|
GADD45B
Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta, also known as GADD45B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''GADD45B'' gene. Function This gene is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The genes in this group respond to environmental stresses by mediating activation of the p38/ JNK pathway. This activation is mediated via their proteins binding and activating MTK1/ MEKK4 kinase, which is an upstream activator of both p38 and JNK MAPKs. The function of these genes or their protein products is involved in the regulation of growth and apoptosis. These genes are regulated by different mechanisms, but they are often coordinately expressed and can function cooperatively in inhibiting cell growth. Gadd45b is required for activity-induced DNA demethylation of specific promoters and expression of corresponding genes necessary for adult neurogenesis, including br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
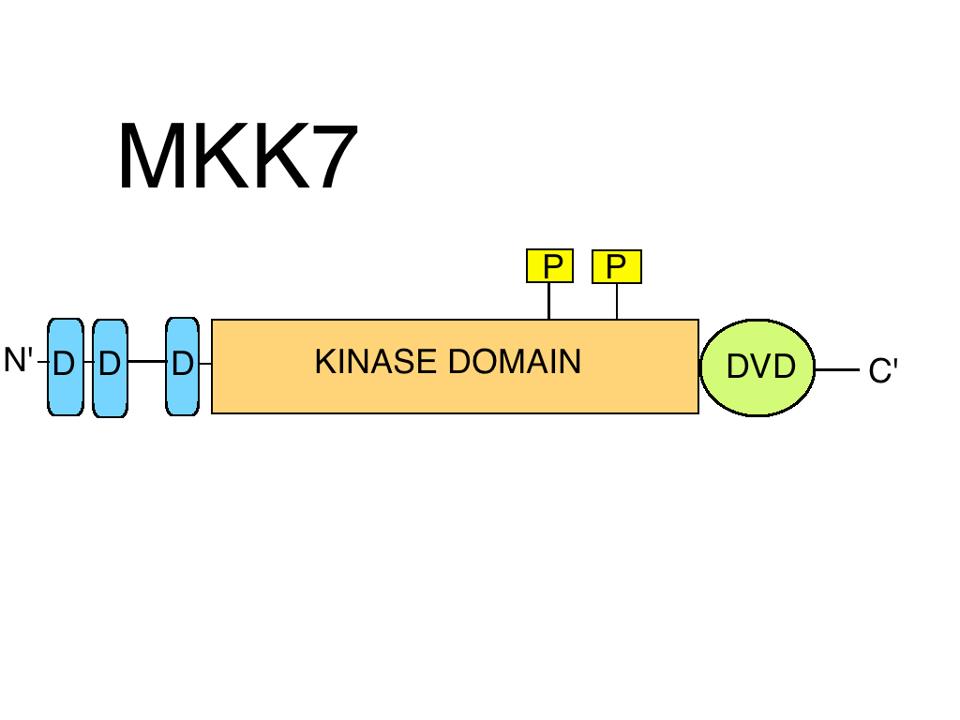
MAP2K7
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7, also known as MAP kinase kinase 7 or MKK7, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K7'' gene. This protein is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase family. The MKK7 protein exists as six different isoforms with three possible N-termini (α, β, and γ isoforms) and two possible C-termini (1 and 2 isoforms). MKK7 is involved in signal transduction mediating the cell responses to proinflammatory cytokines, and environmental stresses. This kinase specifically activates MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK9/JNK2, and this kinase itself is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase kinase kinases including MAP3K1/MEKK1, MAP3K2/MEKK2, MAP3K3/MEKK5, and MAP4K2/GCK. MKK7 is ubiquitously expressed in all tissue. However, it displays a higher level of expression in skeletal muscle. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found. Nomenclature MAP2K7 is also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GADD45GIP1
Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible proteins-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GADD45GIP1'' gene. GADD45GIP1, also known as CRIF1 is newly identified de novo components in large subunit of mitoribosome. It is essential for the translation of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) polypeptides in mammalian mitochondria. CRIF1 interacts with low-sulfur (LSU) proteins, some of which surround the exit tunnel of the mitoribosome, and also interacts with nascent OXPHOS polypeptides and the mitochondrial-specific chaperone Tid1. The essential role of CRIF1 in mitochondrial synthesis and membrane integration of OXPHOS polypeptides was shown in brain-specific CRIF1-deficient mice, which exhibited profound OXPHOS failure and marked neurodegeneration. Interactions GADD45GIP1 has been shown to interact with GADD45G, GADD45B and GADD45A Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible protein GADD45 alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASK1
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 (MAP3K5) is a member of MAP kinase family and as such a part of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. It activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in a Raf-independent fashion in response to an array of stresses such as oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and calcium influx. ASK1 has been found to be involved in cancer, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. ''MAP3K5'' gene coding for the protein is located on chromosome 6 at locus 6q22.33. and the transcribed protein contains 1,374 amino acids with 11 kinase subdomains. Northern blot analysis shows that MAP3K5 transcript is abundant in human heart and pancreas. Mechanism of activation Under nonstress conditions ASK1 is oligomerized (a requirement for its activation) through its C-terminal coiled-coil domain (CCC), but remains in an inacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP3K4
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP3K4'' gene. The central core of each mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a conserved cascade of 3 protein kinases: an activated MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK) phosphorylates and activates a specific MAPK kinase (MAPKK), which then activates a specific MAPK. While the ERK MAPKs are activated by mitogenic stimulation, the CSBP2 (p38α) and JNK MAPKs are activated by environmental stresses such as osmotic shock, UV irradiation, wound stress, and inflammatory factors. This gene encodes a MAPKKK, the MEKK4 protein, also called MTK1. This protein contains a protein kinase catalytic domain at the C terminus. The N-terminal nonkinase domain may contain a regulatory domain. Expression of MEKK4 in mammalian cells activated the CSBP2 (p38α) and JNK MAPK pathways, but not the ERK pathway. In vitro kinase studies indicated that recombinant MEKK4 can specifically phosphorylate and act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein found in the and the periphery. that, in humans, is encoded by the ''BDNF'' gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical nerve growth factor (NGF), a family which also includes NT-3 and NT-4/NT-5. Neurotrophic factors are found in the brain and the periphery. BDNF was first isolated from a pig brain in 1982 by Yves-Alain Barde and Hans Thoenen. BDNF activates the TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Function BDNF acts on certain neurons of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system expressing TrkB, helping to support survival of existing neurons, and encouraging growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses. In the brain it is active in the hippocampus, cortex, and basal forebrain—areas vital to learning, memory, and higher thinking. BDNF is also expressed in the retina, kidneys, prostate, motor neurons, and skeleta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and Tim Bliss first described the now widely studied phenomenon of long-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans and are released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is also kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesis d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Demethylation
For molecular biology in mammals, DNA demethylation causes replacement of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in a DNA sequence by cytosine (C) (see figure of 5mC and C). DNA demethylation can occur by an active process at the site of a 5mC in a DNA sequence or, in replicating cells, by preventing addition of methyl groups to DNA so that the replicated DNA will largely have cytosine in the DNA sequence (5mC will be diluted out). Methylated cytosine is frequently present in the linear DNA sequence where a cytosine is followed by a guanine in a 5' → 3' direction (a CpG site). In mammals, DNA methyltransferases (which add methyl groups to DNA bases) exhibit a strong sequence preference for cytosines at CpG sites. There appear to be more than 20 million CpG dinucleotides in the human genome (see genomic distribution). In mammals, on average, 70% to 80% of CpG cytosines are methylated, though the level of methylation varies with different tissues. Methylated cytosines often occur in groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |