|
Futurematic
The Futurematic is a self-windingAd in Life magazine 1951. wrist without a crown. It was manufactured between 1951 and 1959 by the Swiss watch manufacturer Jaeger-LeCoultre. The Futurematic was the world's first watch without a crown for winding the mainspring, having a flat crown on the back that was used solely for setting the time.Zaf Basha: ''Jaeger LeCoultre''. . Watch face The Futurematic was produced with two different[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaeger-LeCoultre E502 Futurematic
Manufacture Jaeger-LeCoultre SA, or simply Jaeger-LeCoultre (), is a Swiss luxury watch and clock manufacturer founded by Antoine LeCoultre in 1833 and is based in Le Sentier, Switzerland. Since 2000, the company has been a fully owned subsidiary of the Swiss luxury group Richemont. Jaeger-LeCoultre is regarded as a top-tier Richemont brand. It has hundreds of inventions, patents, and more than one thousand movements to its name, including the world's smallest movement, one of the world's most complicated wristwatches (Grande Complication), and a timepiece of near-perpetual movement (the '' Atmos clock''). History Early history The earliest records of the LeCoultre family in Switzerland date from the 16th century, when Pierre LeCoultre (circa 1530 – circa 1600), a French Huguenot, fled to Geneva from Lizy-sur-Ourcq, France to escape religious persecution. In 1558, he obtained the status of “inhabitant” but left the following year to acquire a plot of land in the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaeger-LeCoultre
Manufacture Jaeger-LeCoultre SA, or simply Jaeger-LeCoultre (), is a Swiss luxury watch and clock manufacturer founded by Antoine LeCoultre in 1833 and is based in Le Sentier, Switzerland. Since 2000, the company has been a fully owned subsidiary of the Swiss luxury group Richemont. Jaeger-LeCoultre is regarded as a top-tier Richemont brand. It has hundreds of inventions, patents, and more than one thousand movements to its name, including the world's smallest movement, one of the world's most complicated wristwatches (Grande Complication), and a timepiece of near-perpetual movement (the '' Atmos clock''). History Early history The earliest records of the LeCoultre family in Switzerland date from the 16th century, when Pierre LeCoultre (circa 1530 – circa 1600), a French Huguenot, fled to Geneva from Lizy-sur-Ourcq, France to escape religious persecution. In 1558, he obtained the status of “inhabitant” but left the following year to acquire a plot of land in the Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Spring
A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of the timepiece turn, thus the rate of movement of the hands. A regulator lever is often fitted, which can be used to alter the free length of the spring and thereby adjust the rate of the timepiece. The balance spring is a fine spiral or helical torsion spring used in mechanical watches, alarm clocks, kitchen timers, marine chronometers, and other timekeeping mechanisms to control the rate of oscillation of the balance wheel. The balance spring is an essential adjunct to the balance wheel, causing it to oscillate back and forth. The balance spring and balance wheel together form a harmonic oscillator, which oscillates with a precise period or "beat" resisting external disturbances, and is responsible for timekeeping accuracy. The addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Gold
Pure gold is slightly reddish yellow in color, but colored gold in various other colors can be produced by alloying gold with other elements. Colored golds can be classified in three groups: * Alloys with silver and copper in various proportions, producing white, yellow, green and red golds. These are typically malleable alloys. * Intermetallic compounds, producing blue and purple golds, as well as other colors. These are typically brittle, but can be used as gems and inlays. * Surface treatments, such as oxide layers. Pure 100% (in practice, 99.9% or better) gold is 24 karat by definition, so all colored golds are less pure than this, commonly 18K (75%), 14K (58.5%), 10K (41.6%), or 9K (37.5%). Alloys White gold White gold is an alloy of gold and at least one white metal (usually nickel, silver, or palladium). Like yellow gold, the purity of white gold is given in karats. White gold's properties vary depending on the metals used and their proportions. As a result, white gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a passive film that can protect the material and self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both aluminium and copper, having a biological cleanability comparable to glass. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act
The Tariff Act of 1930 (codified at ), commonly known as the Smoot–Hawley Tariff or Hawley–Smoot Tariff, was a law that implemented protectionist trade policies in the United States. Sponsored by Senator Reed Smoot and Representative Willis C. Hawley, it was signed by President Herbert Hoover on June 17, 1930. The act raised US tariffs on over 20,000 imported goods. The tariffs under the act, excluding duty-free imports (see Tariff levels below), were the second highest in United States history, exceeded by only the Tariff of 1828. The Act prompted retaliatory tariffs by affected states against the United States. The Act and tariffs imposed by America's trading partners in retaliation were major factors of the reduction of American exports and imports by 67% during the Depression. Economists and economic historians have a consensus view that the passage of the Smoot–Hawley Tariff worsened the effects of the Great Depression. Sponsors and legislative history In 1922 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slogan
A slogan is a memorable motto or phrase used in a clan, political, commercial, religious, and other context as a repetitive expression of an idea or purpose, with the goal of persuading members of the public or a more defined target group. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines a slogan as "a short and striking or memorable phrase used in advertising." A slogan usually has the attributes of being memorable, very concise and appealing to the audience. Etymology The word slogan is derived from ''slogorn'' which was an Anglicisation of the Scottish Gaelic and Irish ''sluagh-ghairm'' (''sluagh'' "army", "host" + ''gairm'' "cry").Merriam-Webster (2003), p. 1174. Irish Slogans vary from the written and the visual to the chanted and the vulgar. Their simple rhetorical nature usually leaves little room for detail, and a chanted slogan may serve more as social expression of unified purpose than as communication to an intended audience. George E. Shankel's (1941, as cited in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Protection
Shock may refer to: Common uses Collective noun *Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names * Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves Healthcare * Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergency ** Cardiogenic shock, resulting from dysfunction of the heart ** Distributive shock, resulting from an abnormal distribution of blood flow *** Septic shock, a result of severe infection *** Toxic shock syndrome, a specific type of severe infection *** Anaphylactic shock ** Hemorrhagic shock, from a large volume of blood loss ** Neurogenic shock, due to a high spinal cord injury disrupting the sympathetic nervous system * Cold shock response of organisms to sudden cold, especially cold water * Electric shock ** Defibrillation, electric shock to restore heart rhythm ** Electroconvulsive therapy or shock treatment, psychiatric treatment * Hydrostatic shock, from ballistic impact * Insulin shock or diabetic hypoglycemia, from too much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
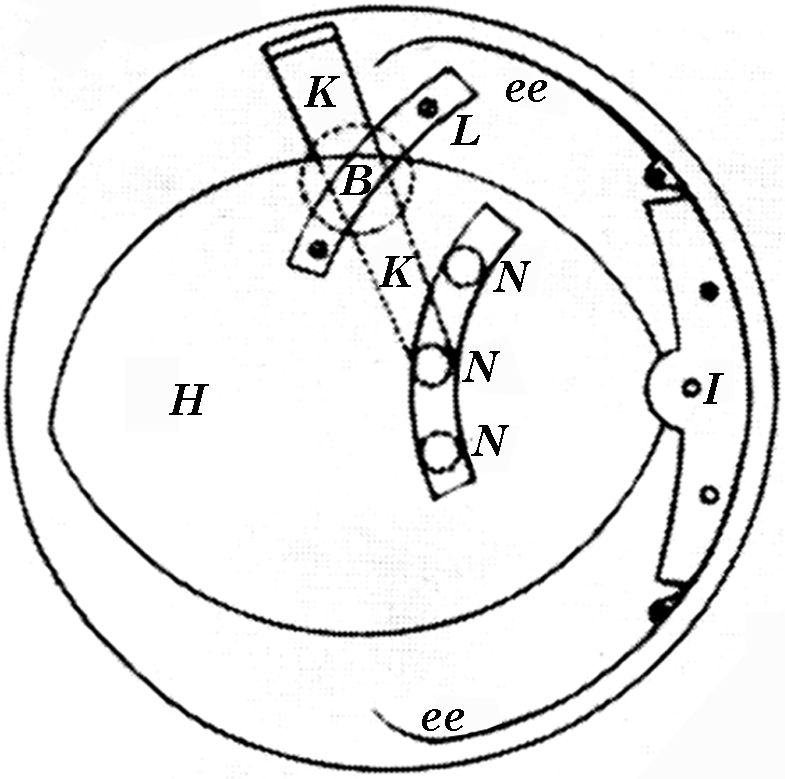
Balance Wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a spiral torsion spring, known as the balance spring or ''hairspring''. It is driven by the escapement, which transforms the rotating motion of the watch gear train into impulses delivered to the balance wheel. Each swing of the wheel (called a "tick" or "beat") allows the gear train to advance a set amount, moving the hands forward. The balance wheel and hairspring together form a harmonic oscillator, which due to resonance oscillates preferentially at a certain rate, its resonant frequency or "beat", and resists oscillating at other rates. The combination of the mass of the balance wheel and the elasticity of the spring keep the time between each oscillation or "tick" very constant, accounting for its nearly universal use as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-winding
An automatic watch, also known as a self-winding watch or simply an automatic, is a mechanical watch where the natural motion of the wearer provides energy to wind the mainspring, making manual winding unnecessary if worn enough. It is distinguished from a ''manual watch'' in that a manual watch must have its mainspring wound by hand at regular intervals. Operation In a mechanical watch the watch's gears are turned by a spiral spring called a mainspring. In a ''manual watch'' energy is stored in the mainspring by turning a knob, the ''crown'' on the side of the watch. Then the energy from the mainspring powers the watch movement until it runs down, requiring the spring to be wound again. A self-winding watch movement has a mechanism which winds the mainspring using the natural motions of the wearer's body. The watch contains an oscillating weight that turns on a pivot. The normal movements of the watch in the user's pocket (for a pocketwatch) or on the user's arm (for a wristwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliber (horology)
In horology, a movement, also known as a caliber or calibre (British English), is the mechanism of a watch or timepiece, as opposed to the ''case'', which encloses and protects the movement, and the ''face'', which displays the time. The term originated with mechanical timepieces, whose clockwork movements are made of many moving parts. The movement of a digital watch is more commonly known as a module. In modern mass-produced clocks and watches, the same movement is often inserted into many different styles of case. When buying a quality pocketwatch from the mid-19th to the mid-20th century, for example, the customer would select a movement and case individually. Mechanical movements get dirty and the lubricants dry up, so they must periodically be disassembled, cleaned, and lubricated. One source recommends servicing intervals of: 3–5 years for watches, 15–20 years for grandfather clocks, 10–15 years for wall or mantel clocks, 15–20 years for anniversary clocks, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)