|
Fylax
''Fylax'' (meaning "keeper") is a genus of hadrosauroid ornithopod from the Late Cretaceous Figuerola Formation of Spain. The genus contains a single species, ''Fylax thyrakolasus'', known from a nearly complete left dentary. Discovery and naming The holotype of ''Fylax'', IPS-36338, a left dentary, was discovered in the early 1990s. It was found in the Figuerola Formation in Lleida province, northeastern Spain. It was initially described in 1999.Casanovas, M.L., Pereda Suberbiola, X.P., Santafé, J.V., and Weishampel, D.B. 1999. "A primitive euhadrosaurian dinosaur from the uppermost Cretaceous of the Ager syncline (southern Pyrenees, Catalonia)". ''Geologie en Mijnbouw'' 78: 345–356 In 2021, Albert Prieto-Márquez and Miguel Ángel Carrera Farias described the dentary as belonging to a new genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur. The generic name, ''Fylax,'' comes from the modern Greek, fýlax (keeper), and the specific name, ''thyrakolasus'', comes from the Greek thýra (gate) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethyshadros
''Tethyshadros'' (" Tethyan hadrosauroid") is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur from Trieste, Italy. The type and only species is ''T. insularis''. Discovery and naming Sometime in the 1980s, Alceo Tarlao and Giorgio Rimoli reported finding fragments of dinosaur bone while prospecting for rare bones. The abandoned quarry these were found in was only 100m inland, at Villagio del Pescatore, Trieste Province, Italy. It was from this quarry that a nearly complete hadrosaur skeleton was discovered in 1994. Lying on a vertical rockface, the specimen required a difficult excavation process, involving the removal of over 300 cubic metres of mineral and use of large equipment. Palaeontologist Fabio Della Vacchia among others served as scientific director for the excavation. Many other fossils, including various other hadrosaur specimens, were uncovered in the process. The main skeleton was not extracted until 1999. The significance of the find was immediately recognized, being the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2021. General research * A study on the relationship between full potential joint mobility and the poses used during locomotion in extant American alligator and helmeted guineafowl, evaluating its implications for reconstructions of locomotion of extinct archosaurs, is published by Manafzadeh, Kambic & Gatesy (2021). * A study on the femoral shape variation and on the relationship between femoral morphology and locomotor habits in early archosaurs and non-archosaur archosauriforms is published by Pintore ''et al.'' (2021). * A study estimating moment arms for major pelvic limb muscles in extant and fossil archosaurs, aiming to investigate the idea that bird-line archosaurs switched from hip-based to knee-based locomotion between Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
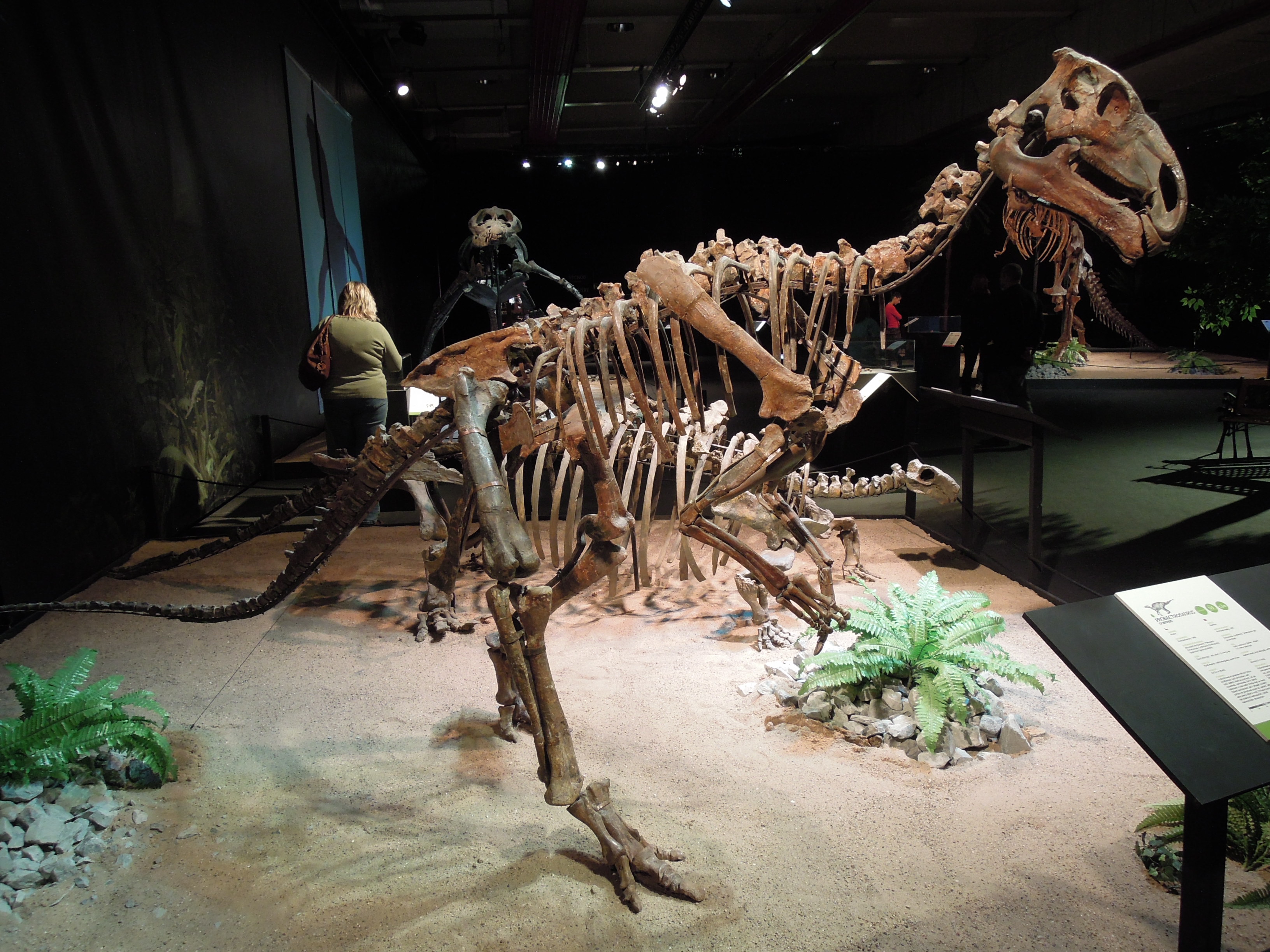
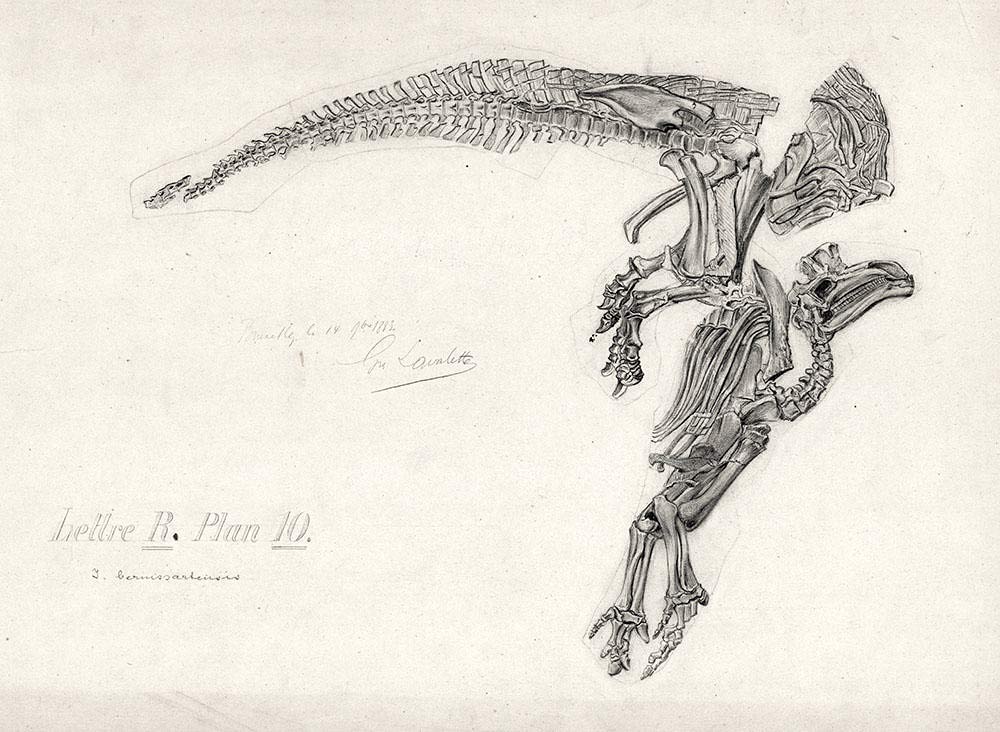
Hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as '' Edmontosaurus'' and ''Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as '' Edmontosaurus'' and '' Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauromorpha
Hadrosauromorpha is a clade of iguanodontian ornithopods, defined in 2014 by David B. Norman to divide Hadrosauroidea into the basal taxa with compressed manual bones and a pollex, and the derived taxa that lack them. The clade is defined as all the taxa closer to ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' than '' Probactrosaurus gobiensis''. This results in different taxon inclusion depending on the analysis. Classification Hadrosauromorpha was first used in literature by David B. Norman in 2014 in a discussion of phylogenetics of ''Hypselospinus''. In his 2014 paper Norman references another of his publications as the authority for Hadrosauromorpha, a chapter in the book ''Hadrosaurs''. However, the book was in fact published later, in 2015. Following Article 19.4 of the PhyloCode, the authorship of the clade is thus Norman (2015), while the authorship of the definition is Norman (2014). Definition Hadrosauromorpha was defined by Norman (2014 and 2015) as hadrosauroid taxa closer to ''Edmon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrosaurus
''Bactrosaurus'' (; meaning "Club lizard," "baktron" = club + ''sauros'' = lizard) is a genus of herbivorous hadrosauroid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, about 96-85 million years ago. The position ''Bactrosaurus'' occupies in the Cretaceous makes it one of the earliest known hadrosauroids, and although it is not known from a full skeleton, ''Bactrosaurus'' is one of the best known of these early hadrosauroids, making its discovery a significant finding. Discovery The first ''Bactrosaurus'' remains recovered from the Iren Dabasu Formation in the Gobi Desert of China were composed of partial skeletons of six individual ''B. johnsoni''. The specimens collected appear to come from a variety of age groups, from individuals that may be hatchlings to full-sized adults. The fossils were described in 1933 by Charles W. Gilmore, who named the new animal ''Bactrosaurus'', or "club lizard", in reference to the large club-shaped neural spines projecting from some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophorhothon
''Lophorhothon'' is a genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, the first genus of dinosaur discovered in Alabama, in the United States. Discovery and naming Remains of this small, poorly known perhaps saurolophine dinosaur were first discovered during the 1940s, from extensive erosional outcrops of the lower unnamed member of the Mooreville Chalk Formation (Selma Group; lower and middle Campanian) in Dallas County, west of the town of Selma, Alabama. The taxon has since also been reported from Black Creek Formation (Campanian) of North Carolina. The holotype, which is housed in the collections of the Field Museum in Chicago, consists of a fragmentary and disarticulated skull and incomplete postcranial skeleton. The length on the holotype specimen has been estimated as . The genus was named by Wann Langston in 1960. It was thought to be the only species of hadrosaur from that fossil formation, until 2016 with the discovery of the primitive hadrosaur, '' Eotr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Spain
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Spain
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotrachodon
''Eotrachodon orientalis'' (meaning "dawn ''Trachodon'' from the east") is a species of hadrosaurid that was described in 2016. The holotype was found in the Mooreville Chalk Formation (Upper Santonian) in Alabama in 2007 and includes a well-preserved skull and partial skeleton, making it a rare find among dinosaurs of Appalachia. Another primitive hadrosaur, ''Lophorhothon'', is also known from the same formation, although ''Eotrachodon'' lived a few million years prior. A phylogenetic study has found ''Eotrachodon'' to be the sister taxon to the hadrosaurid subfamilies Lambeosaurinae and Saurolophinae. This, along with the other Appalachian hadrosaur ''Hadrosaurus'' and possibly ''Lophorhothon'', '' Claosaurus'' and both species of '' Hypsibema'', suggests that Appalachia was the ancestral area of Hadrosauridae. See also * Timeline of hadrosaur research *2016 in paleontology Flora Plants Fungi Cnidarians Research * '' Yunnanoascus haikouensis'', previously thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiohadros
''Plesiohadros'' (meaning "near to hadrosaurids") is an extinct genus of hadrosauroid dinosaur. It is known from a partial skeleton including the skull collected at Alag Teg locality, from the Campanian Alagteeg Formation of southern Mongolia. The type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ... is ''Plesiohadros djadokhtaensis''. Paleoecology ''Plesiohadros'' is the only known hadrosaur from the Alagteeg Formation. References Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Djadochta fauna Iguanodonts Fossil taxa described in 2014 Taxa named by David B. Weishampel Ornithischian genera {{Ornithopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |