|
G. Michael Bancroft
George "G." Michael Bancroft, , (born 1942) is a Canadian chemist and emeritus professor at the University of Western Ontario. One of the world's leading experts in Mössbauer spectroscopy, he is also known as one of the driving forces behind the development of synchrotron science in Canada, becoming the first director of the Canadian Light Source synchrotron after a 30-year "Odyssey". Early life and education Bancroft was born in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, the son of an accountant, but grew up in Winnipeg, Manitoba where he attended Kelvin High School. He graduated from the University of Manitoba in 1963, subsequently earning an MSc in chemistry (1964) from the same institution. Later that year he went to the University of Cambridge, England to study for a PhD at Corpus Christi College. He worked under the supervision of A.G. Maddock on the development of Mössbauer spectroscopy, obtaining his PhD in 1967. Over a 20-year period Bancroft would become one of the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
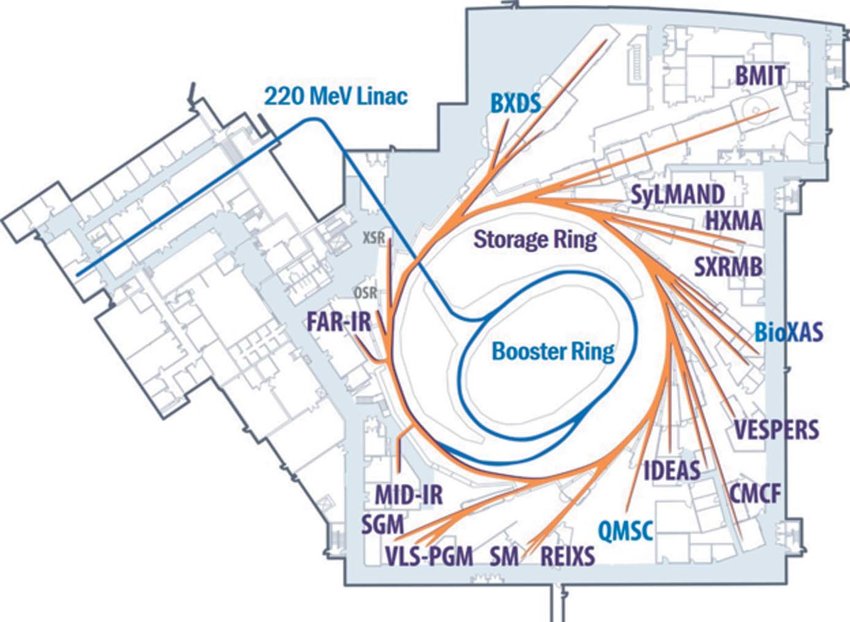
Canadian Light Source
The Canadian Light Source (CLS) (french: link=no, Centre canadien de rayonnement synchrotron – CCRS) is Canada's national synchrotron light source facility, located on the grounds of the University of Saskatchewan in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. The CLS has a third-generation 2.9 GeV storage ring, and the building occupies a footprint the size of a Canadian football field. It opened in 2004 after a 30-year campaign by the Canadian scientific community to establish a synchrotron radiation facility in Canada. It has expanded both its complement of beamlines and its building in two phases since opening. As a national synchrotron facility with over 1000 individual users, it hosts scientists from all regions of Canada and around 20 other countries. Research at the CLS has ranged from viruses to superconductors to dinosaurs, and it has also been noted for its industrial science and its high school education programs. History The road to the CLS: 1972–1999 Canadian inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beamline
In accelerator physics, a beamline refers to the trajectory of the beam of particles, including the overall construction of the path segment (guide tubes, diagnostic devices) along a specific path of an accelerator facility. This part is either * the line in a linear accelerator along which a beam of particles travels, or * the path leading from particle generator (e.g. a cyclic accelerator, synchrotron light sources, cyclotrons, or spallation sources) to the experimental end-station. Beamlines usually end in experimental stations that utilize particle beams or synchrotron light obtained from a synchrotron, or neutrons from a spallation source or research reactor. Beamlines are used in experiments in particle physics, materials science, life science, chemistry, and molecular biology, but can also be used for irradiation tests or to produce isotopes. Beamline in a particle accelerator In particle accelerators the beamline is usually housed in a tunnel and/or unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Radiation Center
The Synchrotron Radiation Center (SRC), located in Stoughton, Wisconsin and operated by the University of Wisconsin–Madison, was a national synchrotron light source research facility, operating the Aladdin storage ring. From 1968 to 1987 SRC was the home of Tantalus, the first storage ring dedicated to the production of synchrotron radiation. History The Road to SRC: 1953–1968 15 universities formed the Midwest Universities Research Association (MURA) in 1953 to promote and design a high energy proton synchrotron, to be built in the Midwest. With the intent of constructing a large accelerator, MURA purchased a suitable area of land with an underlying flat limestone base near Stoughton, Wisconsin, about from the Madison campus of the University of Wisconsin. MURA's first accelerator was a 45 MeV synchrotron, built in a concrete underground "vault", mostly for radiation protection purposes. A small electron storage ring, operating at 240 MeV, was designed by Ed Row ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
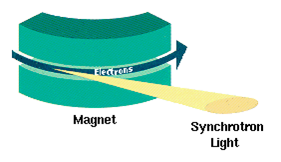
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Windsor
, mottoeng = Goodness, Discipline and Knowledge , established = , academic_affiliations = CARL, COU, Universities Canada , former_names = Assumption College (1857-1956)Assumption University of Windsor (1956-1963) , type = Public university , president = Robert Gordon , chancellor = Mary Jo Haddad , address = 401 Sunset AvenueWindsor, OntarioN9B 3P4 , coordinates = , academic_staff = 524 , students = 16,321 (2018) , undergrad = 10,572 (full-time), 1,711 (part-time) , postgrad = 3,934 (full-time), 104 (part-time) , campus = Urban, , mascot = The Lancer , colours = , endowment = C$118.734 million (2019) , athletics_affiliations = U Sports - CIS, OUA , sports_nickname = Windsor Lancers , website = , logo = The University of Windsor (U of W or UWindsor) is a public research university in Windsor, Ontario, Canada. It is Canada's southernmost university. It has approximately 12,000 full-time and part-time undergraduate students and 4,000 graduate stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada. Originally controlled by the Church of England, the university assumed its present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. As a collegiate university, it comprises eleven colleges each with substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs and significant differences in character and history. The university maintains three campuses, the oldest of which, St. George, is located in downtown Toronto. The other two satellite campuses are located in Scarborough and Mississauga. The University of Toronto offers over 700 undergraduate and 200 graduate programs. In all major rankings, the university consistently ranks in the top ten public universities in the world and as the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are Massless particle, massless, so they always move at the speed of light, speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. There is no universally accepted, strict definition of the bounds of the X-ray band. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |