|
G.983
ITU-T Recommendation G.983 is a family of recommendations that defines broadband passive optical network (BPON) for telecommunications Access networks. It originally comprised ten recommendations, G.983.1 through G.983.10, but recommendations .6–.10 were withdrawn when their content was incorporated into G.983.2. The current view is that the BPON standards are mature, and no further work will be done on them after the 2007 round. The GPON OMCI definition has been revised to stand alone, rather than citing G.983.2. Although G.983 is directed at BPON, the GPON recommendations draw heavily on it, especially G.984 ITU-T G.984 is the series of standards for implementing a gigabit-capable passive optical network (GPON). It is commonly used to implement the link to the customer (the Last mile (telecommunications), ''last kilometre'', or ''last mile'') of fib ....4, which defines the management model for GPON ONTs. Current recommendations The current recommendations are: G.98 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churning (cipher)
Churning is an encryption function used to scramble downstream user data of the ATM passive optical network system defined by the ITU G.983.1 standard. The standard states that churning "offers a low level of protection for data confidentiality". Cryptanalysis had shown that "the churning cipher is robustly weak". Algorithm Churning uses 24 bits of the key, designated X1..X8 and P1..P16. Ten static K bits are generated from the key: K1 = (X1×P13×P14) + (X2×P13×not P14) + (X7×not P13×P14) + (X8×not P13×not P14) K2 = (X3×P15×P16) + (X4×P15×not P16) + (X5×not P15×P16) + (X6×not P15×not P16) K3 = (K1×P9) + (K2×not P9) K4 = (K1×not P9) + (K2×P9) K5 = (K1×P10) + (K2×not P10) K6 = (K1×not P10) + (K2×P10) K7 = (K1×P11) + (K2×not P11) K8 = (K1×not P11) + (K2×P11) K9 = (K1×P12) + (K2×not P12) K10 = (K1×not P12) + (K2×P12) The churning transforms eight bits into eight bits: (Z1..Z4) = TransformNibble(Y1..Y4, K1, P1, K3, K2, P2, K4, K1, K3, K5, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Optical Network
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications network that uses only ''unpowered'' devices to carry signals, as opposed to electronic equipment. In practice, PONs are typically used for the '' last mile'' between Internet service providers (ISP) and their customers. In this use, a PON has a point-to-multipoint topology in which an ISP uses a single device to serve many end-user sites using a system such as 10G-PON or GPON. In this one-to-many topology, a single fiber serving many sites branches into multiple fibers through a passive splitter, and those fibers can each serve multiple sites through further splitters. The light from the ISP is divided through the splitters to reach all the customer sites, and light from the customer sites is combined into the single fiber. Many fiber ISPs prefer this system. Components and characteristics A passive optical network consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NG-PON2
NG-PON2 (also known as TWDM-PON), ''Next-Generation Passive Optical Network 2'' is a 2015 telecommunications network standard for a passive optical network (PON). The standard was developed by ITU and details an architecture capable of total network throughput of 40 Gbit/s, corresponding to up to 10 Gbit/s symmetric upstream/downstream speeds available at each subscriber. A passive optical network is a last mile, fibre-to-the-x telecommunications network that broadcasts data through fibre optic cables. PONs are managed by passive optics such as unpowered splitters and filters, offering high reliability and low cost compared to active networks. The PON data stream is generally converted to a more traditional service such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi at the subscriber's location. NG-PON2 is compatible with existing PON fibre by replacing optical line terminal (OLT) at the central office, and the optical network unit (ONU) near each end-user. Unique to this standard is the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPON
ITU-T G.984 is the series of standards for implementing a gigabit-capable passive optical network (GPON). It is commonly used to implement the link to the customer (the ''last kilometre'', or ''last mile'') of fibre-to-the-premises ( FTTP) services. GPON puts requirements on the optical medium and the hardware used to access it, and defines the manner in which Ethernet frames are converted to an optical signal, as well as the parameters of that signal. The bandwidth of the single connection between the OLT ( optical line termination) and the ONTs ( optical network terminals) is 2.4Gbit/s down, 1.2Gbit/s up, or rarely symmetric 2.4Gbit/s, shared between up to 128 ONTs using a time-division multiple access (TDMA) protocol, which the standard defines. GPON specifies protocols for error correction ( Reed–Solomon) and encryption ( AES), and defines a protocol for line control ( OMCI) which includes authentication (GPON serial number and/or PLOAM password). Unlike the previous EPON ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-T
The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating Standardization, standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology, such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. The World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), the sector's governing conference, convenes every four years. ITU-T has a permanent Secretariat (administrative office), secretariat called the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), which is based at the ITU headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. The current director of the TSB is Seizo Onoe (of Japan), whose 4-year term commenced on 1 January 2023. Seizo Onoe succeeded Chaesub Lee of South Korea, who was director from 1 J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-T Study Group 15
The ITU-T Study Group 15 (SG15) 'Transport' is a standardization committee of ITU-T concerned with networks, technologies and infrastructures for transport, access and home. It responsible for standards such as GPON, G.fast, etc. Administratively, SG15 is a statutory meeting of the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), which creates the ITU-T Study Groups and appoints their management teams. The secretariat is provided by the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (under Director Chaesub Lee). The goal of SG15 is to produce recommendations (international standards) for networks. Area of work SG15 focuses on developing standards and recommendations related to optical transport networks, access network transport, and associated technologies. Some of the key responsibilities of SG15 include: # Developing international standards for optical and transport networks, which covers fiber-optic communication systems, dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10G-PON
10G-PON (also known as XG-PON or G.987) is a 2010 computer networking standard for Osi model#Layer 2: data link layer, data links, capable of delivering shared Internet access rates up to 10 Gbit/s (gigabits per second) over dark fiber. This is the ITU-T's next-generation standard following on from GPON or gigabit-capable PON. Optical fibre is shared by many subscribers in a network known as FTTx in a way that centralises most of the telecommunications equipment, often displacing copper phone lines that connect premises to the phone exchange. Passive optical network (PON) architecture has become a cost-effective way to meet performance demands in access networks, and sometimes also in large optical local networks for ''fibre-to-the-desk''. Passive optical networks are used for the ''fibre-to-the-home'' or ''fibre-to-the-premises'' Last mile (telecommunications), last mile with splitters that connect each central transmitter to many subscribers. The 10 Gbit/s shared capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadband
In telecommunications, broadband or high speed is the wide-bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth data transmission that exploits signals at a wide spread of frequencies or several different simultaneous frequencies, and is used in fast Internet access. The transmission medium can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, wireless Internet (radio), twisted pair cable, or satellite broadband, satellite. Originally used to mean 'using a wide-spread frequency' and for services that were analog at the lowest level, nowadays in the context of Internet access, 'broadband' is often used to mean any high-speed Internet access that is seemingly always 'on' and is faster than Dial-up Internet access, dial-up access over traditional plain old telephone service, analog or ISDN public switched telephone network, PSTN services. The ideal telecommunication network has the following characteristics: ''broadband'', ''multi-media'', ''multi-point'', ''multi-rate'' and economical implementation for a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
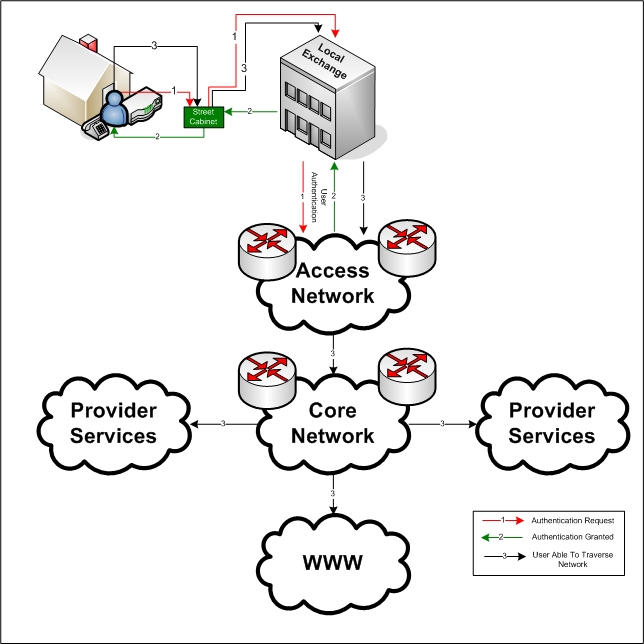
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications telecommunications network, network which connects subscribers to their immediate telecommunications service provider, service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-T Recommendations
The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology, such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. The World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), the sector's governing conference, convenes every four years. ITU-T has a permanent secretariat called the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), which is based at the ITU headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. The current director of the TSB is Seizo Onoe (of Japan), whose 4-year term commenced on 1 January 2023. Seizo Onoe succeeded Chaesub Lee of South Korea, who was director from 1 January 2015 until 31 December 2022. Primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |