|
Fronthaul
The fronthaul portion of a C-RAN ( Cloud Radio Access Network) telecommunications architecture comprises the intermediate links between the centralized radio controllers and the radio heads (or masts) at the "edge" of a cellular network. In recent years fronthaul is becoming more essential as 5G becomes more mainstream. In general it is coincident with the backhaul network, but subtly different. Technically in a C-RAN the backhaul data is only decoded from the fronthaul network at the centralised controllers, from where it is then transferred to the core network. It comprises dedicated fibers carrying data in the CPRI or OBSAI format. This fiber network is either owned or leased by the mobile network operator. In the UK for example BT Openworld owns a majority of the fiber network to radio masts. There are proposals to modify Ethernet to make it more suitable for the Fronthaul network.http://www.ieee1904.org/3/meeting_archive/2015/02/tf3_1502_ashwood_1a.pdf Recently, a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Public Radio Interface
The Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) standard defines an interface between Radio Equipment Control (REC) and Radio Equipment (RE). Oftentimes, CPRI links are used to carry data between cell sites and base stations. The purpose of CPRI is to allow replacement of a copper or coax cable connection between a radio transceiver (used example for mobile-telephone communication and typically located in a tower) and a base station (typically located at the ground nearby), so the connection can be made to a remote and more convenient location. This connection (often referred to as the Fronthaul network) can be a fiber to an installation where multiple remote base stations may be served. This fiber supports both single and multi mode communication. The fiber end is connected with the transceiver device called Small form-factor pluggable transceiver. The companies working to define the specification include Ericsson AB, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, NEC Corporation and Nokia. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-RAN
C-RAN (Cloud-RAN), also referred to as Centralized-RAN, is an architecture for cellular networks. C-RAN is a centralized, cloud computing-based architecture for radio access networks that supports 2G, 3G, 4G and future wireless communication standards. Its name comes from the four 'C's in the main characteristics of C-RAN system, "Clean, Centralized processing, Collaborative radio, and a real-time Cloud Radio Access Network". Background Traditional cellular, or Radio Access Networks (RAN), consist of many stand-alone base stations (BTS). Each BTS covers a small area, whereas a group BTS provides coverage over a continuous area. Each BTS processes and transmits its own signal to and from the mobile terminal, and forwards the data payload to and from the mobile terminal and out to the core network via the backhaul. Each BTS has its own cooling, back haul transportation, backup battery, monitoring system, and so on. Because of limited spectral resources, network operators 'reuse' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Networked Flying Platform
Networked flying platforms (NFPs) are unmanned flying platforms of various types including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), drones, tethered balloon and high-altitude/medium-altitude/low-altitude platforms (HAPs/MAPs/LAPs) carrying RF/ mmWave/ FSO payload ( transceivers) along with an extended battery life capabilities, and are floating or moving in the air at a quasi-stationary positions with the ability to move horizontally and vertically to offer 5G and beyond 5G (B5G) cellular networks and network support services. Deployment configurations There are following two possible NFPs deployment configurations: * Deployment configuration 1: NFPs are expected to complement the conventional cellular networks to further enhance the wireless capacity, expand the coverage and improve the network reliability for temporary events, where there is a high density of mobile users or small cell Small cells are low-powered cellular radio access nodes that operate in licensed and unl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded dru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Band (waveguide)
The waveguide E band is the range of radio frequencies from 60 GHz to 90 GHz in the electromagnetic spectrum, corresponding to the recommended frequency band of operation of WR12 waveguides. These frequencies are equivalent to wave lengths between 5 mm and 3.333 mm. The E band is in the EHF range of the radio spectrum. Atmospheric effects At these high frequencies, the short wavelengths give the radiation a very directional quality, similar to visible light. Many molecules possess rotational and vibrational states excited by very specific wavelengths in this band, thus the atmospheric gases such as oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide and nitrogen can absorb, and be excited causing variable beam attenuation effects dependent on meteorological and atmospheric conditions. Applications In October 2003, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) ruled that spectrum at 71 to 76 GHz, 81 to 86 GHz and 92 to 95 GHz was available for high-density fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Network
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and business installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure. Examples of wireless networks include cell phone networks, WLAN, wireless local area networks (WLANs), wireless sensor networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks. History Wireless networks The first professional wireless network was developed under the brand ALOHAnet in 1969 at the University of Hawaii and became operational in June 1971. The first commercial wireless network was the WaveLAN product family, developed by NC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transceivers
In radio communication, a transceiver is an electronic device which is a combination of a radio ''trans''mitter and a re''ceiver'', hence the name. It can both transmit and receive radio waves using an antenna, for communication purposes. These two related functions are often combined in a single device to reduce manufacturing costs. The term is also used for other devices which can both transmit and receive through a communications channel, such as ''optical transceivers'' which transmit and receive light in optical fiber systems, and ''bus transceivers'' which transmit and receive digital data in computer data buses. Radio transceivers are widely used in wireless devices. One large use is in two-way radios, which are audio transceivers used for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication. Examples are cell phones, which transmit and receive the two sides of a phone conversation using radio waves to a cell tower, cordless phones in which both the phone handset and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-space Optical Communication
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. "Free space" means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable. The technology is useful where the physical connections are impractical due to high costs or other considerations. History Optical communications, in various forms, have been used for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks used a coded alphabetic system of signalling with torches developed by Cleoxenus, Democleitus and Polybius. In the modern era, semaphores and wireless solar telegraphs called heliographs were developed, using coded signals to communicate with their recipients. In 1880, Alexander Graham Bell and his assistant Charles Sumner Tainter created the photophone, at Bell's newly established Volta Laboratory in Washington, DC. Bell considered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethered Balloon
A tethered, moored or captive balloon is a balloon that is restrained by one or more tethers attached to the ground and so it cannot float freely. The base of the tether is wound around the drum of a winch, which may be fixed or mounted on a vehicle, and is used to raise and lower the balloon. A balloon is a form of aerostat, along with the powered free-flying airship, although the American GAO has used the term "aerostat" to describe a tethered balloon in contrast to the powered airship. Tethered balloons have been used for advertising, recreation, observation, and civil or military uses. Design principles Early balloons were simple round spheres, with a payload hung beneath. The round shape uses the minimum material to accommodate a given volume of lifting gas, making it the lightest construction. However, in any significant wind the round shape is aerodynamically unstable and will bob about, risking damage or the balloon breaking free. To avoid this problem, the kite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
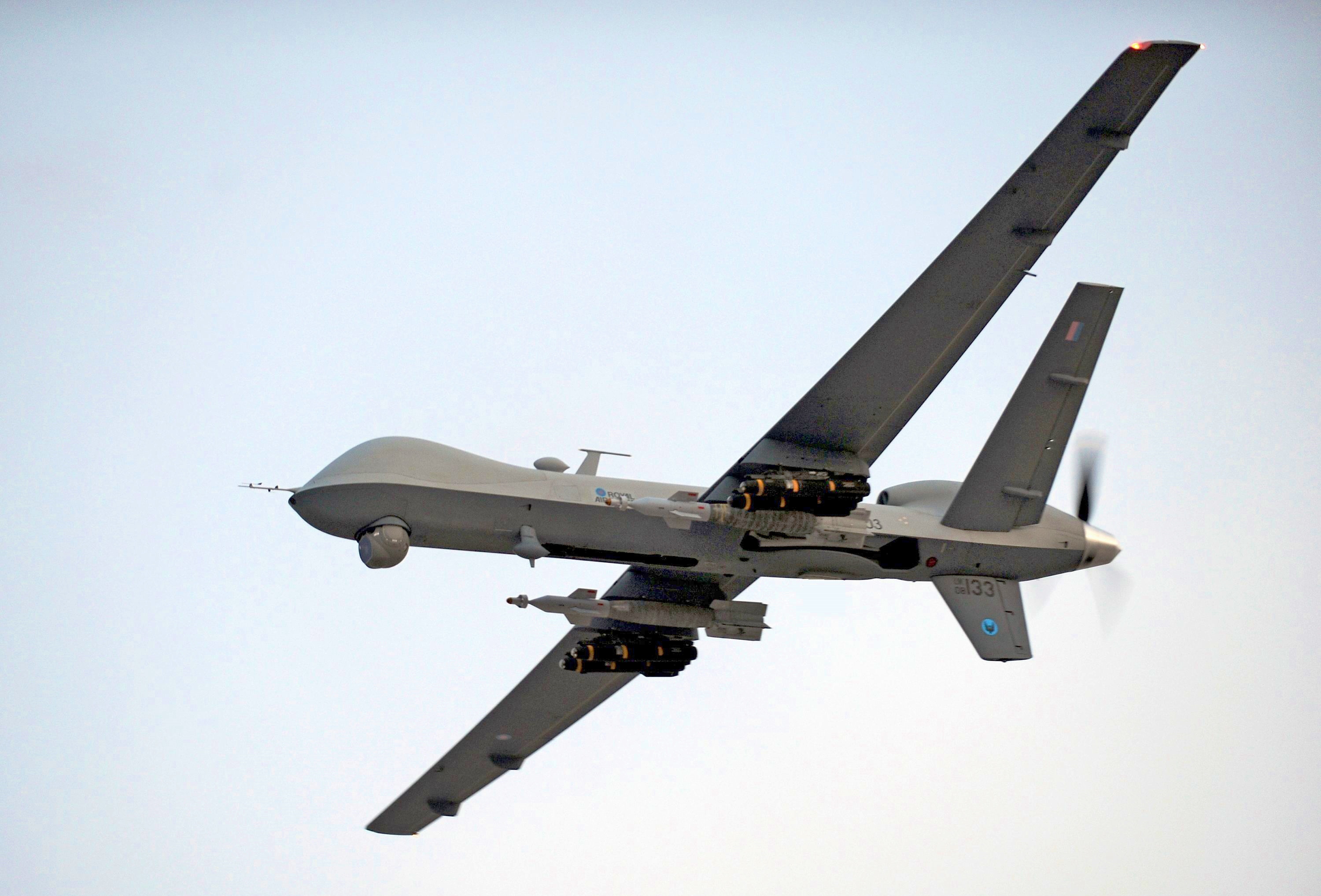
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller and a system of communications with the UAV. The flight of UAVs may operate under remote control by a human operator, as remotely-piloted aircraft (RPA), or with various degrees of autonomy, such as autopilot assistance, up to fully autonomous aircraft that have no provision for human intervention. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Jang, I.; Arvin, F.; Lanzon, A.,A Decentralized Cluster Formation Containment Framework for Multirobot Systems IEEE T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV), also known as a combat drone, colloquially shortened as drone or battlefield UAV, is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that is used for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance and carries aircraft ordnance such as missiles, ATGMs, and/or bombs in hardpoints for drone strikes. These drones are usually under real-time human control, with varying levels of autonomy. Unlike unmanned surveillance and reconnaissance aerial vehicles, UCAVs are used for both drone strikes and battlefield intelligence. Aircraft of this type have no onboard human pilot. As the operator runs the vehicle from a remote terminal, equipment necessary for a human pilot is not needed, resulting in a lower weight and a smaller size than a manned aircraft. Many countries have operational domestic UCAVs, and many more have imported armed drones or are in the process of developing them. History One of the earliest explorations of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Cell
Small cells are low-powered cellular radio access nodes that operate in licensed and unlicensed spectrum that have a range of 10 meters to a few kilometers. In other words, they are base stations with low power consumption and cheap cost that are operated in a licensed spectrum. They can provide high data rates by being deployed densely to achieve high spatial spectrum efficiency. Recent FCC orders have provided size and elevation guidelines to help more clearly define small cell equipment. They are "small" compared to a mobile macrocell, partly because they have a shorter range and partly because they typically handle fewer concurrent calls or sessions. As wireless carriers seek to 'densify' existing wireless networks to provide for the data capacity demands of "5G", small cells are currently viewed as a solution to allow re-using the same frequencies, and as an important method of increasing cellular network capacity, quality, and resilience with a growing focus using LTE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |