|
Functional Renormalization Group
In theoretical physics, functional renormalization group (FRG) is an implementation of the renormalization group (RG) concept which is used in quantum and statistical field theory, especially when dealing with strongly interacting systems. The method combines functional methods of quantum field theory with the intuitive renormalization group idea of Kenneth G. Wilson. This technique allows to interpolate smoothly between the known microscopic laws and the complicated macroscopic phenomena in physical systems. In this sense, it bridges the transition from simplicity of microphysics to complexity of macrophysics. Figuratively speaking, FRG acts as a microscope with a variable resolution. One starts with a high-resolution picture of the known microphysical laws and subsequently decreases the resolution to obtain a coarse-grained picture of macroscopic collective phenomena. The method is nonperturbative, meaning that it does not rely on an expansion in a small coupling constant. Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Fixed Point (mathematics)
In mathematics, a fixed point (sometimes shortened to fixpoint), also known as an invariant point, is a value that does not change under a given transformation (mathematics), transformation. Specifically, for function (mathematics), functions, a fixed point is an element that is mapped to itself by the function. Any set of fixed points of a transformation is also an invariant set. Fixed point of a function Formally, is a fixed point of a function if belongs to both the domain of a function, domain and the codomain of , and . In particular, cannot have any fixed point if its domain is disjoint from its codomain. If is defined on the real numbers, it corresponds, in graphical terms, to a curve in the Euclidean plane, and each fixed-point corresponds to an intersection of the curve with the line , cf. picture. For example, if is defined on the real numbers by f(x) = x^2 - 3 x + 4, then 2 is a fixed point of , because . Not all functions have fixed points: for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Quantum Gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics. It deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects, as well as in the early stages of the universe moments after the Big Bang. Three of the four fundamental forces of nature are described within the framework of quantum mechanics and quantum field theory: the Electromagnetism, electromagnetic interaction, the Strong interaction, strong force, and the Weak interaction, weak force; this leaves gravity as the only interaction that has not been fully accommodated. The current understanding of gravity is based on Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which incorporates his theory of special relativity and deeply modifies the understanding of concepts like time and space. Although general relativity is highly regarded for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Kondo Effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities, resulting in a characteristic change i.e. a minimum in electrical resistivity with temperature. The cause of the effect was first explained by Jun Kondo, who applied third-order perturbation theory to the problem to account for scattering of s-orbital conduction electrons off d-orbital electrons localized at impurities ( Kondo model). Kondo's calculation predicted that the scattering rate and the resulting part of the resistivity should increase logarithmically as the temperature approaches 0 K. Extended to a lattice of ''magnetic impurities'', the Kondo effect likely explains the formation of ''heavy fermions'' and ''Kondo insulators'' in intermetallic compounds, especially those involving rare earth elements such as cerium, praseodymium, and ytterbium, and actinide elements such as uranium. The Kondo effect has also been observed in quantum dot systems. Theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
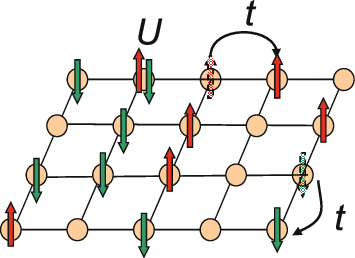 |
Hubbard Model
The Hubbard model is an Approximation, approximate model used to describe the transition between Conductor (material), conducting and Electrical insulation, insulating systems. It is particularly useful in solid-state physics. The model is named for John Hubbard (physicist), John Hubbard. The Hubbard model states that each electron experiences competing forces: one pushes it to tunnel to neighboring atoms, while the other pushes it away from its neighbors. Its Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics), Hamiltonian thus has two terms: a kinetic term allowing for Quantum tunneling, tunneling ("hopping") of particles between lattice sites and a potential term reflecting on-site interaction. The particles can either be fermions, as in Hubbard's original work, or bosons, in which case the model is referred to as the "Bose–Hubbard model". The Hubbard model is a useful approximation for particles in a periodic potential at sufficiently low temperatures, where all the particles may be assumed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Phase Transitions
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic State of matter, states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma (physics), plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical property, physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Statistical Field Theory
In theoretical physics, statistical field theory (SFT) is a theoretical framework that describes phase transitions. It does not denote a single theory but encompasses many models, including for magnetism, superconductivity, superfluidity, topological phase transition, wetting as well as non-equilibrium phase transitions. A SFT is any model in statistical mechanics where the degrees of freedom comprise a field or fields. In other words, the microstates of the system are expressed through field configurations. It is closely related to quantum field theory, which describes the quantum mechanics of fields, and shares with it many techniques, such as the path integral formulation and renormalization. If the system involves polymers, it is also known as polymer field theory. In fact, by performing a Wick rotation from Minkowski space to Euclidean space, many results of statistical field theory can be applied directly to its quantum equivalent. The correlation functions of a statistica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Normal Order
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson * ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie * ''Normal'' (2009 film), an adaptation of Anthony Neilson's 1991 play ''Normal: The Düsseldorf Ripper'' * '' Normal!'', a 2011 Algerian film * ''The Normals'' (film), a 2012 American comedy film * "Normal" (''New Girl''), an episode of the TV series Mathematics * Normal (geometry), an object such as a line or vector that is perpendicular to a given object * Normal basis (of a Galois extension), used heavily in cryptography * Normal bundle * Normal cone, of a subscheme in algebraic geometry * Normal coordinates, in differential geometry, local coordinates obtained from the exponential map (Riemannian geometry) * Normal distribution, the Gaussian continuous probability distribution * Normal equations, describing the solution of the linear least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Effective Interaction
Effectiveness or effectivity is the capability of producing a desired result or the ability to produce desired output. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression. Etymology The origin of the word ''effective'' stems from the Latin word , which means "creative, productive, or effective". It surfaced in Middle English between 1300 and 1400 AD. Usage Science and technology Mathematics and logic In mathematics and logic, ''effective'' is used to describe metalogical methods that fit the criteria of an effective procedure. In group theory, a group element acts ''effectively'' (or ''faithfully'') on a point, if that point is not fixed by the action. Physics In physics, an effective theory is, similar to a phenomenological theory, a framework intended to explain certain (observed) effects without the claim that the theory correctly models the underlying (unobserved) processes. In heat t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Hubbard–Stratonovich Transformation
The Hubbard–Stratonovich (HS) transformation is an exact mathematical transformation invented by Russian physicist Ruslan L. Stratonovich and popularized by British physicist John Hubbard. It is used to convert a particle theory into its respective field theory by linearizing the density operator in the many-body interaction term of the Hamiltonian and introducing an auxiliary scalar field. It is defined via the integral identity : \exp \left( - \frac x^2 \right) = \sqrt \; \int_^\infty \exp \left( - \frac - i x y \right) \, dy, where the real constant a > 0. The basic idea of the HS transformation is to reformulate a system of particles interacting through two-body potentials into a system of independent particles interacting with a fluctuating field. The procedure is widely used in polymer physics, classical particle physics, spin glass theory, and electronic structure theory. Calculation of resulting field theories The resulting field theories are well-suited for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid State of matter, phases, that arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms and electrons. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconductivity, superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic temperatures, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of Spin (physics), spins on crystal lattices of atoms, the Bose–Einstein condensates found in ultracold atomic systems, and liquid crystals. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theoretical physics, physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Quantum Chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the study of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group special unitary group, SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called ''color''. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of Quantum chromodynamics#Experimental tests, experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years. QCD exhibits three salient properties: * Color confinement. Due to the force between two color charges remaining constant as they are separated, the energy grows until a quark–antiquark pair is mass–energy equivalence, spontaneously produced, turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |