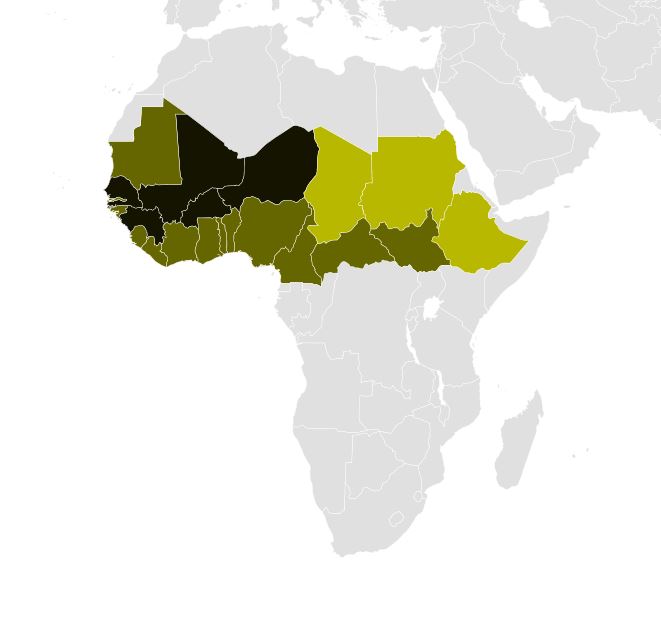
|
Fula Jihad States Map General C1830
Fula may refer to: *Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe) *Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani) **The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language **The Fula variety known as the Pular language **The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde *Fula alphabets writing systems of Fula language in the Latin script. *Al-Fula *Fula jihads The Fula (or Fulani) jihads () sometimes called the Fulani revolution were a series of jihads that occurred across West Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries, led largely by the Muslim Fula people, Fulani people. The jihads and the jihad sta ... series of Jihads across West Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 7 to 10 million – are pastoralism, pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani – Fulbe Laddi – who also farm, although they argue that they do so out of necessity, not choice. The major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula Language
Fula ( ),Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh also known as Fulani ( ) or Fulah (, , ; Adlam script, Adlam: , , ; Ajami script, Ajami: , , ), is a Senegambian languages, Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a Dialect continuum, continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West Africa, West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer language, Serer and Wolof language, Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic languages, Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian languages, Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have Tone (linguistics), tones. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people ("Fulani", ) from the Senegambia, Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulaar Language
Pulaar (in Latin: , in Ajami: ), often referred to as Pulaar du Nord, is dialect of the Fula language spoken primarily as a first language by the Fula and Toucouleur peoples in the Senegal River valley area traditionally known as Futa Tooro and further south and east. Pulaar speakers, known as '' Haalpulaar'en'' live in Senegal, Mauritania, the Gambia, and western Mali. The two main speakers of Pulaar are the Toucouleur people and the Fulɓe (also known as Fulani or Peul). Fula, considered as a single language, is the second most spoken local language in Senegal, being a first language for around 22% of the population. This correlates with 23.7% of the country in which Fulbe is the population's ethnicity. Pulaar is one of the national languages of Senegal alongside 13 others. It was admitted as an official language of Senegal by Presidential decree in 1971. There are around 28 known dialects of Fula, most of which are mutually intelligible with each other. The Fula dialects, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pular Language
Pular (), often referred to as Pula Futa, is a Fula language spoken primarily by the Fula people of Fouta Djallon, Guinea. It is also spoken in Guinea-Bissau, Gambia, Senegal and in parts of Sierra Leone. There are a small number of speakers in Mali. Pular is spoken by 4.3 million Guineans, about 55% of the national population. This makes Pular the most widely spoken indigenous language in the country. Substantial numbers of Pular speakers have migrated to other countries in West Africa, notably Senegal and Ivory Coast. Pular is not to be confused with Pulaar, another Fula language spoken natively in Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, and western Mali (including the Futa Tooro region). Pular is written in three alphabets: Adlam script, Ajami script and the Latin script. Linguistic features There are some particularities to this version of Fula, including: *Use of plural form for politeness (such as in German or French, unlike other varieties of Fula) *A number of separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maasina Fulfulde
Maasina Fulfulde is a variety of the Fula language. It is spoken mainly in Mali, Ivory Coast, and Ghana by 1.6 million people. The language has several mutually intelligible dialects albeit with some differences. The variety is named after the Macina region in Mali. Maasinankoore is the most widely spoken dialect of Fula spoken in Mali and is a national language of the country. According to Ethnologue there are two dialects - Western and Eastern - and "There are some dialect differences, but popular opinion is that all dialects in Mali are inherently intelligible." Maasina Fulfulde is grammatically basically the same as other varieties of Fula, with some particularities. For instance there are some slight differences in some verb endings. The counting system retains a recapitulation of older systems historically used by other groups in what is now Mali. Tens from 60-90 have alternative versions not used in other varieties of Fula. In the table the general form, which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula Alphabets
The Fula language (, ''Pulaar'', or ''Pular'') is written primarily in the Latin script, but in some areas is still written in an older Arabic script called the Ajami script or in the recently invented Adlam script. Latin-based alphabets Background The Latin script was introduced to Fula-speaking regions of West and Central Africa by Europeans during, and in some cases immediately before, invasion. Various people — missionaries, colonial administrators, and scholarly researchers — devised various ways of writing . One issue similar to other efforts by Europeans to use their alphabet and home orthographic conventions was how to write African languages with unfamiliar sounds. In the case of Fula, these included how to represent sounds such as the implosive b and d, the ejective y, the velar n (the latter being present in European languages, but never in initial position), prenasalised consonants, and long vowels, all of which can change meaning. Major influences on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Fula
Merhavia () is a kibbutz in northern Israel. Located to the east of Afula, it falls under the jurisdiction of Jezreel Valley Regional Council. In it had a population of . Etymology The name Merhavia is derived from Psalm 118: In the figurative sense, the phrase connotes 'freedom from distress and anxiety', which resonated with the experience of Jews immigrating to the Land of Israel and achieving a new homeland without the straits, or distress, of persecution. History Bronze Age According to the Survey of Western Palestine (SWP, 1882), it was possibly the place called ''Alpha'' in the list of Thutmes III. Crusader-Ayyubid period In the Crusader period it was known as ''La Fève'' or ''Castrum Fabe''. It had a Templar castle (first mentioned in 1169/72), of which just some mounds remain. The area was under Crusader control between 1099 and 1187. In 1183 the Battle of Al-Fule took place here, between the Crusaders and the forces of Saladin. An aerial photograph taken in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula Jihads
The Fula (or Fulani) jihads () sometimes called the Fulani revolution were a series of jihads that occurred across West Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries, led largely by the Muslim Fula people, Fulani people. The jihads and the jihad states came to an end with Scramble for Africa, European colonization. The earliest Fulbe polity was established in Bundu (state), Bundu in 1690. The first armed uprising took place in Futa Jallon in 1725, when Fula pastoralists, assisted by Muslim traders, rose against the indigenous chiefdoms. By 1750, the Fula had established the Imamate of Futa Jallon and placed the region under sharia law. Their success inspired the Toucouleur people, Toucouleurs on the banks of the lower Senegal river, Senegal to establish their own state, the Imamate of Futa Toro, through a series of wars between 1769 and 1776. In the early 19th century, the jihad movement spread eastward to the Hausa states. The revolutionary Usman dan Fodio, through Fulani War, a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |