|
GNAS1
GNAS complex locus is a gene locus in humans. Its main product is the heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunit Gs-α, a key component of G protein-coupled receptor-regulated adenylyl cyclase signal transduction pathways. GNAS stands for Guanine Nucleotide binding protein, Alpha Stimulating activity polypeptide. Gene This gene locus has a highly complex imprinted expression pattern. It gives rise to maternally-, paternally- and biallelically-expressed transcripts that are derived from four alternative promoters with distinct 5' exons. Some transcripts contain a differentially methylated region (DMR) within their 5' exons; such DMRs are commonly found in imprinted genes and correlate with transcript expression. An antisense transcript also exists, and this antisense transcript and one of the sense transcripts are paternally expressed, produce non-coding RNAs and may regulate imprinting in this region. In addition, one of the transcripts contains a second frame-shifted open r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (PPHP) is an inherited disorder, named for its similarity to pseudohypoparathyroidism in presentation. It is more properly Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, although without resistance of parathyroid hormone (PTH), as frequently seen in that affliction. The term is used to describe a condition where the individual has the phenotypic appearance of pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a, but has (unexpected for the phenotype) normal labs, including calcium and PTH. It can be considered a variant of Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1A), as they present with the same constellation of signs and symptoms, including short stature, brachydactyly, subcutaneous calcification, and obesity. Presentation Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism can be best understood by comparing it to other conditions: Hormone resistance is not present in pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Short stature may be present. Obesity is less common in pseudopseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a rare autosomal dominant genetic condition associated primarily with resistance to the parathyroid hormone. Those with the condition have a low serum calcium and high phosphate, but the parathyroid hormone level (PTH) is inappropriately high (due to the low level of calcium in the blood). Its pathogenesis has been linked to dysfunctional G proteins (in particular, Gs alpha subunit). Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a very rare disorder, with estimated prevalence between 0.3 and 1.1 cases per 100,000 population depending on geographic location. Types Types include: ;Type 1a : Has a characteristic phenotypic appearance ( Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy), including short fourth and fifth metacarpals and a rounded facies. It is most likely an autosomal dominant disorder. It is also associated with thyroid stimulating hormone resistance. Caused by GNAS1 mutation. ; Type 1b : Lacks the physical appearance of type 1a, but is biochemically similar. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McCune–Albright Syndrome
McCune–Albright syndrome is a complex genetic disorder affecting the bone, skin and endocrine systems. It is a mosaic disease arising from somatic activating mutations in '' GNAS'', which encodes the alpha-subunit of the Gs heterotrimeric G protein. It was first described in 1937 by American pediatrician Donovan James McCune and American endocrinologist Fuller Albright. Signs and symptoms McCune–Albright syndrome is suspected when two or more of the following features are present: * Fibrous dysplasia (specifically, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) * Hyperpigmented skin lesions with characteristic features, including jagged "coast of Maine" borders and tendency occur along the midline of the body. These lesions are historically termed café au lait macules, however the term "cafe-au-lait" only describes their appearance on lighter-skinned individuals. * Hyperfunctioning endocrine disease Patients may have one or many of these features, which may occur in any combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STX16
Syntaxin-16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STX16'' gene. It has been associated with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ib. Losing this gene causes loss of methylation at GNAS1 exon A/B. Interactions STX16 has been shown to interact with VAMP4 Vesicle-associated membrane protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAMP4'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides i .... References Further reading * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy
Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy is a form of osteodystrophy, and is classified as the phenotype of pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1A; this is a condition in which the body does not respond to parathyroid hormone. Signs and symptoms The disorder is characterized by the following: * Hypogonadism * Brachydactyly syndrome * Choroid plexus calcification * Hypoplasia of dental enamel * Full cheeks * Hypocalcemic tetany Individuals with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy exhibit short stature, characteristically shortened fourth and fifth metacarpals, rounded facies, and often mild intellectual deficiency. Genetics This condition is associated with genetic imprinting. It is thought to be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and seems to be associated with a Gs alpha subunit deficiency. Mechanism The mechanism of this condition is due to Gs signaling decrease in hormones having to do with signal transduction which is when a signal from outside cell causes change within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
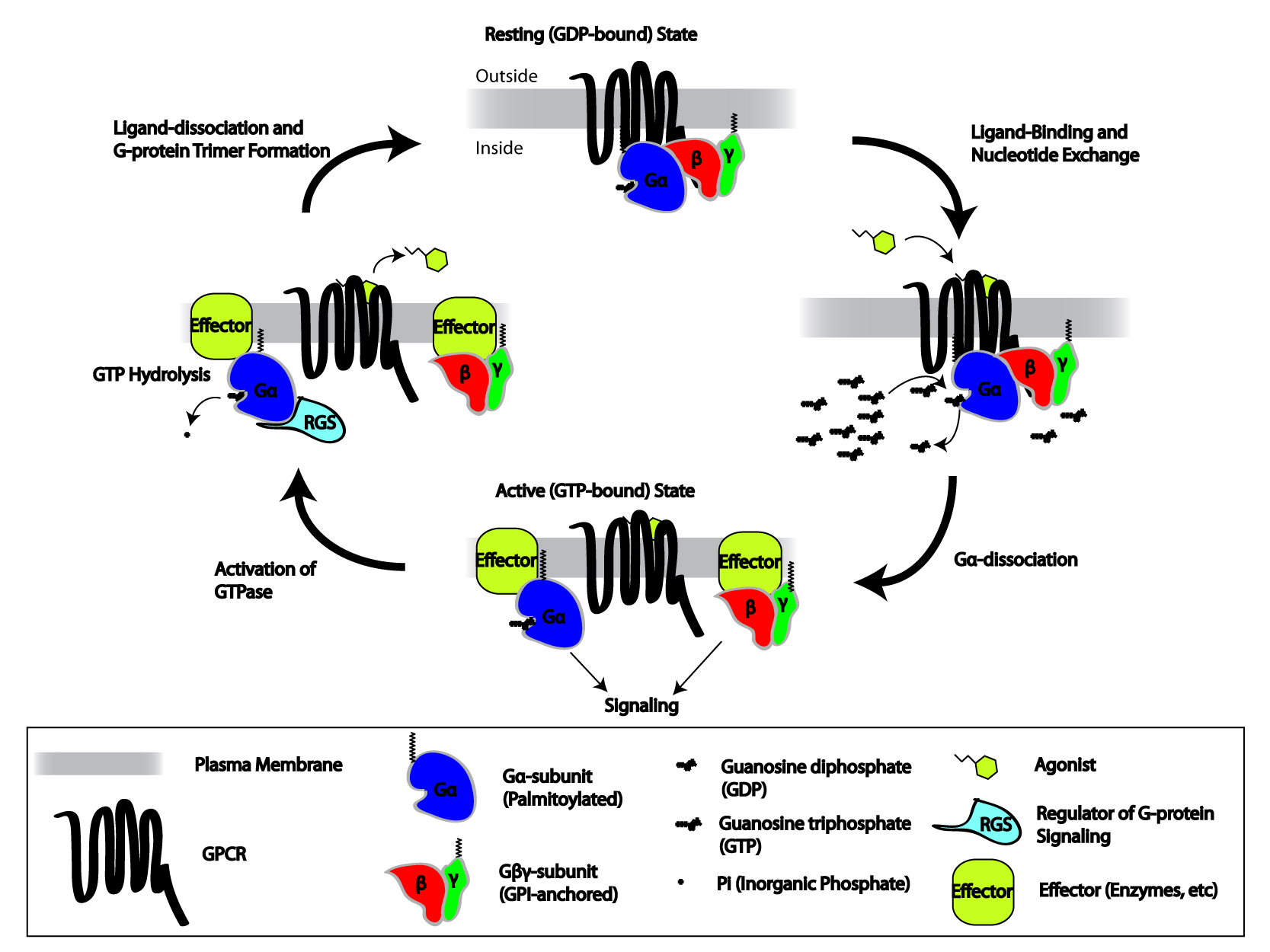
Heterotrimeric G-protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a Heteromer, heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), directly. These G proteins are made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) Protein subunit, subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein. When ligands bind a GPCR, the GPCR acquires GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) ability, which activates the G-protein by exchanging the GDP on the ''alpha'' subunit to GTP. The binding of GTP to the ''alpha'' subunit results in a structural change and its dissociation from the rest of the G-protein. Generally, the ''alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure Prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its Protein secondary structure, secondary and Protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure from Protein primary structure, primary structure. Structure prediction is different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by computational biology and addresses Levinthal's paradox. Accurate structure prediction has important applications in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in novel enzyme design). Starting in 1994, the performance of current methods is assessed biannually in the ''Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction'' (CASP) experiment. A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project ''Continuous Automated Model EvaluatiOn'' (CAMEO3D). Protein structure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Startle Reflex
In animals, including humans, the startle response is a largely unconscious defensive response to sudden or threatening stimuli, such as sudden noise or sharp movement, and is associated with negative affect.Rammirez-Moreno, David. "A computational model for the modulation of the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex". ''Biological Cybernetics'', 2012, p. 169 Usually the onset of the startle response is a startle reflex reaction. The startle reflex is a brainstem reflectory reaction (reflex) that serves to protect vulnerable parts, such as the back of the neck (whole-body startle) and the eyes (eyeblink) and facilitates escape from sudden stimuli. It is found across many different species, throughout all stages of life. A variety of responses may occur depending on the affected individual's emotional state, body posture, preparation for execution of a motor task, or other activities. The startle response is implicated in the formation of specific phobias. Startl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
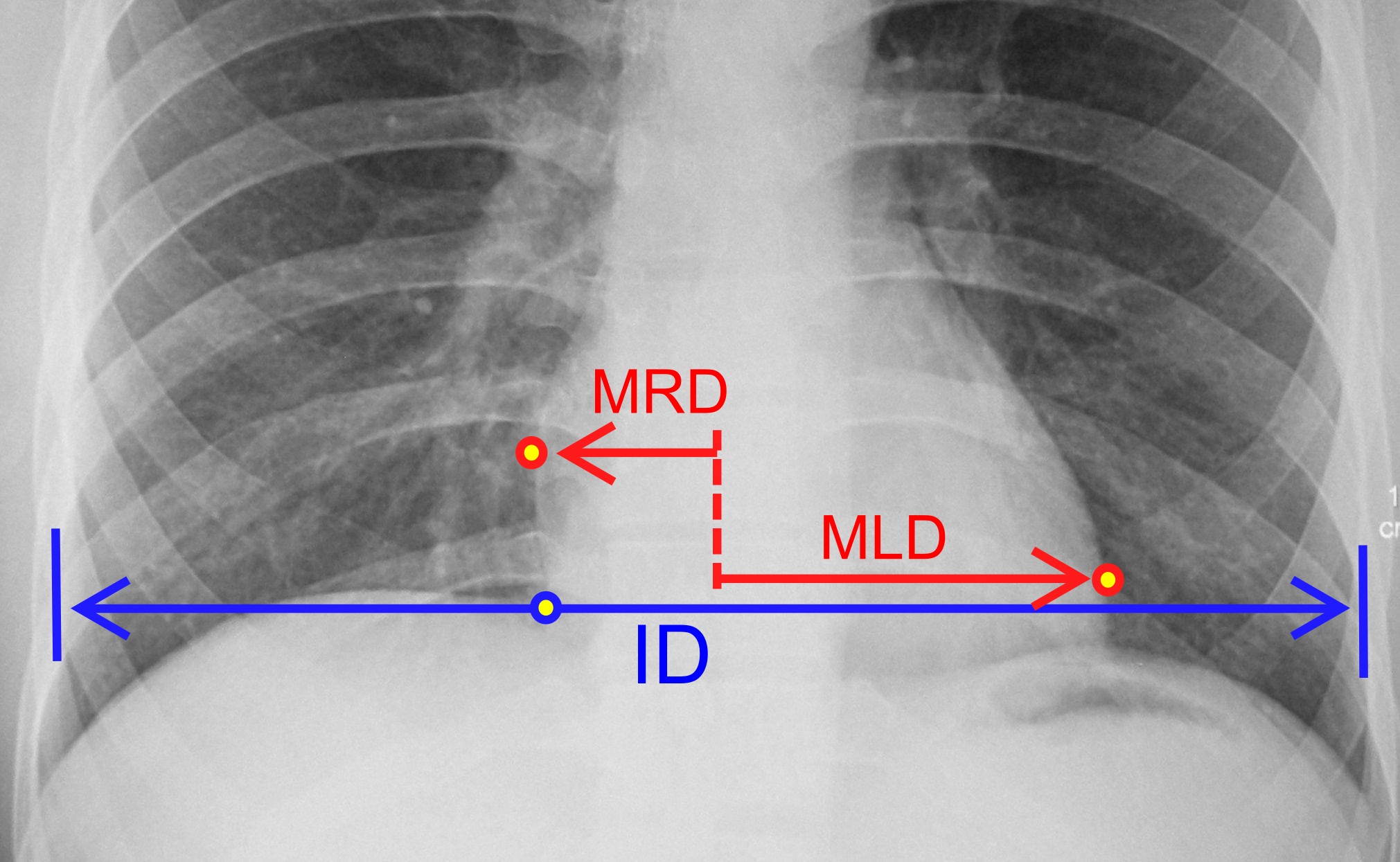
Cardiomegaly
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the heart becomes enlarged. It is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity, heart valve disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly can be serious and can result in congestive heart failure. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death. Cardiomegaly may diminish over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong medication. Having a family history of cardiomegaly may indicate an increased risk for this condition. Lifestyle factors that can help prevent cardiomegaly include eating a healthy diet, controlling blood pressure, exercise, medications, and not abusing anabolic-androgenic steroids, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial , with an estimated prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be |