|
GLR Parser
A GLR parser (generalized left-to-right rightmost derivation parser) is an extension of an LR parser algorithm to handle non-deterministic and ambiguous grammars. The theoretical foundation was provided in a 1974 paper by Bernard Lang (along with other general context-free parsers such as GLL). It describes a systematic way to produce such algorithms, and provides uniform results regarding correctness proofs, complexity with respect to grammar classes, and optimization techniques. The first actual implementation of GLR was described in a 1984 paper by Masaru Tomita, it has also been referred to as a "parallel parser". Tomita presented five stages in his original work, though in practice it is the second stage that is recognized as the GLR parser. Though the algorithm has evolved since its original forms, the principles have remained intact. As shown by an earlier publication, Lang was primarily interested in more easily used and more flexible parsers for extensible programming l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LR Parser
In computer science, LR parsers are a type of bottom-up parsing, bottom-up parser that analyse deterministic context-free languages in linear time. There are several variants of LR parsers: SLR parsers, LALR parsers, canonical LR parser, canonical LR(1) parsers, canonical LR parser, minimal LR(1) parsers, and generalized LR parsers (GLR parsers). LR parsers can be generated by a parser generator from a formal grammar defining the syntax of the language to be parsed. They are widely used for the processing of computer languages. An LR parser (left-to-right, rightmost derivation in reverse) reads input text from left to right without backing up (this is true for most parsers), and produces a rightmost derivation in reverse: it does a bottom-up parsing, bottom-up parse – not a top-down parsing, top-down LL parse or ad-hoc parse. The name "LR" is often followed by a numeric qualifier, as in "LR(1)" or sometimes "LR(''k'')". To avoid backtracking or guessing, the LR parser is allowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries. In the more general approach, an optimization problem consists of maxima and minima, maximizing or minimizing a Function of a real variable, real function by systematically choosing Argument of a function, input values from within an allowed set and computing the Value (mathematics), value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations constitutes a large area of applied mathematics. Optimization problems Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packrat Parser
The Packrat parser is a type of Parsing, parser that shares similarities with the recursive descent parser in its construction. However, it differs because it takes parsing expression grammar, parsing expression grammars (PEGs) as input rather than LL grammar, LL grammars. In 1970, Alexander Birman laid the groundwork for packrat parsing by introducing the "TMG recognition scheme" (TS), and "generalized TS" (gTS). TS was based upon Robert M. McClure's TMG (language), TMG compiler-compiler, and gTS was based upon Dewey Val Schorre's META II, META compiler-compiler. Birman's work was later refined by Aho and Ullman; and renamed as Top-Down Parsing Language (TDPL), and Generalized TDPL (GTDPL), respectively. These algorithms were the first of their kind to employ deterministic top-down parsing with backtracking. Bryan Ford developed PEGs as an expansion of GTDPL and TS. Unlike Context-free grammar, CFGs, PEGs are unambiguous and can match well with machine-oriented languages. PE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMS Software Reengineering Toolkit
The DMS Software Reengineering Toolkit is a proprietary set of program transformation tools available for automating custom source program analysis, modification, translation or generation of software systems for arbitrary mixtures of source languages for large scale software systems. DMS was originally motivated by a theory for maintaining designs of software called ''Design Maintenance Systems.'' DMS and "Design Maintenance System" are registered trademarks of Semantic Designs. Usage DMS has been used to implement domain-specific languages (such as code generation for factory control), test coverage and profiling tools, clone detection, language migration tools, C++ component reengineering., and for research into difficult topics such as refactoring C++ reliably. Features The toolkit provides means for defining language grammars and will produce parsers which automatically construct abstract syntax trees (ASTs), and prettyprinters to convert original or modified ASTs back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Parser Generators
This is a list of notable lexer generators and parser generators for various language classes. Regular languages Regular languages are a category of languages (sometimes termed Chomsky Type 3) which can be matched by a state machine (more specifically, by a deterministic finite automaton or a nondeterministic finite automaton) constructed from a regular expression. In particular, a regular language can match constructs like "A follows B", "Either A or B", "A, followed by zero or more instances of B", but cannot match constructs which require consistency between non-adjacent elements, such as "some instances of A followed by the same number of instances of B", and also cannot express the concept of recursive "nesting" ("every A is eventually followed by a matching B"). A classic example of a problem which a regular grammar cannot handle is the question of whether a given string contains correctly nested parentheses. (This is typically handled by a Chomsky Type 2 grammar, also te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LALR
In computer science, an LALR parser (look-ahead, left-to-right, rightmost derivation parser) is part of the compiling process where human readable text is converted into a structured representation to be read by computers. An LALR parser is a software tool to process (parse) text into a very specific internal representation that other programs, such as compilers, can work with. This process happens according to a set of production rules specified by a formal grammar for a computer language. An LALR parser is a simplified version of a canonical LR parser. The LALR parser was invented by Frank DeRemer in his 1969 PhD dissertation, ''Practical Translators for LR(k) languages'', in his treatment of the practical difficulties at that time of implementing LR(1) parsers. He showed that the LALR parser has more language recognition power than the LR(0) parser, while requiring the same number of states as the LR(0) parser for a language that can be recognized by both parsers. This makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earley Parser
In computer science, the Earley parser is an algorithm for parsing strings that belong to a given context-free language, though (depending on the variant) it may suffer problems with certain nullable grammars. The algorithm, named after its inventor Jay Earley, is a chart parser that uses dynamic programming; it is mainly used for parsing in computational linguistics. It was first introduced in his dissertation in 1968 (and later appeared in abbreviated, more legible form in a journal). Earley parsers are appealing because they can parse all context-free languages, unlike LR parsers and LL parsers, which are more typically used in compilers but which can only handle restricted classes of languages. The Earley parser executes in cubic time in the general case (n^3), where ''n'' is the length of the parsed string, quadratic time for unambiguous grammars (n^2), and linear time for all deterministic context-free grammars. It performs particularly well when the rules are written l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Algorithm
In computer science, an online algorithm is one that can process its input piece-by-piece in a serial fashion, i.e., in the order that the input is fed to the algorithm, without having the entire input available from the start. In contrast, an offline algorithm is given the whole problem data from the beginning and is required to output an answer which solves the problem at hand. In operations research Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve management and ..., the area in which online algorithms are developed is called online optimization. As an example, consider the sorting algorithms selection sort and insertion sort: selection sort repeatedly selects the minimum element from the unsorted remainder and places it at the front, which requires access to the entire input; it is thus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earley Algorithm
In computer science, the Earley parser is an algorithm for parsing strings that belong to a given context-free language, though (depending on the variant) it may suffer problems with certain nullable grammars. The algorithm, named after its inventor Jay Earley, is a chart parser that uses dynamic programming; it is mainly used for parsing in computational linguistics. It was first introduced in his dissertation in 1968 (and later appeared in abbreviated, more legible form in a journal). Earley parsers are appealing because they can parse all context-free languages, unlike LR parsers and LL parsers, which are more typically used in compilers but which can only handle restricted classes of languages. The Earley parser executes in cubic time in the general case (n^3), where ''n'' is the length of the parsed string, quadratic time for unambiguous grammars (n^2), and linear time for all deterministic context-free grammars. It performs particularly well when the rules are written le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
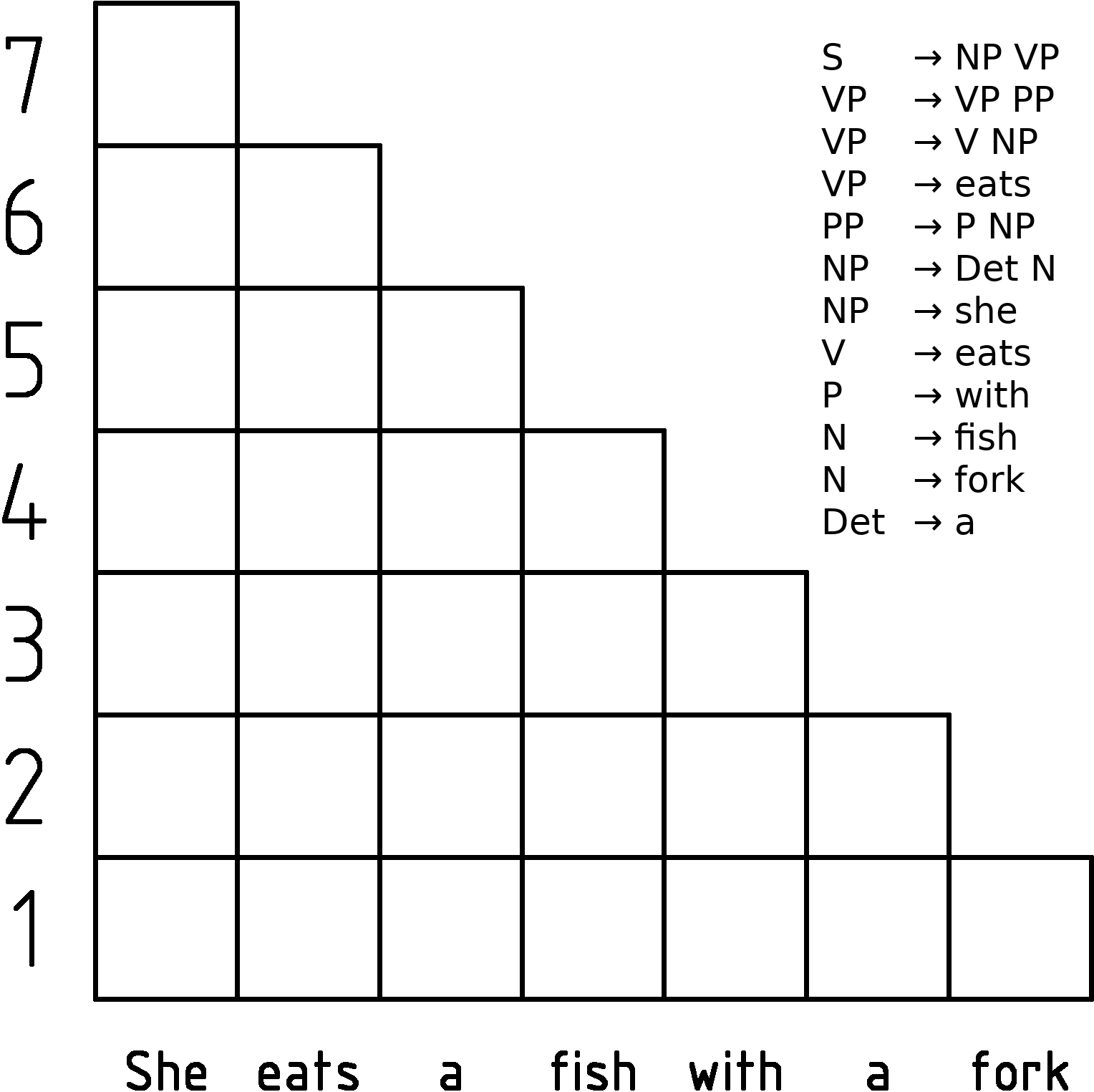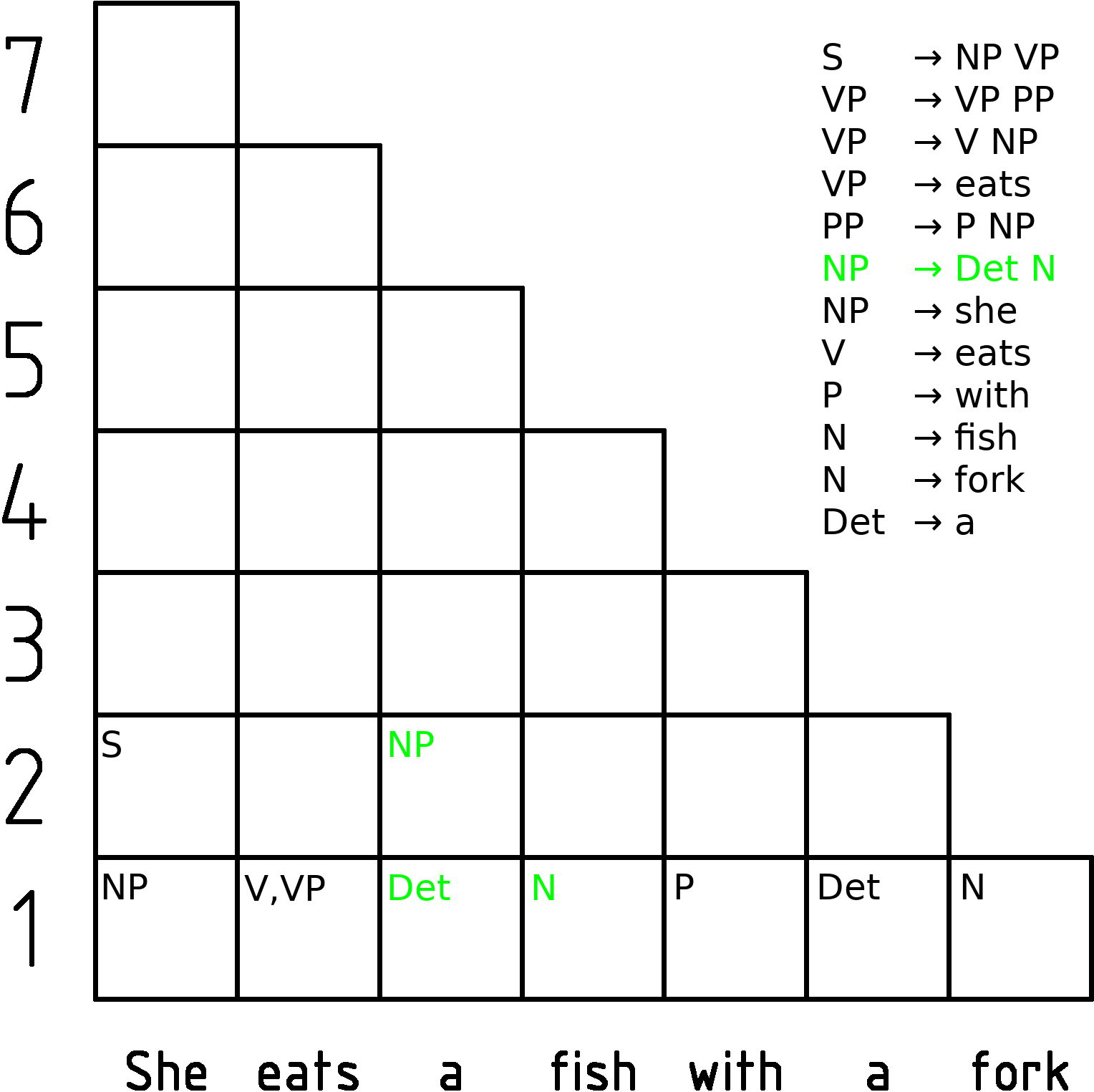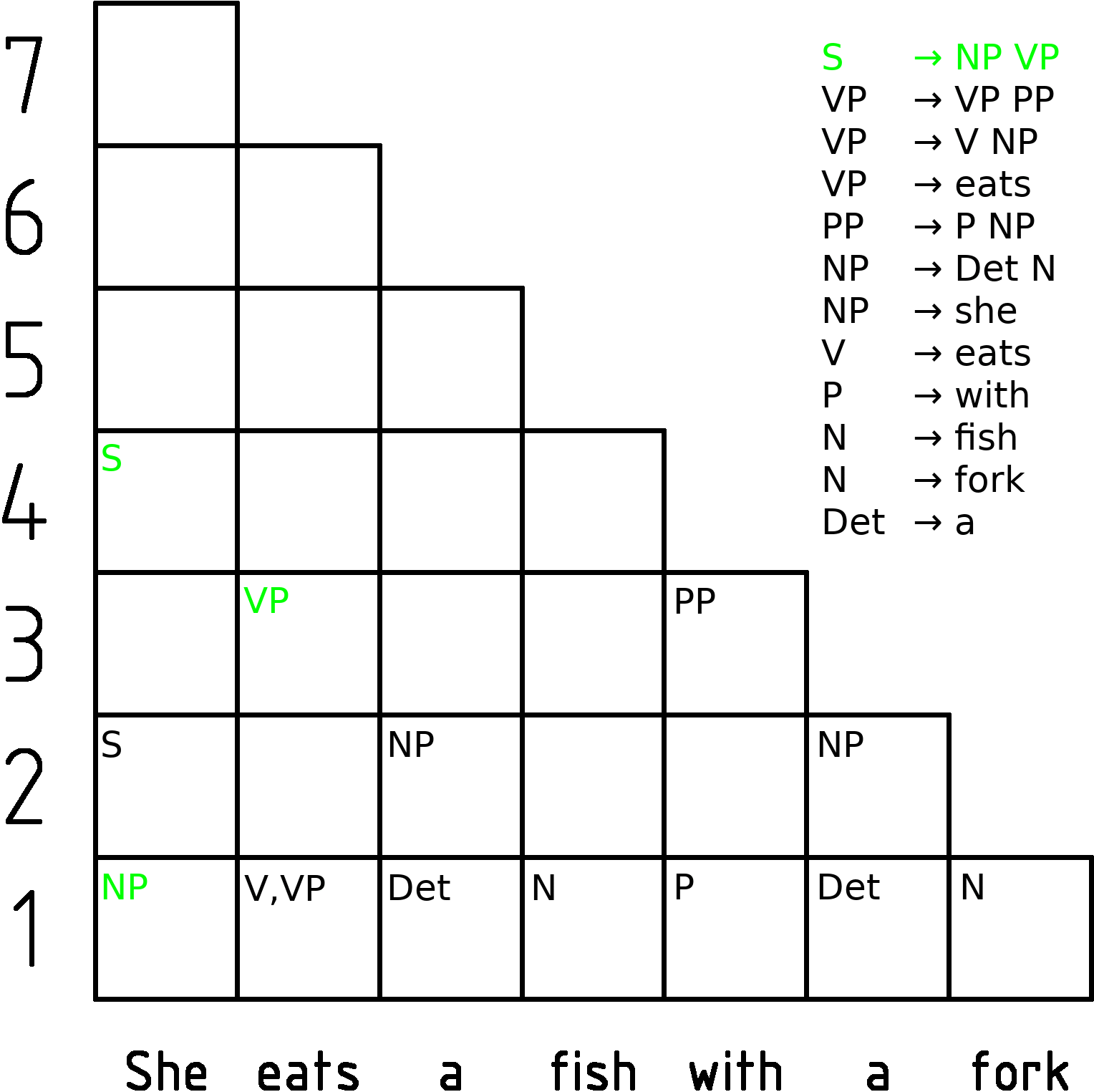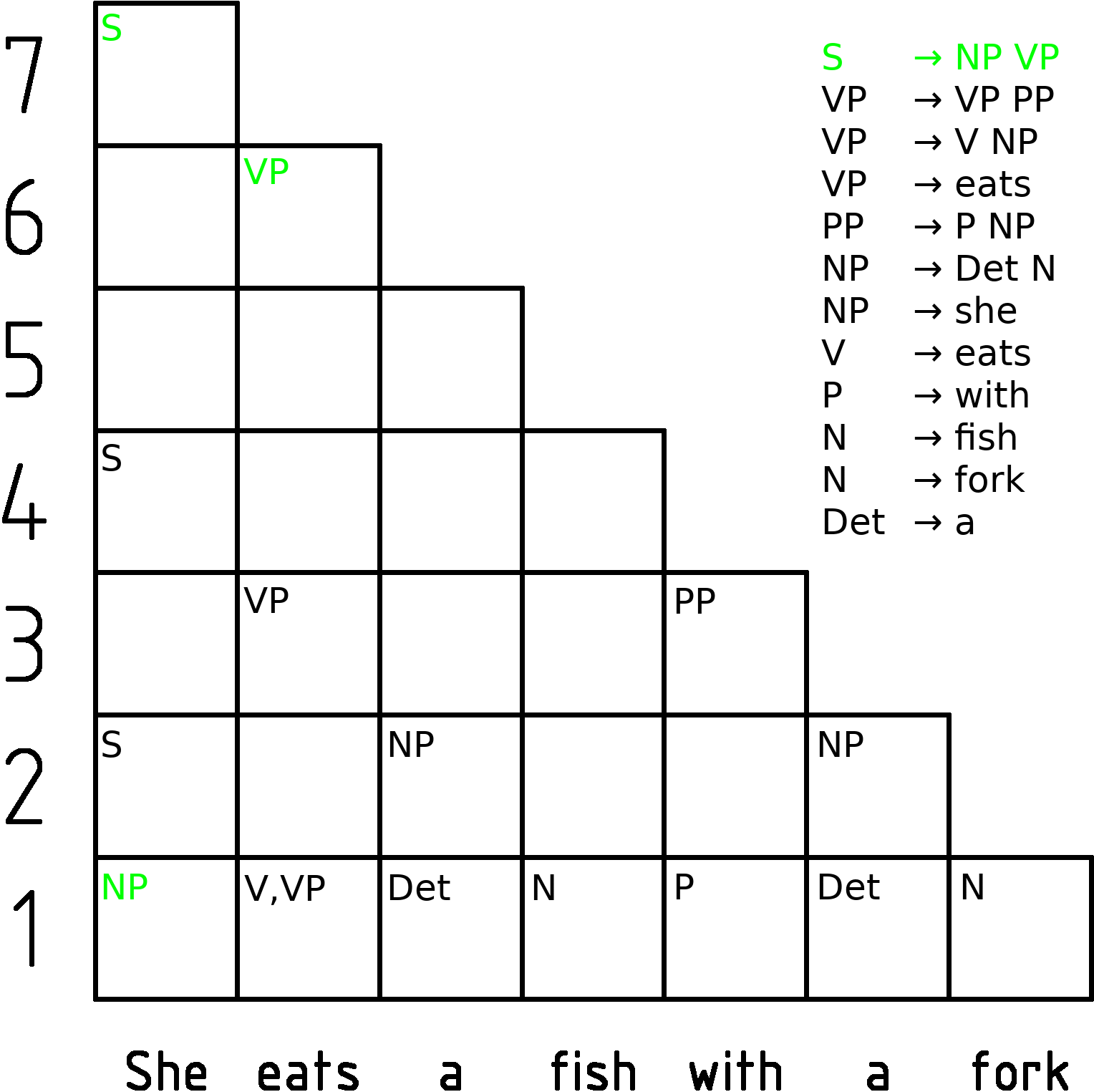
CYK Algorithm
In computer science, the Cocke–Younger–Kasami algorithm (alternatively called CYK, or CKY) is a parsing algorithm for context-free grammars published by Itiroo Sakai in 1961. The algorithm is named after some of its rediscoverers: John Cocke, Daniel Younger, Tadao Kasami, and Jacob T. Schwartz. It employs bottom-up parsing and dynamic programming. The standard version of CYK operates only on context-free grammars given in Chomsky normal form (CNF). However any context-free grammar may be algorithmically transformed into a CNF grammar expressing the same language . The importance of the CYK algorithm stems from its high efficiency in certain situations. Using big ''O'' notation, the worst case running time of CYK is \mathcal\left( n^3 \cdot \left, G \ \right), where n is the length of the parsed string and \left, G \ is the size of the CNF grammar G . This makes it one of the most efficient parsing algorithms in terms of worst-case asymptotic complexity, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Acyclic Graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one vertex to another, such that following those directions will never form a closed loop. A directed graph is a DAG if and only if it can be topologically ordered, by arranging the vertices as a linear ordering that is consistent with all edge directions. DAGs have numerous scientific and computational applications, ranging from biology (evolution, family trees, epidemiology) to information science (citation networks) to computation (scheduling). Directed acyclic graphs are also called acyclic directed graphs or acyclic digraphs. Definitions A graph is formed by vertices and by edges connecting pairs of vertices, where the vertices can be any kind of object that is connected in pairs by edges. In the case of a directed graph, each edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |