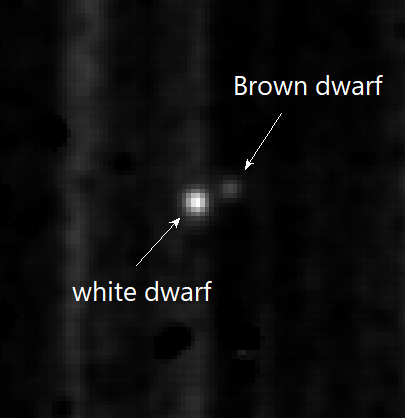
|
GD 165
GD 165 is a Binary star, binary white dwarf and brown dwarf system located in the Boötes constellation, roughly 109 light-years from Earth. Neither of the stars have any known exoplanets. Nomenclature and observation The system GD 165 is named after Henry L. Giclas, an American Astronomer who lived throughout the 20th century. In 1990, GD 165 A was discovered to be a variable star by Pierre Bergeron and John Thomas McGraw. It was given its variable star designation, CX Boötes, in 1993. GD 165 B was discovered in 1988 by Eric Becklin and Benjamin Zuckerman at the University of California, Los Angeles. GD 165 B was the first brown dwarf discovered to be cooler than M-type star, M-Type stars and was initially assigned the spectral type ≥M10. It would not be regarded as a brown dwarf until 1999, when new spectral types L-type star, L-Type and T-type star, T-Type for objects cooler than M-type stars were established, reclassifying GD 165 B as L4. Physical properties G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GD 165 Legacy Dr10
GD may refer to: Arts and entertainment * G-Dragon (born 1988), leader of the South Korean musical group Big Bang * Grateful Dead, an American rock band * Green Day, an American rock band * ''Geometry Dash'', a side-scrolling music platforming video game Business and economics * Gardner Denver, a US-based manufacturer of industrial equipment * General Dynamics, a US-based defense conglomerate * Good Delivery, a specification for gold and silver bars * ''Gudbrandsdølen Dagningen'', a Norwegian newspaper * Composite Index on the Athens Stock Exchange (stock symbol GD) Mathematics, science and technology Biology and medicine * Gaucher's disease, a lipid storage diseases * Gender dysphoria, distress caused by a difference between the sex and gender a person was assigned at birth * Generalized dystonia, a neurological movement disorder * Gestational diabetes, a form of diabetes associated with pregnancy * Graves' disease, an autoimmune thyroid disorder * ''Gain of deiodinas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-type Star
An object with the spectral type T (also called T dwarf or methane brown dwarf) is either a brown dwarf or young free-floating planetary-mass object. A directly imaged exoplanet with a young age can also be a T-dwarf. T dwarfs are colder than L dwarfs, but warmer than Y dwarfs. Prototype Gliese 229B The first T-dwarf discovered was Gliese 229B, which was discovered in 1995. This object had a temperature below 1000 K and showed methane (CH4), water vapor (H2O) and carbon monoxide (CO) in its spectrum. In the upper atmosphere CO is converted into CH4 and H2O, while the opposite is true for the hotter lower atmosphere. It also showed absorption due to caesium (Cs), but absorption features commonly found in M-dwarfs ( CaH, FeH, TiO, and VO) were missing. Ammonia (NH3) was included in the analysis of the spectrum. Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are also detected in this T-dwarf. Later work found a dynamical mass of 70 ± 5 for Gliese 229B, which is much higher than the coolin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre De Données Astronomiques De Strasbourg
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity * Central tendency, measures of the central tendency (center) in a set of data Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIMBAD
SIMBAD (the Set of Identifications, Measurements and Bibliography for Astronomical Data) is an astronomy, astronomical database of objects beyond the Solar System. It is maintained by the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS), France. SIMBAD was created by merging the Catalog of Stellar Identifications (CSI) and the Bibliographic Star Index as they existed at the Meudon Computer Centre until 1979, and then expanded by additional source data from other catalogues and the academic literature. The first on-line interactive version, known as Version 2, was made available in 1981. Version 3, developed in the C (programming language), C language and running on UNIX stations at the Volgograd Observatory, was released in 1990. Fall of 2006 saw the release of Version 4 of the database, now stored in PostgreSQL, and the supporting software, now written entirely in Java (programming language), Java. , SIMBAD contains information for 5,800,000 stars and about 5,500,000 nons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelu-1
Kelu-1 is a system of two brown dwarfs of spectral types L2 and L4 located in constellation Hydra at approximately 60.6 light-years from Earth. It is among the first free-floating later-than-M-type brown dwarfs discovered, and sometimes considered as prototype of L-type brown dwarfs. History of observations Discovery In 1987 María Teresa Ruiz decided to start The Calán-ESO proper-motion survey using red plates taken (starting from the 1970s) with the 1-m ESO Schmidt Camera at La Silla Observatory, Chile. The survey was not specially designed for search for brown dwarfs, but in the main for search for another type of celestial bodies—white dwarfs. Pairs of plates, separated by long span of time, were compared with blink comparator to detect objects with high proper motion. Objects with high proper motion, which were found, were selected for follow-up spectroscopy using the 3.6-m telescope, equipped with EFOSC1, at the same observatory. In March 1997 was carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J1228
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-metre telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are also located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observato .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 229 B
Gliese 229 (also written as Gl 229 or GJ 229) is a multiple system composed of a red dwarf and two brown dwarf, brown dwarfs, located 18.8 light years away in the constellation Lepus (constellation), Lepus. The primary component has 58% of the solar mass, mass of the Sun, 55% of the solar radius, Sun's radius, and a very low stellar rotation, projected rotation velocity of 1 km/s at the stellar equator. The star is known to be a low activity flare star, which means it undergoes random increases in luminosity because of Stellar magnetic field, magnetic activity at the surface. The spectrum shows emission lines of calcium in the H band (infrared), H and K band (infrared), K bands. The emission of X-rays has been detected from the stellar corona, corona of this star. These may be caused by magnetic loops interacting with the gas of the star's outer atmosphere. No large-scale star spot activity has been detected. The Space velocity (astronomy), space velocity compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHL 5038
PHL 5038AB (or just PHL 5038) is a binary system consisting out of a white dwarf and a brown dwarf on a wide orbit. The system is 240 light years (74 parsec) distant from earth. The white dwarf PHL 5038A was discovered in 2006 in data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and the brown dwarf companion was discovered in 2009 from UKIDSS infrared excess and confirmed with Gemini North to be a spacially resolved binary. It was only the fourth known brown dwarf to orbit a white dwarf at the time. The others were GD 165B, WD 0137-349B and GD 1400B. Physical parameters The white dwarf was first classified as a DA white dwarf, which indicates a hydrogen-dominated atmosphere without any metal pollution. A later work found weak pollution due to calcium in the atmosphere of the white dwarf thanks to XSHOOTER spectra from the Very Large Telescope. The calcium is detected as the K-line in two spectra. No infrared excess due to a disk was detected. PHL 5038A has either accreted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012. The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. One au is approximately equivalent to 499 light-seconds. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical unit. In the astronomical literature, the symbol AU is common. In 2006, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had recommended ua as the symbol for the unit, from the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |