|
GEOS 3
GEOS-3, or Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite 3, or GEOS-C, was the third and final satellite as part of NASA's Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite/Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite program (NGSP)Henriksen, S. W. (ed) (1977National Geodetic Satellite Program NASA SP-365 to better understand and test satellite tracking systems. For GEOS 1 and GEOS 2, the acronym stands for ''Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite''; this was changed for GEOS-3. Introduction The satellite mission was designed to further an understanding of the earth's gravitational field, size and shape of the terrestrial geoid, deep ocean tides, sea state, current structure, crustal structure, solid earth dynamics, and remote sensing technology. Jerome Rosenburg at NASA Headquarters initiated the GEOS-3 project in 1970. The project was to serve as a stepping stone between the GEOS program and the emerging NASA Earth and Ocean Physics Application Program. GEOS-1 and GEOS-2 had provided useful information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
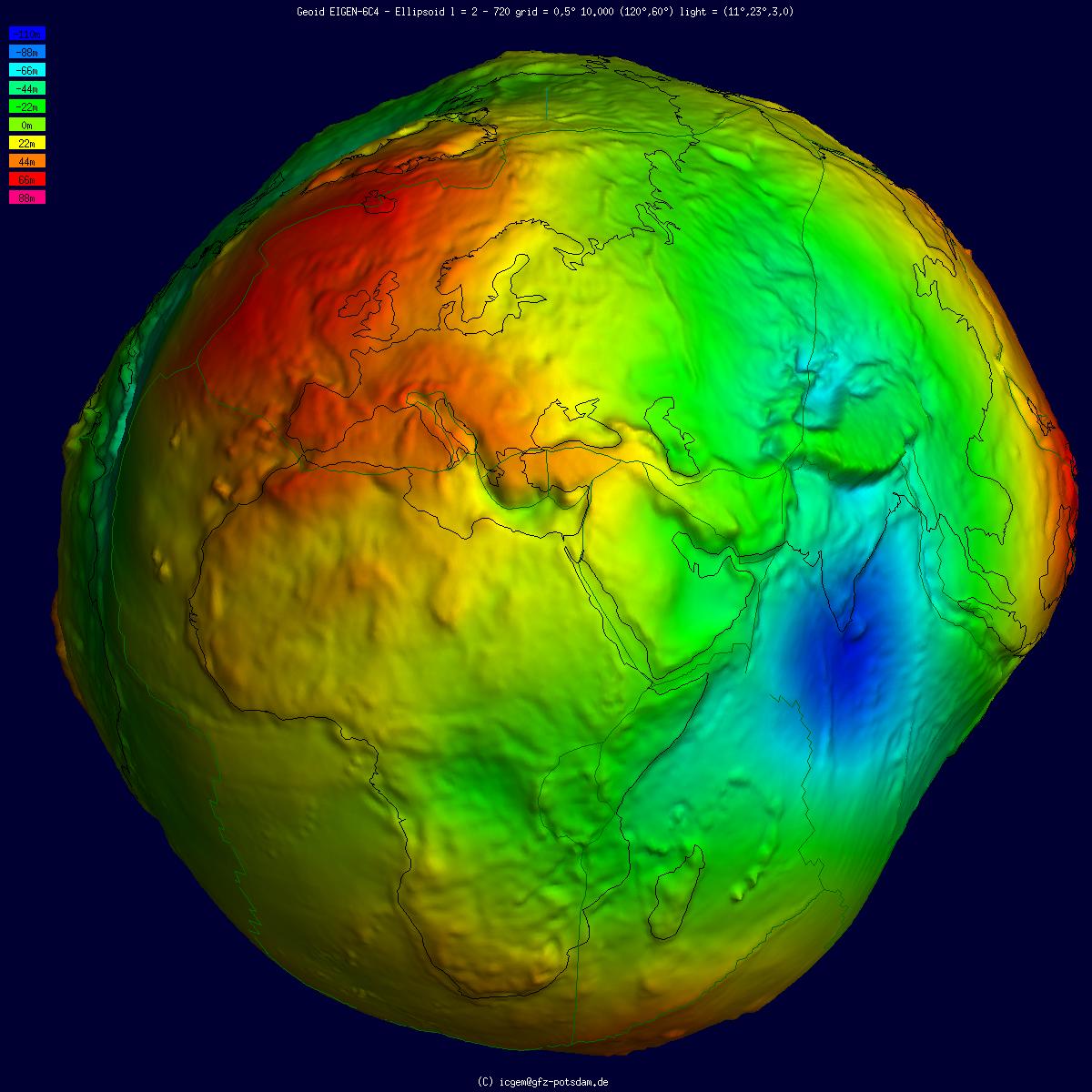
Geoid
The geoid ( ) is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as might be approximated with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. The geoid is often expressed as a geoid undulation or geoidal height above a given reference ellipsoid, which is a slightly flattene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellites In Low Earth Orbit
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellations. Becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic Satellites
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the geometry, gravity, and spatial orientation of the Earth in temporally varying 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical bodies, such as planets or circumplanetary systems. Geodynamical phenomena, including crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses appear to an observer as circular shadows and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1975
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific research are space prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries; ecosystem dynamics; and plate tectonics and seabed geology. Oceanographers draw upon a wide range of disciplines to deepen their understanding of the world’s oceans, incorporating insights from astronomy, biology, chemistry, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Observations on tides were recorded by Aristotle and Strabo in 384–322 BC. Early exploration of the oceans was primarily for cartography and mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Gravity
The gravity of Earth, denoted by , is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm g=\, \mathit\, . In SI units, this acceleration is expressed in metres per second squared (in symbols, m/ s2 or m·s−2) or equivalently in newtons per kilogram (N/kg or N·kg−1). Near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity, accurate to 2 significant figures, is . This means that, ignoring the effects of air resistance, the speed of an object falling freely will increase by about every second. The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies with location. The agreed-upon value for is by definition. This quantity is denoted variously as , (though this sometimes means the normal gravity at the equator, ), , or simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Surface Topography
Ocean surface topography or sea surface topography, also called ocean dynamic topography, are highs and lows on the ocean surface, similar to the hills and valleys of Earth's land surface depicted on a topographic map. These variations are expressed in terms of average sea surface height (SSH) relative to Earth's geoid. The main purpose of measuring ocean surface topography is to understand the large-scale ocean circulation. Time variations Unaveraged or instantaneous sea surface height (SSH) is most obviously affected by the tidal forces of the Moon and by the seasonal cycle of the Sun acting on Earth. Over timescales longer than a year, the patterns in SSH can be influenced by ocean circulation. Typically, SSH anomalies resulting from these forces differ from the mean by less than ± at the global scale. Other influences include changing interannual patterns of temperature, salinity, waves, tides and winds. Ocean surface topography can be measured with high accuracy and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATS-6
ATS-6 (Applications Technology Satellite-6) was a NASA experimental satellite, built by Fairchild Space and Electronics Division It has been called the world's first educational satellite as well as world's first experimental Direct Broadcast Satellite as part of the Satellite Instructional Television Experiment between NASA and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was launched May 30, 1974, and decommissioned July 1979. At the time of launch, it was the most powerful telecommunication satellite in orbit. ATS-6 carried no fewer than 23 different experiments, and introduced several breakthroughs. It was the first 3-axis stabilized spacecraft in geostationary orbit. It was also the first to use experimentally with some success electric propulsion in geostationary orbit. It also carried several particle physics experiments, including the first heavy ion detector in geostationary orbit. During its five-year life, ATS-6 transmitted connection programming to various countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEOS 2
Explorer 36 (also called GEOS 2 or GEOS B, acronym for Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite) was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorer program, being the second of the two satellites GEOS. Explorer 36 was launched on 11 January 1968 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, with Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 36 was a gravity-gradient stabilized, solar cell powered spacecraft that carried electronic and geodetic instrumentation. The spacecraft's thermal control system was notable for the first non-experimental use of a heat pipe in a spacecraft. Instruments The geodetic instrumentation systems included: * C-Band Radar Transponder * Laser Tracking Reflector * Magnetometer * NASA Minitrack System * Optical Beacon System * Precipitating Electron Detector * Radio Doppler System * Radio Range/Rate System * SECOR Range Transponder Non-geodetic systems included a laser detector and a Minitrack interferometer beacon. The objectives of the spacecraft were to optimize opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |