|
Frizatik
Frizatik was a silver currency minted in the town of Friesach in Carinthia since early 12th until mid-14th century. It was primarily coined by the Archbishops of Salzburg. Croatian frizatik There existed so-called Croatian frizatik's, used in the Kingdom of Croatia since the end of the 12th century until mid-13th century, minted by the Hungarians noblemen/rulers, like Andrew II of Hungary, who held the title of Duke of Slavonia (i.e. of Croatia and Dalmatia), and sometimes Ban of Croatia. Some coin types showcase a moving leopard/lion The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the .... Since the 13th century was minted more widespread and notable Banovac. References External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20061022035043/http://www.hnb.hr/novcan/povijest/h-nastavak-3.htm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia In Personal Union With Hungary
The Kingdom of Croatia (; ; ), also known with full diplomatic name Kingdom of Croatia and Dalmatia (), entered a personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary in 1102, after a period of rule of kings from the Trpimirović and Svetoslavić dynasties and a succession crisis following the death of king Demetrius Zvonimir. With the coronation of King Coloman of Hungary as "King of Croatia and Dalmatia" in 1102 in Biograd, the realm passed to the Árpád dynasty until 1301, when the (male) line of the dynasty died out. Then, kings from the Capetian House of Anjou, who were also cognatic descendants of the Árpád kings, ruled the kingdoms. Later centuries were characterized by conflicts with the Mongols, who sacked Zagreb in 1242, competition with Venice for control over Dalmatian coastal cities, and internal warfare among Croatian nobility. Various individuals emerged during the period, such as Paul I Šubić of Bribir, who was representing the most powerful Croatian dynasty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
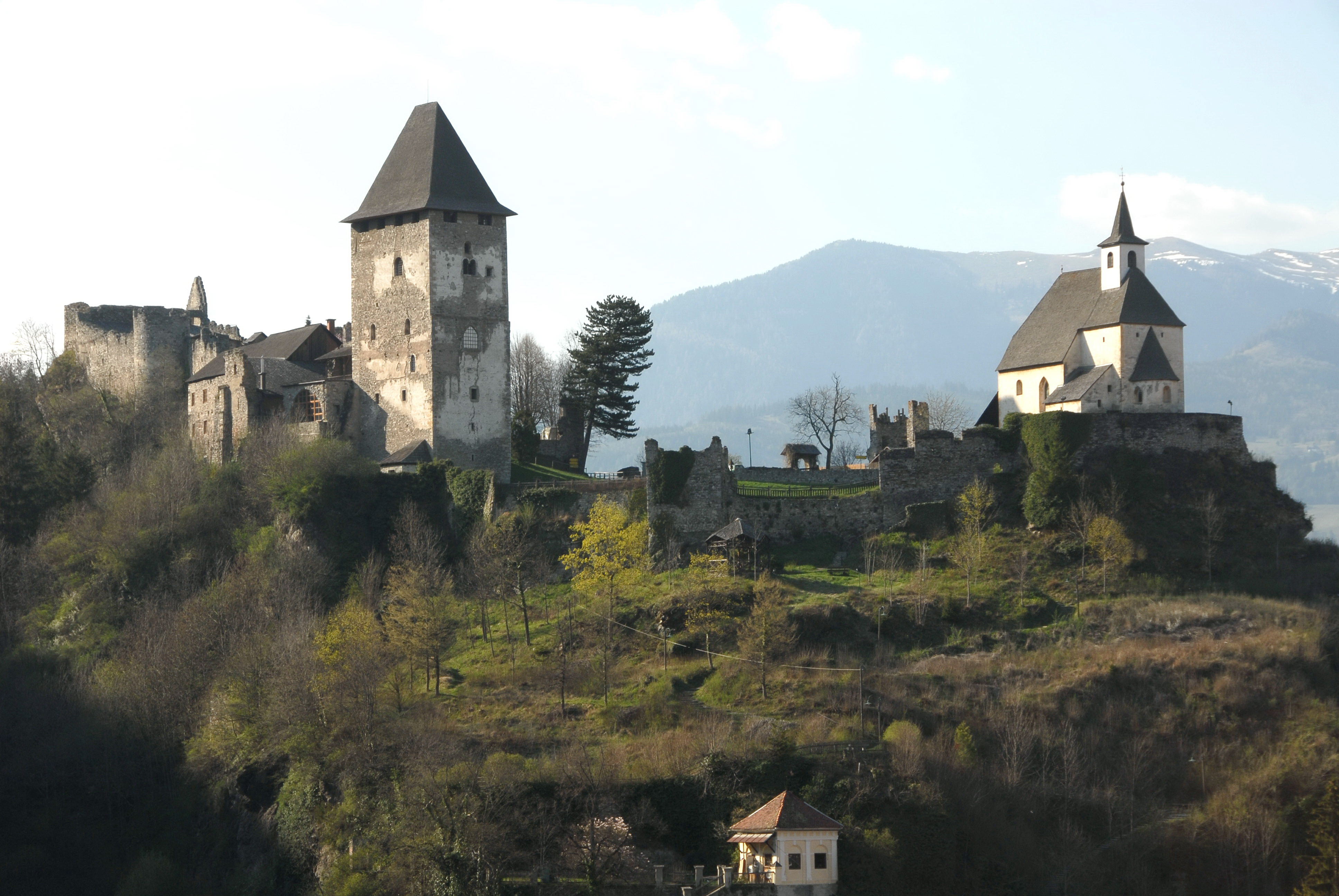
Friesach
Friesach () is a historic town in the Sankt Veit an der Glan (district), Sankt Veit an der Glan district of Carinthia (state), Carinthia, Austria. First mentioned in an 860 deed, it is known as the oldest town in Carinthia. Geography Location Friesach covers an area of 120.83 km2 and its mean elevation is 631 meters above sea level. It is located in northern Carinthia near the border with Styria, about north of its capital Klagenfurt. Populated places The municipality of Friesach consists of the following cadastral community, cadastral communities (or ''katastralgemeinden''): Friesach, St. Salvator and Zeltschach; while further subdivided into 43 populated places (with population in brackets as of 1 January 2022). * Dobritsch (13) * Dörfl (13) * Engelsdorf (377) * Friesach (Breže) (1933) * Gaisberg (77) * Grafendorf (246) * Guldendorf (4) * Gundersdorf (5) * Gunzenberg (8) * Gwerz (51) * Harold (18) * Hartmannsdorf (11) * Hundsdorf (5) * Ingolsthal (90) * Judendor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew II Of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and 1210. He was the younger son of Béla III of Hungary, who entrusted him with the administration of the newly conquered Principality of Halych in 1188. Andrew's rule was unpopular, and the boyars (or noblemen) expelled him. Béla III willed property and money to Andrew, obliging him to lead a crusade to the Holy Land. Instead, Andrew forced his elder brother, King Emeric of Hungary, to cede Kingdom of Croatia (1102–1526), Croatia and Dalmatia as an appanage to him in 1197. The following year, Andrew occupied Zachlumia, Hum. Although Andrew did not stop conspiring against Emeric, the dying king made Andrew guardian of his son, Ladislaus III of Hungary, Ladislaus III, in 1204. After the premature death of Ladislaus, Andrew ascended the thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Slavonia
The Duke of Slavonia (; ), also meaning the Duke of Dalmatia and Croatia (; ) was a title of Nobility in the Kingdom of Hungary, nobility granted several times in the 12th and 14th centuries, mainly to relatives of King of Hungary, Hungarian monarchs or other noblemen. The title of duke of "whole of Slavonia" didn't mean Slavonia in the narrow sense, but specifically all Slavic lands of the Kingdom of Hungary, being a synonym for the Kingdom of Croatia and Dalmatia (and Slavonian domain). An example being 1231 charter by Coloman of Galicia, Coloman in which protected "''omnes templarios, qui infra ducatum Sclavonie sunt, tam in Dalmatia, quam in Croatia''" ("all the Templars who are within the Duchy of Sclavonia, both in Dalmatia and in Croatia"). The title of duke signified a more extensive power than that of the Ban of Slavonia or Ban of Croatia. In cca. 1185 during Hungarian king Béla III of Hungary, Béla III, the "''dux Sclauonie''" paid to the king each year ten thousand silv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carinthia (duchy)
The Duchy of Carinthia (; ; ) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial State after the original German stem duchies. Carinthia remained a State of the Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, though from 1335 it was ruled within the Austrian dominions of the Habsburg dynasty. A constituent part of the Habsburg monarchy and of the Austrian Empire, it remained a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary until 1918. By the 1920 Carinthian plebiscite in October 1920, the main area of the duchy formed the Austrian state of Carinthia. History In the seventh century the area was part of the Slavic principality of Carantania, which fell under the suzerainty of Duke Odilo of Bavaria in about 743. The Bavarian stem duchy was incorporated into the Carolingian Empire when Charlemagne deposed Odilo's son Duke Tassilo III in 788. In the 843 partition by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of Salzburg
The Archdiocese of Salzburg (; ) is a Latin rite archdiocese of the Catholic Church centered in Salzburg, Austria. It is also the principal diocese of the ecclesiastical province of Salzburg. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian archdioceses, serving alongside the Archdiocese of Vienna. During the late medieval and early modern period, Archbishops of Salzburg were also prince-archbishops of the Holy Roman Empire, ruling over the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg, a territorially distinctive polity that existed until 1803, when it was secularized and transformed into the Electorate of Salzburg, thus relieving the archbishops of Salzburg of all temporal powers. History The earliest evidence for Christianity in the area of Salzburg is the establishment of a religious community at or near Juvavia by a follower of Severinus of Noricum, a priest named Maximus. He and his followers were killed by invading Herulians in 477. The only contemporary notice of him occurs in the "Life o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrvatska Revija
''Hrvatska revija'' ( or HR) is a Croatian quarterly published by Matica hrvatska (MH) based in Zagreb. History and profile The magazine's original run lasted between 1928 and 1945 when it was published by MH and during which it became a renowned literary and cultural magazine. The magazine was published regularly from 1929 onwards and its editor from 1930 was Blaž Jurišić. In 1932 Miroslav Krleža, August Cesarec and a group of younger left leaning authors left the magazine which exposed them to nationalist and clerical attacks on them. The publication of the magazine came to an abrupt end in 1945 as the magazine was banned by the Yugoslav communist authorities following the end of World War II. In 1951 it was re-established abroad in Buenos Aires, Argentina by Croatian émigrés Vinko Nikolić and Antun Bonifačić. Apart from literary pieces, the magazine started publishing memoir and travel writing as well as nonfiction. In 1966 the magazine moved to Europe and was publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matica Hrvatska
Matica hrvatska () is the oldest independent, non-profit and non-governmental Croatian national institution. It was founded on February 2, 1842 by the Croatian Count Janko Drašković and other prominent members of the Illyrian movement during the Croatian National Revival (1835–1874). Its main goals are to promote Croatian national and cultural identity in the fields of art, science, spiritual creativity, economy and public life as well as to care for social development of Croatia. Today, in the Palace of Matica hrvatska in the centre of Zagreb more than hundred book presentations, scientific symposia, round table discussions, professional and scientific lectures and concerts of classical music are being organized annually. Matica Hrvatska is also one of the largest and most important book and magazine publishers in Croatia. Magazines issued by Matica are '' Vijenac'', '' Hrvatska revija'' and '' Kolo''. Matica Hrvatska also publishes many books in one of its most famous edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Of Croatia
Ban of Croatia () was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by Ban (title), bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) and supreme military commander. In the 18th century, Croatian bans eventually became the chief government officials in Croatia. They were at the head of the Ban's Government, effectively the first prime ministers of Croatia. The institution of ban persisted until the first half of the 20th century, when it was officially superseded in function by that of a parliamentary prime minister. Origin of title South Slavic ''ban'' (, with a long ), is directly attested in 10th-century Constantine VII, Constantine Porphyrogenitus' book ''De Administrando Imperio'' as ', in a chapter dedicated to Croats and the organization of their state, describing how their ban "has under his rule Krbava, Lika and Gacka." Bans during the Trpimirović dynasty Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopard (heraldry)
The leopard in heraldry is traditionally depicted the same as a lion, but in a walking position with its head turned to full face, thus it is also known as a lion passant guardant in some texts, though leopards more naturally depicted make some appearances in modern heraldry. ''The Oxford Guide to Heraldry'' makes little mention of leopards but glosses ''leopard'' as a "term used in medieval heraldry for ''lion passant guardant''. Now used for the natural beast." Another name for this beast is the ounce. Early heraldic leopards The typical heraldic leopard differs from the natural leopard (''Panthera pardus'') in that it has no spots and often has a mane, but is generally similar in appearance to a heraldic lion, other than its attitude. In the Middle Ages, leopards were thought to be a crossbreed between a lion and a pard. Arthur Charles Fox-Davies wrote in 1909 that the distinction between lions (which were constantly rampant) and leopards (which were necessarily walkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lion (heraldry)
The lion is a common Charge (heraldry), charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, Royal family, royalty, strength, stateliness and Courage, valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Christian symbolism. The Lion of Judah stands in the Emblem of Jerusalem, coat of arms of Jerusalem. Similar-looking lions can be found elsewhere, such as in the coat of arms of the Swedish royal House of Bjälbo, from there in turn derived into the coat of arms of Finland, formerly belonging to Sweden. History The animals of the "barbarian" (Eurasian nomads, Eurasian) predecessors of heraldic designs are likely to have been used as totemism, clan symbols. Confronted animals, Symmetrically paired animals in particular find continuation from Migration Period art via Insular art to Romanesque art and heraldry. Adopted in Germanic art, Germanic tradition around the Germanic Iron Age, 5th century, they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |