|
Functional Integration (neurobiology)
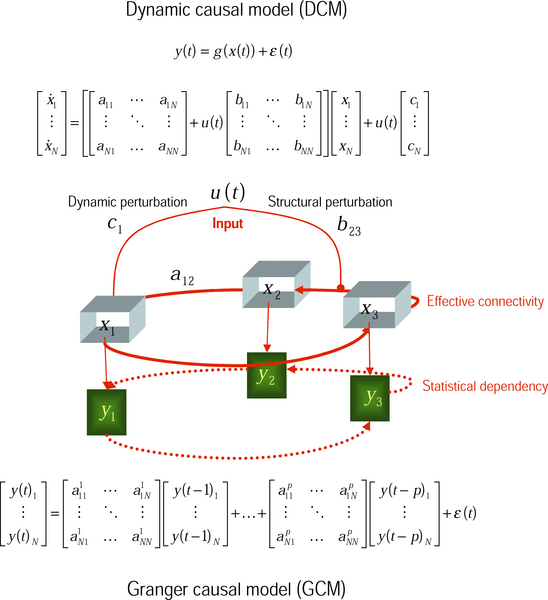
Functional integration is the study of how brain regions work together to process information and effect responses. Though functional integration frequently relies on anatomic knowledge of the connections between brain areas, the emphasis is on how large clusters of neurons – numbering in the thousands or millions – fire together under various stimuli. The large datasets required for such a whole-scale picture of brain function have motivated the development of several novel and general methods for the statistical analysis of interdependence, such as dynamic causal modelling and statistical linear parametric mapping. These datasets are typically gathered in human subjects by non-invasive methods such as Electroencephalography, EEG/Magnetoencephalography, MEG, fMRI, or Positron emission tomography, PET. The results can be of clinical value by helping to identify the regions responsible for psychiatric disorders, as well as to assess how different activities or lifestyles affect th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
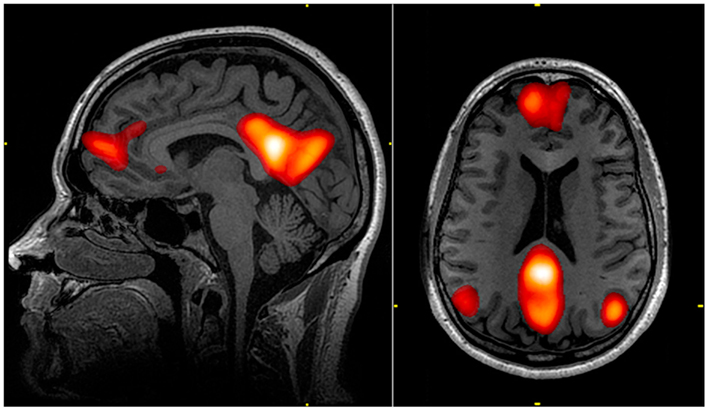
Figure 1 Of Voxel-Based Morphometry In Women With Borderline Personality Disorder With And Without Comorbid Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration *Figure (wood), wood appearance *Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif *Noise figure, in telecommunication *Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance *Figure–ground (perception), the distinction between a visually perceived object and its surroundings Arts *Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature *Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine *Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form *Figure drawing *Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) *Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure *Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number *Significant figures in a decimal number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms Prodrome, develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorder, mood, anxiety disorder, anxiety, and substance use disorders, substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). About 0.3% to 0.7% of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supramarginal Gyrus
The supramarginal gyrus is a portion of the parietal lobe. This area of the brain is also known as Brodmann area 40 based on the brain map created by Korbinian Brodmann to define the structures in the cerebral cortex. It is probably involved with language perception and processing, and lesions in it may cause receptive aphasia. Important functions The supramarginal gyrus is part of the somatosensory association cortex, which interprets tactile sensory data and is involved in perception of space and limbs location. It is also involved in identifying postures and gestures of other people and is thus a part of the mirror neuron system. The right-hemisphere supramarginal gyrus appears to play a central role in controlling empathy towards other people. When this structure is not working properly or when individuals have to make very quick judgements, empathy becomes severely limited. Research has shown that disrupting the neurons in the right supramarginal gyrus causes humans to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baddeley's Model Of Working Memory
Baddeley's model of working memory is a model of human memory proposed by Alan Baddeley and Graham Hitch in 1974, in an attempt to present a more accurate model of primary memory (often referred to as short-term memory). Working memory splits primary memory into multiple components, rather than considering it to be a single, unified construct. Baddeley and Hitch proposed their three-part working memory model as an alternative to the short-term store in Atkinson and Shiffrin's 'multi-store' memory model (1968). This model is later expanded upon by Baddeley and other co-workers to add a fourth component, and has become the dominant view in the field of working memory. However, alternative models are developing, providing a different perspective on the working memory system. The original model of Baddeley & Hitch was composed of three main components: the ''central executive'' which acts as a supervisory system and controls the flow of information from and to its ''slave systems' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. Originally, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction (quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern #Current tests, IQ tests, the test score, raw score is Data transformation (statistics), transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2 percent each Intellectual giftedness, above 130 and Intellectual disability, below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for example, distance and mass, a concrete measure of intelligence cannot be achieved given the abstract nature of the concept o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striatum
The striatum (: striata) or corpus striatum is a cluster of interconnected nuclei that make up the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. However, some authors believe it is made up of caudate nucleus, putamen, and ventral striatum. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Functional Connectivity
Dynamic functional connectivity (DFC) refers to the observed phenomenon that functional connectivity changes over a short time. Dynamic functional connectivity is a recent expansion on traditional functional connectivity analysis which typically assumes that functional networks are static in time. DFC is related to a variety of different neurological disorders, and has been suggested to be a more accurate representation of functional brain networks. The primary tool for analyzing DFC is fMRI, but DFC has also been observed with several other mediums. DFC is a recent development within the field of functional neuroimaging whose discovery was motivated by the observation of temporal variability in the rising field of steady state connectivity research. Overview and history Static connectivity Functional connectivity refers to the functionally integrated relationship between spatially separated brain regions. Unlike structural connectivity which looks for physical connections in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. It appears pinkish-white to the naked eye otherwise, because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows saltatory conduction, electrical signals to jump, rather than cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distinguished from white matter in that it contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons, while white matter contains relatively few cell bodies and is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axons. The colour difference arises mainly from the whiteness of myelin. In living tissue, grey matter actually has a very light grey colour with yellowish or pinkish hues, which come from capillary blood vessels and neuronal cell bodies. Structure Grey matter refers to unmyelinated neurons and other cells of the central nervous system. It is present in the brain, brainstem and cerebellum, and present throughout the spinal cord. Grey matter is distributed at the surface of the cerebral hemisp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Field
In physics and mathematics, a random field is a random function over an arbitrary domain (usually a multi-dimensional space such as \mathbb^n). That is, it is a function f(x) that takes on a random value at each point x \in \mathbb^n(or some other domain). It is also sometimes thought of as a synonym for a stochastic process with some restriction on its index set. That is, by modern definitions, a random field is a generalization of a stochastic process where the underlying parameter need no longer be real or integer valued "time" but can instead take values that are multidimensional vectors or points on some manifold. Formal definition Given a probability space (\Omega, \mathcal, P), an ''X''-valued random field is a collection of ''X''-valued random variables indexed by elements in a topological space ''T''. That is, a random field ''F'' is a collection : \ where each F_t is an ''X''-valued random variable. Examples In its discrete version, a random field is a list of ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |