|
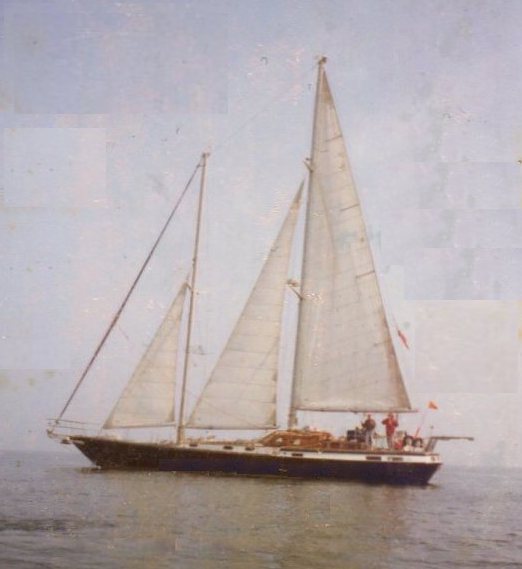
Friendship Sloop
The Friendship sloop, also known as a Muscongus Bay sloop or lobster sloop, is a Gaff rig, gaff-rigged working boat design that originated in Friendship, Maine around 1880 and has survived as a traditional-style sailboat. History Fishermen in Friendship and neighboring Bremen, Maine, Bremen collectively originated the boat's design, influenced in part, by the fishing sailboats of Gloucester, Massachusetts. The boat was used primarily for lobstering or local commerce. Boat builder Wilbur A. Morse was principle among five major Muscongus Bay builders that produced the design from the 1880s to the 1910s. From then until 1960 four major builders continued the tradition, three from the region. One person could manage its single-masted rig and haul traps unassisted, yet the boat could carry sizable loads. With an open cockpit aft, and a small forward cabin outfitted with bunks and a stove, it made fishing during cold weather much less arduous than in an open boat. By 1900 thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic Matrix (composite), matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic. Cheaper and more flexible than Carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon fiber, it is stronger than many metals by weight, non-magnetic, non-conductive, transparent to electromagnetic radiation, can be molded into complex shapes, and is chemically inert under many circumstances. Applications include aircraft, boats, automobiles, bath tubs and enclosures, swimming pools, hot tubs, septic tanks, water tanks, roofing, pipes, cladding, orthopedic casts, surfboards, and external door skins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Jib
A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its forward corner ( tack) is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on a modern boat. Modern yachts and small craft Boats may be sailed using a jib alone, but more commonly jibs make a minor direct contribution to propulsion compared to a main sail. Generally, a jib's most crucial function is as an airfoil, increasing performance and overall stability by reducing turbulence on the main sail's leeward side. On boats with only one jib, it is common for the clew of the jib to be abaft the mast, meaning the jib and mainsail overlap. An overlapping jib is called a ''genoa jib'' or simply a genoa (see illustration). These are efficiently used when reaching more broadly than a close reach. Alternatively, a boat may carry smaller jibs, to compensate aerodynamics when the main sail is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topsail
A topsail ("tops'l") is a sail set above another sail; on square-rigged vessels further sails may be set above topsails. Square rig On a square rigged vessel, a topsail is a typically trapezoidal shaped sail rigged above the course sail and below the topgallant sail where carried, on any mast (i.e., a fully rigged ship would have a foremast topsail, a mainmast topsail, and a mizzen topsail). A full rigged ship will have either single or double (i.e., "split" upper and lower) topsails on all masts, the single or lower topsail being the second sail above the deck and the upper topsail where so rigged being the third. Although described as a "square" sail, a topsail on a full rigged ship refers not to the sail's shape but to it and its yard being rigged square (i.e., at a right angle) to the vessel's keel rather than in line with it (in which case it would be called a fore-and-aft rig or a fore-and-aft rigged sail) ; a square rigged topsail is nearly always trapezoidal in sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topmast
The masts of traditional sailing ships were not single spars, but were constructed of separate sections or masts, each with its own rigging. The topmast is one of these. The topmast is semi-permanently attached to the upper front of the lower mast, at the top. Its shrouds run to the edges of the top, rather than to the sides of the hull, though long shrouds leading well aft to the hull, more in the manner of backstays, are sometimes seen. In accordance with the standard square rig sail plan, the topmast carries the topsail. In the late 19th century, however, topsails became so big that merchant ships began to divide them into two separate sails for easier handling; since these were still on the topmast they were known as upper and lower topsails to preserve the consistency of the naming scheme. The majority of large square-riggers today carry separate upper and lower topsails. The main topmast carries the upper end of the main-topmast-staysail; a mizzen-topmast may carry th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staysail
A staysail ("stays'l") is a fore-and-aft rigged sail whose luff can be affixed to a stay running forward (and most often but not always downwards) from a mast to the deck, the bowsprit, or to another mast. Description Most staysails are triangular; however, some are four-cornered, notably some fisherman's staysails. Triangular staysails set forward of the foremost mast are called jibs, headsails, or foresails. The innermost such sail on a cutter, schooner, and many other rigs having two or more foresails is referred to simply as ''the staysail'', while the others are referred to as jibs, flying jibs, etc. Types of staysail include the tallboy staysail (a narrow staysail carried between the spinnaker and the mainsail on racing yachts), the genoa staysail (a larger one carried inside the spinnaker when broad reaching), and the bigboy staysail (another name for the shooter or blooper, carried on the leeward side of the spinnaker). Unlike the cutter staysail, none of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainsail
A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast (sailing), mast of a sailing vessel. * On a square rigged vessel, it is the lowest and largest sail on the main mast. * On a fore-and-aft rigged vessel, it is the sail rigged aft of the main mast. The sail's foot is normally attached to a Boom (sailing), boom. (In extremely heavy weather, the mainsail may be lowered, and a much smaller trysail hoisted in its place). Historical fore-and-aft rigs used a four-sided gaff rigged mainsail, sometimes setting a gaff topsail above it. Whereas once the mainsail was typically the largest sail, today the mainsail may be smaller than the jib or genoa; G. Prout & Sons, Prout Catamaran#History, catamarans typically have a Mast-aft rig, mainmast stepped further aft than in a standard sloop, so that the mainsail is much smaller than the foresail. Bermuda rig The modern Bermuda rig uses a triangular mainsail aft of the mast, closely coordinated with a jib for sailing upwind. A large overlapping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowsprit
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar (sailing), spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestay, forestays. The bowsprit’s purpose is to create anchor points for the sails that extend beyond the vessel’s bow, increasing the size of sail that may be held taut. The word ''bowsprit'' is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word ''bōchsprēt'' – ''bōch'' meaning "bow" and ''sprēt'' meaning "pole". On some square-rigged ships a Spritsail (square-rigged), spritsail is flown below the bowsprit; these are sometimes accompanied by a sprit topmast, which serves to assist the spritsail while tacking (sailing), tacking. The bowsprit may also be used to hold up the Figurehead (object), figurehead. References External links * {{Sailing ship elements Sailboat components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
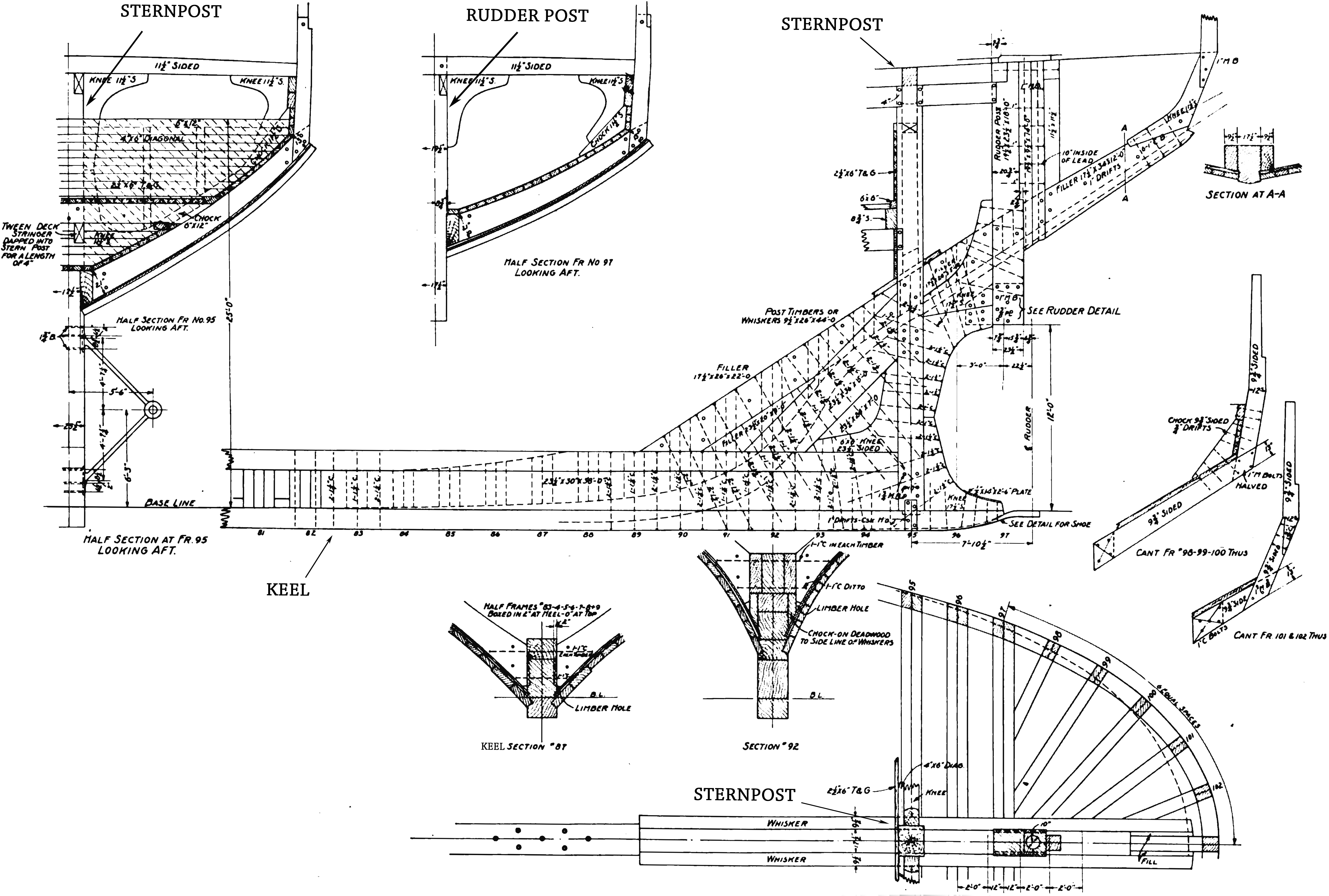
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often the initial step in constructing a ship. In the British and American shipbuilding traditions, this event marks the beginning date of a ship's construction. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English language, Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careening, careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friendship Sloop Bay Lady 2008
Friendship is a relationship of mutual affection between people. It is a stronger form of interpersonal bond than an "acquaintance" or an "association", such as a classmate, neighbor, coworker, or colleague. Although there are many forms of friendship, certain features are common to many such bonds, such as choosing to be with one another, enjoying time spent together, and being able to engage in a positive and supportive role to one another. Sometimes friends are distinguished from family, as in the saying "friends and family", and sometimes from lovers (e.g., "lovers and friends"), although the line is blurred with friends with benefits. Similarly, being in the ''friend zone'' describes someone who is restricted from rising from the status of friend to that of lover (see also unrequited love). Friendship has been studied in academic fields, such as communication, sociology, social psychology, anthropology, and philosophy. Various academic theories of friendship have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |