|
Fáskrúðsfjarðargöng
Fáskrúðsfjarðargöng (, ) is a tunnel in Iceland, located in Eastern Region along Route 1 The following highways are numbered 1. For roads numbered A1, see list of A1 roads. For roads numbered B1, see list of B1 roads. For roads numbered M1, see List of M1 roads. For roads numbered N1, see list of N1 roads. For roads numbered S ... (formerly along Route 96). It has a length of and opened on September 9, 2005. References Road tunnels in Iceland Tunnels completed in 2005 Buildings and structures in Eastern Region (Iceland) {{Europe-tunnel-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route 1 (Iceland)
Route 1 or the Ring Road ( or ) is a National road (Iceland), national road in Iceland that circles the entire country. As a major Trunk road, trunk route, it is considered to be the most important piece of transport infrastructure in Iceland as it connects the majority of towns together in the most densely populated areas of the country. Economically, it carries a large proportion of goods traffic as well as Tourism, tourist traffic. The total length of the road is , making it the longest ring road in Europe. The road was completed in 1974, coinciding with the 1,100th anniversary of Settlement of Iceland, the country's settlement when the longest bridge in Iceland, crossing the Skeiðará river in the southeast, was opened. Previously, vehicles intending to travel between southern settlements, e.g. Vík to Höfn, had to travel north of the country through Akureyri, making the opening a major transport improvement to the country. Many popular tourist attractions in Iceland, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjarðabyggð
Fjarðabyggð () is a municipality located in eastern Iceland, in the Eastern Region. History The municipality was formed in 1998 with the union of the former municipalities of Eskifjörður, Neskaupstaður and Reyðarfjörður. Austurbyggð, Fáskrúðsfjarðarhreppur and Mjóafjarðarhreppur were merged into Fjarðabyggð in 2006, and Breiðdalshreppur merged in 2018. Geography The municipality is composed by the following villages: Twin towns – sister cities Fjarðabyggð is twinned with: * Esbjerg, Denmark * Eskilstuna, Sweden * Gravelines, France * Jyväskylä, Finland * Qeqqata, Greenland * Stavanger, Norway * Vágar Vágar (; ) is one of the 18 islands in the archipelago of the Faroe Islands and the most westerly of the ''large islands''. With a size of , it ranks third in size, behind Streymoy and Eysturoy. Vágar Regions of the Faroe Islands, region also ..., Faroe Islands References External links Official websiteVisit Fjarðabyggð Municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
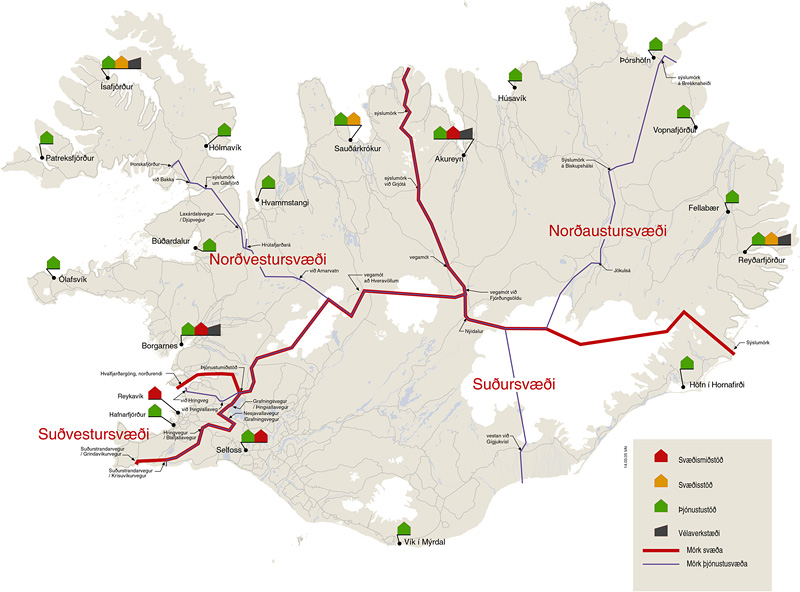
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegagerðin
The Road and Coastal Administration ( ) is a state run institution in Iceland whose purpose is to construct and maintain roads and infrastructure (land and sea) in rural areas and between urban areas. Formerly belonging to the Ministry of the Interior, it is now part of the Ministry of Infrastructure (until November 2021 named '' Ministry of Transport and Local Government''). Vegagerðin is the legal owner of the roads and has the authority to execute construction of infrastructures on demand from the ministry. History Until the 20th century Until the 18th century there were no official roads in Iceland, only paths and barely visible tracks which people followed with the help of cairns for a few kilometers in either direction. In the 19th century, when fishing villages began to spring up on shores and sandbanks, infrastructure between farms and villages began to improve. As fishermen's camps became villages, with homes and workshops, they also became important trading posts for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fáskrúðsfjörður
Fáskrúðsfjörður (; previously named also Búðir ) is a village (''þorp'') in eastern Iceland. It has a population of 735 (as of 2024) and constitutes one of the villages composing the municipality of Fjarðabyggð. Geography Fáskrúðsfjörður, located on the same-named fjord, lies between Reyðarfjörður and Stöðvarfjörður. It is one of the easternmost settlements of Iceland. The other neighbouring villages which compose the municipality of Fjarðabyggð are: Eskifjörður (1,043 inh.), Mjóifjörður (35 inh.), Neskaupstaður (1,437 inh.), Reyðarfjörður (1,102 inh.) and Stöðvarfjörður (203 inh.). History and culture Fáskrúðsfjörður was home to a hospital founded to serve French fishermen working here until 1935. The former hospital building dating from 1903 has now been restored as a hotel. Even nowadays there are bilingual signs in town indicating the street names in Icelandic and in French. The French cemetery with 49 graves of fishermen from Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Region (Iceland)
Eastern Region (, ) is a region in eastern Iceland. Its area is and in 2024 its population was 11,085. The Eastern Region has a jagged coastline of fjords, referred to as the ''Eastfjords'' ( ). The largest town in the region is Egilsstaðir, with a population of 2,632. The oldest municipality is Djúpivogur, which got their trading licence in 1589 and had a population of 412 in 2024. The only car and passenger ferry that sails between Iceland and the European continent calls at Seyðisfjörður once a week except in the winter season. The region is home to the Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant ( ), officially called Fljótsdalur Power Station ( ) is a hydroelectric power plant in Fljótsdalshérað municipality in eastern Iceland, designed to produce annually for Alcoa's Fjarðaál Aluminium smelting, alu .... Among notable tourist destinations are the Helgustaðir mine, which is known for its Iceland spar, and Stuðlagil. References See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route 96 (Iceland)
Route 96 or (, ) was a Roads in Iceland, national road in the Eastern Region (Iceland), Eastern Region of Iceland. It begins just west of Reyðarfjörður and heads through the Fáskrúðsfjörður road tunnel. It then follows the coast to Stöðvarfjörður and ends just outside Breiðdalsvík. In November 2017, the entire road became part of the Route 1 (Iceland), Ring Road (Route 1), together with a part of Route 92 (Iceland), Route 92, replacing the route over Breiðdalsheiði which in turn was re-numbered from Route 1 to a new road number, Route 95 (Iceland), Route 95. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Tunnels In Iceland
A road is a thoroughfare used primarily for movement of traffic. Roads differ from streets, whose primary use is local access. They also differ from stroads, which combine the features of streets and roads. Most modern roads are paved. The words "road" and "street" are commonly considered to be interchangeable, but the distinction is important in urban design. There are many types of roads, including parkways, avenues, controlled-access highways (freeways, motorways, and expressways), tollways, interstates, highways, and local roads. The primary features of roads include lanes, sidewalks (pavement), roadways (carriageways), medians, shoulders, verges, bike paths (cycle paths), and shared-use paths. Definitions Historically, many roads were simply recognizable routes without any formal construction or some maintenance. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defines a road as "a line of communication (travelled way) using a stabilized base other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunnels Completed In 2005
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ventilation openings at various points along the length. A pipeline differs significantly from a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube construction techniques rather than traditional tunnel boring methods. A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. The central portions of a rapid transit network are usually in the tunnel. Some tunnels are used as sewers or aqueducts to supply water for consumption or for hydroelectric stations. Utility tunnels are used for routing steam, chilled water, electrical power or telecommunication cables, as well as connecting buildings for convenient passage of people and equipment.Salazar, Waneta. ''Tunnels in Civil Engineering''. Delhi, India : Whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |