT
The GSAT (Geosynchronous Satellite) satellites are India's indigenously developed communications satellites, used for digital audio, data and video broadcasting. As of 5 December 2018, 20 GSAT satellites manufactured by the ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation have been launched, out of which 14 are in service. History The GSAT series of Geosynchronous satellite, geosynchronous satellites is a system developed by the ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) with an objective to make India self-reliant in broadcasting services. The system includes a total of 168 Transponder (satellite communications), transponders (out of which 95 are leased out to provide services to broadcasters) in the C band (IEEE), C, Extended C and Ku band, Ku bands, providing services to telecommunications, television broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster warning and search and rescue operations. List of GSAT satellites This is a list of GSAT satellites and their status. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPS-aided Geo-augmented Navigation
The GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation (GAGAN) is an implementation of a regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) by the Government of India. It is a system to improve the accuracy of a GNSS receiver by providing reference signals. The Airports Authority of India (AAI)'s efforts towards implementation of operational SBAS can be viewed as the first step towards introduction of modern communication, navigation and surveillance / air traffic management system over the Indian airspace. The project has established 15 Indian Reference Stations (INRES), 2 Indian Master Control Centre (INMCC) and 3 Indian Land Uplink Station (INLUS) and installation of all associated software and communication links. It will be able to help pilots to navigate in the Indian airspace by an accuracy of and will be helpful for landing aircraft in marginal weather and difficult approaches like Mangalore International and Kushok Bakula Rimpochee airports. Implementation The project was deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSAT-12
GSAT-12 was a communication satellite designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation. It was the second satellite to be launched and placed on a GTO using PSLV. Satellite GSAT-12 was considered to be a replacement of the aged satellite INSAT-3B. It provided services like tele-education, tele-medicine, disaster management support and satellite internet access. Payloads GSAT-12 was equipped with 12 Extended C-band transponders. Launch GSAT-12 was launched onboard PSLV-XL C17 from second launch pad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre on July 15, 2011. The tentative life of satellite was 8 years. Replacement and relocation While GSAT-12 was still operational a replacement satellite CMS-01''(formerly GSAT-12R)'' was launched on 17 December 2020. GSAT-12 was relocated from 83°E slot to 48°E slot on 19 March 2021. End of mission In March 2023 GSAT-12 was retired from its operational service. After seven maneuvers to raise the satellite to a circular graveyard o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSAT-8
GSAT-8 or INSAT-4G is communication satellite. It was constructed by the Indian Space Research Organisation, as part of INSAT system. GSAT-8 was launched on May 21, 2011, from Kourou, French Guiana. The rocket, an Ariane 5 was the carrier, marketed by the European Arianespace. First satellite to carry GAGAN payload followed up by GSAT-10 and in-orbit spare GSAT-15. Launch Prior to launch, the spacecraft was transported from India to Cayenne – Rochambeau Airport in French Guiana French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ... by an Antonov An-124 cargo aircraft. The success of the launch is said to have made up for the previous loss of two satellites on the indigenous GSLV rocket. GSAT-8 was co-located with INSAT-3E at 55°E. References {{Orbital launches in 2011 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), low Earth orbit (LEO) or further into space. The launch vehicle had a streak of 82 consecutive successful launches between 9 April 2003 and 12 December 2017. Since 2014, Ariane 6, a direct successor system, first launched in 2024. The system was designed as an expendable launch vehicle by the ''Centre national d'études spatiales'' (CNES), the French government's space agency, in cooperation with various European partners. Despite not being a direct derivative of its predecessor launch vehicle program, it was classified as part of the Ariane rocket family. Aérospatiale, and later ArianeGroup, was the prime contractor for the manufacturing of the vehicles, leading a multi-country consortium of other European con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSAT-7
GSAT-7 or INSAT-4F is a multi-band military communications satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation. The Indian Navy is the user of the multi-band communication spacecraft, which has been operational since September 2013. According to defense experts, the satellite will enable the navy to extend its blue water capabilities and stop relying on foreign satellites like Inmarsat, which provide communication services to its ships. Satellite GSAT-7, the multi-band communication satellite named ''Rukmini'' carries the payloads in UHF, C band and . It is the first dedicated military communication satellite (unlike earlier dual use satellites) built by ISRO that will provide services to the Indian Armed Forces with the main user being the Indian Navy. Its procured launch cost has been put at ₹480 crore, with the satellite costing ₹185 crore. Cost of whole project per Memorandum of Understanding with ISRO was ₹950 crores. The multiple-band spacecraft will be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
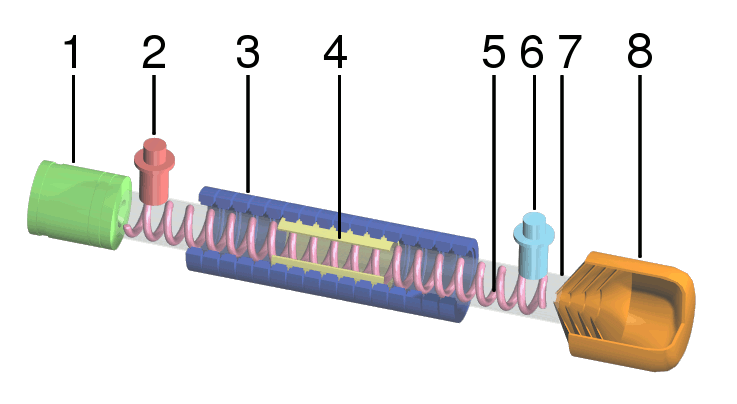
Traveling-wave Tube
A traveling-wave tube (TWT, pronounced "twit") or traveling-wave tube amplifier (TWTA, pronounced "tweeta") is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. It was invented by Andrei Haeff around 1933 as a graduate student at Caltech, and its present form was invented by Rudolf Kompfner in 1942–43. The TWT belongs to a category of "linear beam" tubes, such as the klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube. Although there are various types of TWT, two major categories are: *''Helix TWT'' - in which the radio waves interact with the electron beam while traveling down a wire helix which surrounds the beam. These have wide bandwidth, but output power is limited to a few hundred watts. *''Coupled cavity TWT'' - in which the radio wave interacts with the beam in a series of cavity resonators through which the beam passes. These funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |