|
Frère Jacques
"Frère Jacques" (, ), also known in English as "Brother John", is a nursery rhyme of French origin. The rhyme is traditionally sung in a round. The song is about a friar who has overslept and is urged to wake up and sound the bell for the matins, the midnight or very early morning prayers for which a friar would be expected to be awake. Lyrics Frère Jacques, Frère Jacques, Dormez-vous? Dormez-vous? Sonnez les matines! Sonnez les matines! Din, din, don. Din, din, don. English translation Brother Jacques, Brother Jacques, Are you sleeping? Are you sleeping? Ring/Sound he bells formatins! Ring he bells formatins! Ding, ding, dong. Ding, ding, dong. Traditional English lyrics Are you sleeping? Are you sleeping? Brother John, Brother John, Morning bells are ringing! Morning bells are ringing! Ding, dang, dong. Ding, dang, dong. The song concerns a friar's duty to ring the morning bells (). Frère Jacques has apparently overslept; it is time to ring the mornin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassar College
Vassar College ( ) is a private liberal arts college in Poughkeepsie, New York, United States. Founded in 1861 by Matthew Vassar, it was the second degree-granting institution of higher education for women in the United States. The college became coeducational in 1969. The college offers BA degrees in more than fifty majors. Vassar College's varsity sports teams, known as the Brewers, play in the NCAA Division III as members of the Liberty League. Currently, there are close to 2,500 students. The college is one of the historic Seven Sisters. The Vassar campus comprises over and more than 100 buildings. A designated arboretum, the campus features more than 200 species of trees, a native plant preserve, and a ecological preserve. History Vassar was founded as a women's school under the name "Vassar Female College" in 1861. Its first president was Milo P. Jewett, who had previously been first president of another women's school, Judson College; he led a staff of ten pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Kilenyi
Edward Kilenyi Jr. (1910 – 2000) was a classical pianist. He was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania on May 7, 1910. Kilenyi studied in Hungary with the composer/pianist Ernő Dohnányi at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music, earning a diploma in 1930. He later became a Professor of Music at Florida State University in Tallahassee, Florida in 1953, four years after Dohnanyi began teaching there. He died on January 6, 2000. A collection of recordings of his concerts is located at the International Piano Archives at the University of Maryland (IPAM). His father, (1884 – 1968), also a noted musician, arrived in the United States from Hungary in 1908. Kilenyi Sr. taught music to George Gershwin George Gershwin (; born Jacob Gershwine; September 26, 1898 – July 11, 1937) was an American composer and pianist whose compositions spanned jazz, popular music, popular and classical music. Among his best-known works are the songs "Swan ... for five years and wrote music for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Note
A quarter note ( AmE) or crotchet ( BrE) () is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left (see image). The Unicode symbol is U+2669 (). A quarter rest (or crotchet rest) denotes a silence of the same duration as a quarter note or crotchet. It is notated with the symbol . In some older music it was notated with symbol .''Rudiments and Theory of Music'' Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music, London 1958. I,33 and III,25. The former section shows both forms without distinction, the latter the "old" form only. The book was the Official ABRSM theory manual in the UK up until at least 1975. The "old" form was taugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Note
In music, a half note (American) or minim (British) is a Musical note, note played for half the duration of a whole note (or semibreve) and twice the duration of a quarter note (or crotchet). It was given its Latin name (''minima'', meaning "least or smallest") because it was the shortest of the five note values used in mensural notation, early medieval music notation. Half notes are notated with a hollow oval notehead like a whole note and straight note stem with no flag (music), flags like a quarter note (see Figure 1). The half rest (or minim rest) denotes a silence of the same duration. Half rest (music), rests are drawn as filled-in rectangles sitting on top of the middle line of the musical staff, although in polyphonic music the rest may need to be moved to a different line or even a ledger line. As with all notes with stems, half notes are drawn with upward stems on the right when they are below the middle line of the staff and downward stems on the left when they are on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girolamo Frescobaldi
Girolamo Alessandro Frescobaldi (; also Gerolamo, Girolimo, and Geronimo Alissandro; September 15831 March 1643) was an Italian composer and virtuoso keyboard player. Born in the Duchy of Ferrara, he was one of the most important composers of keyboard instrument, keyboard music in the late Renaissance music, Renaissance and early Baroque music, Baroque periods. A child prodigy, Frescobaldi studied under Luzzasco Luzzaschi in Ferrara, but was influenced by many composers, including Ascanio Mayone, Giovanni Maria Trabaci, and Claudio Merulo. Girolamo Frescobaldi was appointed organist of St. Peter's Basilica, a focal point of power for the Cappella Giulia (a musical organisation), from 21 July 1608 until 1628 and again from 1634 until his death. Frescobaldi's printed collections contain some of the most influential music of the 17th century. His work influenced Johann Jakob Froberger, Johann Sebastian Bach, Henry Purcell, and other major composers. Pieces from his celebrated collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
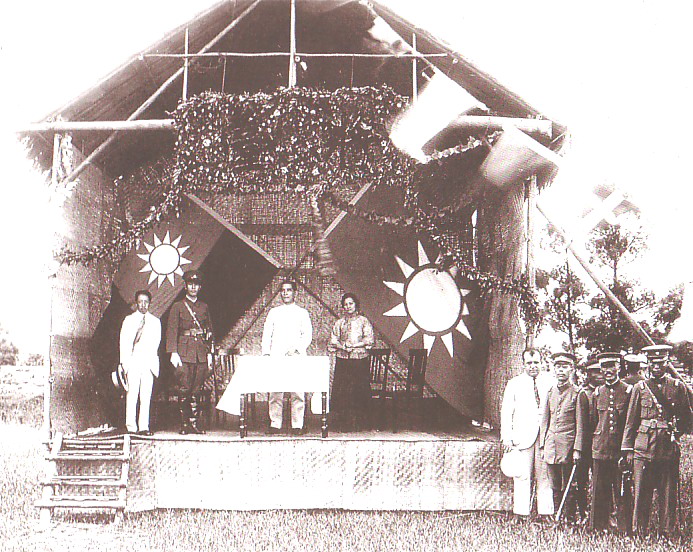
Whampoa Military Academy
The Republic of China Military Academy ( zh, t=中華民國陸軍軍官學校, p=Zhōnghúa Mīngúo Lùjūn Jūnguān Xúexiào, poj=Tiong-hôa Bîn-kok Lio̍k-kun Kun-koaⁿ Ha̍k-hāu), also known as the Chinese Military Academy (CMA), is the service academy for the Republic of China Army. It was founded by the Republic of China as the Whampoa Military Academy at Huangpu (Whampoa), Guangzhou in 1924. At the end of the Chinese Civil War the academy evacuated to the island of Taiwan and took its current name. Its graduates participated in the Northern Expedition, the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War. Establishment By 1924, the Kuomintang (KMT) wanted to build a modern, and politically reliable armed force. The KMT received money, materiel, and advisors from the Soviet Union; military advisors provided training and began reorganizing the KMT's forces along Soviet lines. As part of the reforms, political commissars were introduced for political and techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French National Library
French may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France ** French people, a nation and ethnic group ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), a 2008 film * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a type of military jacket or tunic * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French (catheter scale), a unit of measurement * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French Revolution (other) * French River (other), several rivers and other places * Frenching (other) * Justice French (other) Justice French may refer to: * C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Philippe Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; ; – ) was a French composer and music theory, music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of French opera and is also considered the leading French composer of his time for the harpsichord, alongside François Couperin. Little is known about Rameau's early years. It was not until the 1720s that he won fame as a major theorist of music with his ''Treatise on Harmony'' (1722) and also in the following years as a composer of masterpieces for the harpsichord, which circulated throughout Europe. He was almost 50 before he embarked on the operatic career on which his reputation chiefly rests today. His debut, ''Hippolyte et Aricie'' (1733), caused a great stir and was fiercely attacked by the supporters of Lully's style of music for its revolutionary use of harmony. Nevertheless, Rameau's pre-eminence in the field of French opera was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lebouc
Charles Joseph Lebouc (22 December 1822 – 6 March 1893) was a French cellist and composer. Career Born in Besançon, Lebouc attended the Conservatoire in Paris where he studied under Olive Charlier Vaslin (1794–1889) and Louis Norblin, and later became a cello professor. He played chamber music. He also composed some pieces for the cello with piano accompaniment and wrote a ''Méthode complète et pratique de violoncelle''. He won a first prize at the Conservatoire in 1842 when he was a student of Auguste Franchomme, and a first prize in harmony in 1844 as a student of Fromental Halévy. In later years he organised annual private concerts on Shrove Tuesday, and on one of these occasions, on 9 March 1886, the first performance of the ''Carnival of the Animals'' by Saint-Saëns was given, in which Lebouc played the well-known cello solo, ''The Swan''. Lebouc died in Hyères Hyères (), Provençal dialect, Provençal Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ieras'' in classical norm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
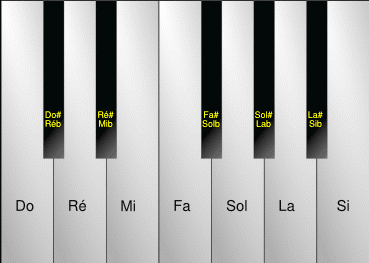
Solfège
In music, solfège (British English or American English , ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a mnemonic used in teaching aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Syllables are assigned to the notes of the Scale (music), scale and assist the musician in Gordon music learning theory#Audiation, audiating, or mentally hearing, the pitches of a piece of music, often for the purpose of singing them aloud. Through the Renaissance music, Renaissance (and much later in some shapenote publications) various interlocking four-, five- and six-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: ''do'' (spelled ''doh'' in tonic sol-fa),''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd Ed. (1998) ''re'', ''mi'', ''fa'', ''so(l)'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliothèque Nationale De France
The (; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris on two main sites, ''Richelieu'' and ''François-Mitterrand''. It is the national repository of all that is published in France. Some of its extensive collections, including books and manuscripts but also precious objects and artworks, are on display at the BnF Museum (formerly known as the ) on the Richelieu site. The National Library of France is a public establishment under the supervision of the Ministry of Culture. Its mission is to constitute collections, especially the copies of works published in France that must, by law, be deposited there, conserve them, and make them available to the public. It produces a reference catalogue, cooperates with other national and international establishments, as well as participates in research programs. History The National Library of France traces its origin to the royal library founded at the Louvre Palace by Charles V in 1368. Charles had received a collection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |