|
Funcusvermis
''Funcusvermis'' is an extinct genus of stem-caecilian from the Late Triassic of Arizona. It is based on a large sample of jaws and other skull and postcranial fragments, discovered in an approximately 220 million years old layer of rock in the Blue Mesa Member of the Chinle Formation at Petrified Forest National Park. There is a single species, called ''Funcusvermis gilmorei''. The identity of ''Funcusvermis'' as a gymnophionan amphibian is supported by a range of traits, including a long additional tooth row in the jaw, a fused maxillopalatine bone in the skull, and a modified jaw with a pseudodentary and pseudoangular. Small femora (thigh bones) indicate that legs were still present in ''Funcusvermis'', despite its modern relatives being completely legless. ''Funcusvermis'' is the oldest known gymnophionan, and has the largest known sample of fossils referred to the group. Previously, both records were held by '' Eocaecilia micropodia'', an amphibian from the Early Juras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acaenasuchus
''Acaenasuchus'' (meaning "thorn crocodile") is an extinct genus of pseudosuchians, endemic to what would be Arizona during the Late Triassic, existing for approximately . Discovery and naming The holotype, UCMP 139576 (a left(?) dorsal paramedian scute), was discovered by Charles Lewis Camp in 1930 and was considered to belong to a juvenile of ''Desmatosuchus''.Heckert, A.B. and Lucas, S. G. (2002). ''Acaenasuchus geoffreyi'' (Archosauria: Aetosauria) from the Upper Triassic Chinle Group: Juvenile of ''Desmatosuchus'' ''haplocerus''. ''Upper Triassic Stratigraphy and Paleontology. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin No. 21''. UCMP 139576 eventually moved into its own taxon, and ''Acaenasuchus'' was named by Long and Murry (1995).R. A. Long and P. A. Murry. (1995). Late Triassic (Carnian and Norian) tetrapods from the southwestern United States. ''New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin'' 4:1-254 The holotype was discovered in the Petrifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocaecilia
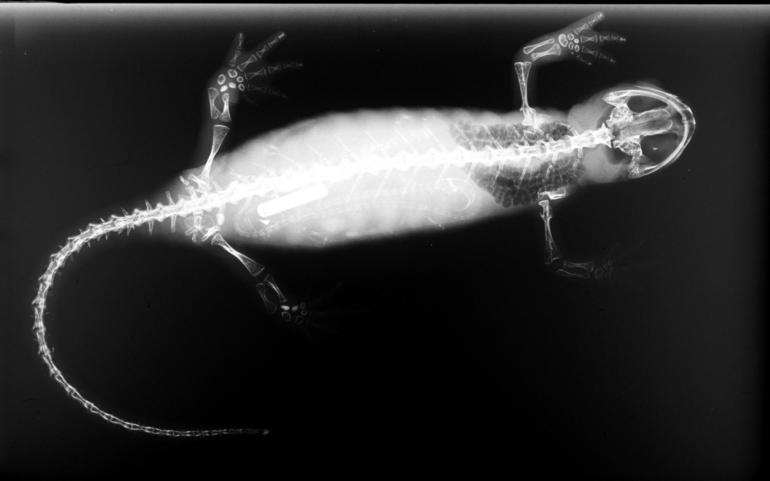
''Eocaecilia'' is an extinct genus of gymnophionan amphibian from the early Jurassic Kayenta Formation of Arizona, United States. One species is described, ''Eocaecilia micropodia''. ''Eocaecilia'' shared some characteristics with salamanders and the now extinct microsaur amphibians. It was of small size, about 15 cm in length. Unlike modern caecilians, which are legless, ''Eocaecilia'' possessed small legs, and while modern caecilians have poorly developed eyes and spend a lot of time under ground, ''Eocaecilias eyes were somewhat better developed. Although the precise ancestry of ''Eocaecilia'' is debated (and other caecilians by extension), it likely resided among the ancestral lepospondyl or temnospondyl Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carb ...Maddin H.C., Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains. Colorado is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, eighth most extensive and List of U.S. states and territories by population, 21st most populous U.S. state. The 2020 United States Census, 2020 United States census enumerated the population of Colorado at 5,773,714, an increase of 14.80% since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census. The region has been inhabited by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans and their Paleo-Indians, ancestors for at least 13,500 years and possibly much longer. The eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains was a major migration route for early peoples who spread throughout the Americas. "''Colorado''" is the Spanish adjective meaning "ruddy", th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospondyli
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Classification and anatomy The group was first defined by Zittel (1888) on the recognition of the distinctive vertebral anatomy of the best known stereospondyls of the time, such as '' Mastodonsaurus'' and ''Metoposaurus''. The term 'stereospondylous' as a descriptor of vertebral anatomy was coined the following year by Fraas, referring to a vertebral position consisting largely or entirely of the intercentrum in addition to the neural arch. While the name 'Stereospondyli' is derived from the stereospondylous vertebral condition, there is a diversity of vertebral morphologies among stereospondyls, including the diplospondylous ('tupilakosaurid') c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinlestegophis
''Chinlestegophis'' is a diminutive Late Triassic stereospondyl that has been interpreted as a putative stem caecilian, a living group of legless burrowing amphibians. If ''Chinlestegophis'' is indeed both an advanced stereospondyl and a relative of caecilians, this means that stereospondyls (in the form of caecilians) survived to the present day; historically the group was thought to have gone extinct by the early Cretaceous. ''Chinlestegophis jenkinsi'', the type and only species, is known from two partial skulls discovered in the Chinle Formation in Colorado. History of study ''Chinlestegophis'' was described in 2017 by Jason Pardo, Adam Huttenlocker, and Bryan Small based on two specimens collected in the late 1990s by Small. The genus name is derived from the name of the formation (Chinle), the Greek root ''stego''- ('roof' or 'cover'), and the Greek root -''ophis'' ('serpent'). The species name honors Farish Jenkins, the longtime curator of the Museum of Comparative Zoolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerobatrachus
''Gerobatrachus'' is an extinct genus of amphibamid temnospondyl (represented by the type species ''Gerobatrachus hottoni'') that lived in the Early Permian, approximately 290 million years ago (Ma), in the area that is now Baylor County, Texas. When it was first described in 2008, ''Gerobatrachus'' was announced to be the closest relative of Batrachia, the group that includes modern frogs and salamanders. It possesses a mixture of characteristics from both groups, including a large frog-like head and a salamander-like tail. These features have led to it being dubbed a frogamander by the press. Some more recent studies place ''Gerobatrachus'' as the closest relative of Lissamphibia, the group that contains all modern amphibians including frogs, salamanders, and caecilians, or place modern amphibians far from ''Gerobatrachus'' within a group called Lepospondyli. Description The only known specimen of ''Gerobatrachus'' is a nearly complete skeleton (USNM 489135) about long, that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissorophoidea
Dissorophoideans are a clade of medium-sized, temnospondyl amphibians that appeared during the Moscovian in Euramerica, and continued through to the Late Permian and the Early Triassic of Gondwana. They are distinguished by various details of the skull, and many forms seem to have been well adapted for life on land. Since 2008, Lissamphibia has been progressively widely considered part of this clade, but this position is still disputed by some authors. It is possible that the small Permo-Carboniferous Micromelerpetontidae and the large Late Permian Melosauridae may also belong in this clade. Phylogeny An extensive phylogenetic analysis of dissorophoids conducted in 2016 and 2018 found that the families Dissorophidae and Trematopidae are more closely related to each other than either is to the family Amphibamidae. Following a 2008 study, the Dissorophidae-Trematopidae clade was called Olsoniformes. Below is the cladogram from the 2018 analysis: References * Huttenlocker, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" '' Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limbs folded underneath, and no tail (the tail of tailed frogs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Ranomafana.jpg)