|
FuG 200 Hohentwiel
The FuG 200 ''Hohentwiel'' was a low-UHF band frequency maritime patrol radar system of the Luftwaffe in World War II. It was developed by C. Lorenz AG of Berlin starting in 1938 under the code name " Hohentwiel", an extinct volcano in the region of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. Originally developed as an anti-aircraft radar for the ''Luftwaffe'', it lost out to the ''Würzburg'' for this role. In 1941, it was modified as an airborne surface search radar for naval patrol aircraft like the Focke-Wulf Fw 200. In 1944 it was further adapted for shipborne use, used on late-war U-boats, some surface ships, and land based installations. Development The device had originally been entered into a design contest held by the ''Luftwaffe'' for the new FuMG 40L (ground-based fire-control radar). When competitor Telefunken won that contract with its " Würzburg radar" in 1939, the device was shelved. In 1941, Lorenz started to re-design it for another design contest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Aviation (Germany)
The Ministry of Aviation (, abbreviated RLM) was a government department during the period of Nazi Germany (1933–45). It is also the original name of the Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus building on the Wilhelmstrasse in central Berlin, Germany, which houses the modern German Finance Ministry (). The Ministry was in charge of development and production of all aircraft developed, designed, and built in Germany during the existence of the Third Reich, overseeing all matters concerning both military and civilian designs – it handled military aviation matters as its top priority, particularly for the Luftwaffe. As was characteristic of government departments in the Nazi era, the Ministry was personality-driven and formal procedures were often ignored in favour of the whims of the Minister, ''Reichsmarschall'' Hermann Göring. As a result, early successes in aircraft development progressed only slowly and erratically during World War II. History The Ministry was formed on 27 April 1933 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Radars
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California, where the company would remain headquartered for the remainder of its lifetime; this HP Garage is now a designated landmark and marked with a plaque calling it the "Birthplace of 'Silicon Valley. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components, as well as software and related services, to consumers, small and medium-sized businesses ( SMBs), and fairly large companies, including customers in government sectors, until the company officially split into Hewlett Packard Enterprise and HP Inc. in 2015. HP initially produced a line of electronic test and measurement equipment. It won its first big contract in 1938 to provide the HP 200B, a variation of its first product, the HP 200A low-distortion frequency oscillator, for W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fachbuchverlag Leipzig
The (''fv''; English: Specialist book publisher Leipzig) was an East German publisher. It continues to exist as an imprint of the Munich publishing firm Carl Hanser Verlag. Company history The publishing house was founded in early 1949 by several shareholders (including FDGB, ). The first managing director was . From 1960 to 1990 the specialist book publisher was a Volkseigener Betrieb (VEB) (English, "publicly owned enterprise"). It was one of the two most renowned technical-scientific publishers in the German Democratic Republic, whose specialist books were also widely distributed in the Federal Republic of Germany. The books were very popular with West-German students because of their low price, but above all because of the good didactics. It also published specialist journals. In 1995, the specialist book publisher was taken over by the Munich Carl Hanser Verlag and continued to exist there as an imprint. Under the brand, some of the editors of Carl Hanser Verlag cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branches, along with the and the , of the , the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945. In violation of the Treaty of Versailles, the grew rapidly during German rearmament, German naval rearmament in the 1930s. The 1919 treaty had limited the size of the German navy and prohibited the building of submarines. ships were deployed to the waters around Spain during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939) under the guise of enforcing non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War, non-intervention, but in reality supporting the Francoist Spain, Nationalists against the Second Spanish Republic, Spanish Republicans. In January 1939, Plan Z, a massive shipbuilding programme, was ordered, calling for surface naval parity with the United Kingdom, British Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Type XXI Submarine
Type XXI submarines were a class of German diesel–electric '' Elektroboot'' (German: "electric boat") submarines designed during the Second World War. One hundred eighteen were completed, with four being combat-ready. During the war only two were put into active service and went on patrols, but these were not used in combat. They were the first submarines designed to operate primarily submerged, rather than spending most of their time as surface ships that could submerge for brief periods as a means of escaping detection. They incorporated many batteries to increase the time they could spend submerged, to as much as several days, and they only needed to surface to periscope depth for recharging via a snorkel. The design included many general improvements as well: much greater underwater speed by an improved hull design, greatly improved diving times, power-assisted torpedo reloading and greatly improved crew accommodations. However, the design was also flawed in many ways, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Type IX Submarine
The Type IX U-boat was designed by Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine'' in 1935 and 1936 as a large ocean-going submarine for sustained operations far from the home support facilities. Type IX boats were briefly used for patrols off the eastern United States in an attempt to disrupt the stream of troops and supplies bound for Europe. It was derived from the Type IA and appeared in various sub-types. Type IXs had six torpedo tubes; four at the bow and two at the stern. They carried six reloads internally and had five external torpedo containers (three at the stern and two at the bow) which stored ten additional torpedoes. The total of 22 torpedoes allowed U-boat commanders to follow a convoy and strike night after night. Some of the IXC boats were fitted for mine operations; as mine-layers they could carry 44 TMA or 60 TMB mines. Secondary armament was provided by one deck gun with 180 rounds. Anti-aircraft armament differed throughout the war. They had two periscopes in the tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
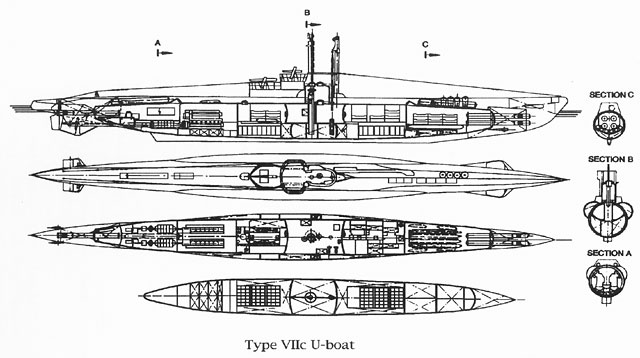
German Type VII Submarine
Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 704 boats were built by the end of the war. The type had several modifications. The Type VII was the most numerous U-boat type to be involved in the Battle of the Atlantic. The lone surviving example, , is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. At the start of the Second World War the ''Type VII'' class wastogether with the British ''U'', ''S'' and ''T'' class and Dutch ''O 21'' classone of the most advanced submarine classes in service. Design After the defeat in World War I, the Treaty of Versailles forbade Germany to build submarines. Germany circumvented the treaty by setting up the Dutch dummy company ''NV Ingenieurskantoor voor Scheepsbouw Den Haag'' (I.v.S) which continued to design submarines. Based on the World War I design of the Type UB III and its never-built successors Type UF and Type UG, IVS designed the Vetehinen-class submarine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel He 177
The Heinkel He 177 ''Greif'' (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed by problems both with the development of its engines and frequent changes to its intended role. Nevertheless, it was the only long-range, heavy bomber to become operational with the ''Luftwaffe'' during the conflict. The He 177 had Payload#Relationship of range and payload, a payload/range capability similar to that of four-engined heavy bombers used by the Allies in the Western Front (World War II), European theatre. Work on the design began in response to a 1936 requirement known as Bomber A, issued by the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) for a purely strategic bomber. Thus, the He 177 was intended originally to be capable of a sustained bombing campaign against Soviet Union, Soviet manufacturing capacity, Ural economic region, dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |