|
Frontal Process Of Maxilla
The frontal process of the maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose. Its ''lateral surface'' is smooth, continuous with the anterior surface of the body, and gives attachment to the quadratus labii superioris, the orbicularis oculi, and the medial palpebral ligament. Its ''medial surface'' forms part of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity; at its upper part is a rough, uneven area, which articulates with the ethmoid, closing in the anterior ethmoidal cells; below this is an oblique ridge, the ethmoidal crest, the posterior end of which articulates with the middle nasal concha, while the anterior part is termed the agger nasi; the crest forms the upper limit of the atrium of the middle meatus. The ''upper border'' articulates with the frontal bone and the ''anterior'' with the nasal; the ''posterior border'' is thick, and hollowed into a groove, which is continuous below wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Human Nose
The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. The nose has an important function in breathing. The nasal mucosa lining the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses carries out the necessary conditioning of inhaled air by warming and moistening it. Nasal conchae, shell-like bones in the walls of the cavities, play a major part in this process. Filtering of the air by nasal hair in the nostrils prevents large particles from entering the lungs. Sneezing is a reflex to expel unwanted particles from the nose that irritate the mucosal lining. Sneezing can Transmission (medicine), transmit infections, because aerosols are created in which the Respiratory droplets, droplets can harbour pathogens. Another major function of the nose is olfactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Quadratus Labii Superioris
The levator labii superioris (: ''levatores labii superioris'', also called quadratus labii superioris, : ''quadrati labii superioris'') is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone. Structure Its medial fibers form the ''angular head'' (also known as the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle) which arises by a pointed extremity from the upper part of the frontal process of the maxilla and passing obliquely downward and lateralward divides into two slips. One of these is inserted into the greater alar cartilage and skin of the nose; the other is prolonged into the lateral part of the upper lip, blending with the infraorbital head and with the orbicularis oris. The intermediate portion or ''infraorbital head'' arises from the lower margin of the orbit immediately above the infraorbital foramen, some of its fibers being attached to the maxilla, others to the zygoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Orbicularis Oculi
The orbicularis oculi is a sphincter-like muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament. From this origin, the fibers are directed laterally, forming a broad and thin layer, which occupies the eyelids or palpebræ, surrounds the circumference of the orbit, and spreads over the temple, and downward on the cheek. Structure There are at least 3 clearly defined sections of the orbicularis muscle. However, it is not clear whether the lacrimal section is a separate section, or whether it is just an extension of the preseptal and pretarsal sections. Orbital orbicularis The orbital portion is thicker and of a reddish color; its fibers form a complete ellipse without interruption at the lateral palpebral commissure; the upper fibers of this portion blend with the fronta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Medial Palpebral Ligament
The medial palpebral ligament (medial canthal tendon) is a ligament of the face. It attaches to the frontal process of the maxilla, the lacrimal groove, and the tarsus of each eyelid. It has a superficial (anterior) and a deep (posterior) layer, with many surrounding attachments. It connects the medial canthus of each eyelid to the medial part of the orbit. It is a useful point of fixation during eyelid reconstructive surgery. Structure The anterior attachment of the medial palpebral ligament is to the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove (near the nasal bone and the frontal bone), and its posterior attachment is the lacrimal bone. Crossing the lacrimal sac, it divides into two parts, upper and lower, each attached to the medial end of the corresponding tarsus of each eyelid. As the ligament crosses the lacrimal sac, a strong aponeurotic lamina is given off from its posterior surface; this expands over the sac, and is attached to the poste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
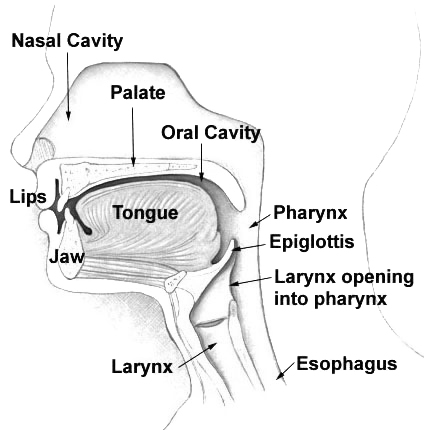 |
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia. Most of these ostia communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Anterior Ethmoidal Cells
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities ("air cells"). The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. Structure The ethmoid air cells consist of numerous thin-walled cavities in the ethmoidal labyrinthOtorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Anniko, Springer, 2010, page 188 that represent invaginations of the mucous membrane of the nasal wall into the ethmoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ethmoidal Crest
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities ("air cells"). The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. Structure The ethmoid air cells consist of numerous thin-walled cavities in the ethmoidal labyrinthOtorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Anniko, Springer, 2010, page 188 that represent invaginations of the mucous membrane of the nasal wall into the ethmoid bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Middle Nasal Concha
The medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid consists of a thin lamella, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and ends below in a free, convoluted margin, the middle nasal concha (middle nasal turbinate). It is rough, and marked above by numerous grooves, directed nearly vertically downward from the cribriform plate; they lodge branches of the olfactory nerves, which are distributed to the mucous membrane covering the superior nasal concha. The middle turbinates insert anteriorly into the frontal process of the maxilla and posteriorly into the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone. There are three mutually perpendicular segments of the middle turbinate: from proximal to distal, there is the horizontal segment ( axial plane), the basal lamella (coronal plane), and the vertical segment (sagittal plane). Additional images File:Illu nose nasal cavities.jpg, Nose and nasal cavities File:Gray152.png, Ethmoid bone from the right side. File:Gray19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Agger Nasi
The agger nasi (from Latin: ''agger'' meaning "mound or heap") is a small ridge on the lateral side of the nasal cavity. It is located midway at the anterior edge of the middle nasal concha, directly above the atrium of the middle meatus. It is formed by a mucous membrane that is covering the ethmoidal crest of the maxilla. It is also called the nasoturbinal concha and the nasal ridge. In 90% of patients an anterior ethmoidal cell (called the "agger nasi cell") can be found in the lacrimal bone below the agger nasi ridge. An enlarged agger nasi cell may encroach the frontal recess area, constricting it and causing mechanical obstruction to frontal sinus drainage. The agger nasi cell may be removed during sinus surgery to open an obstructed frontal sinus The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
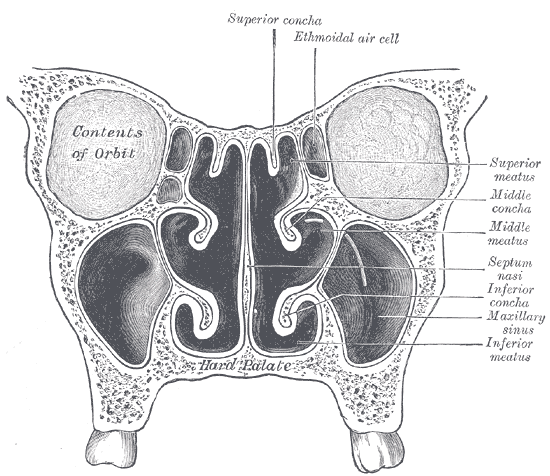 |
Middle Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are the spaces beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |