|
French Submarine Surcouf
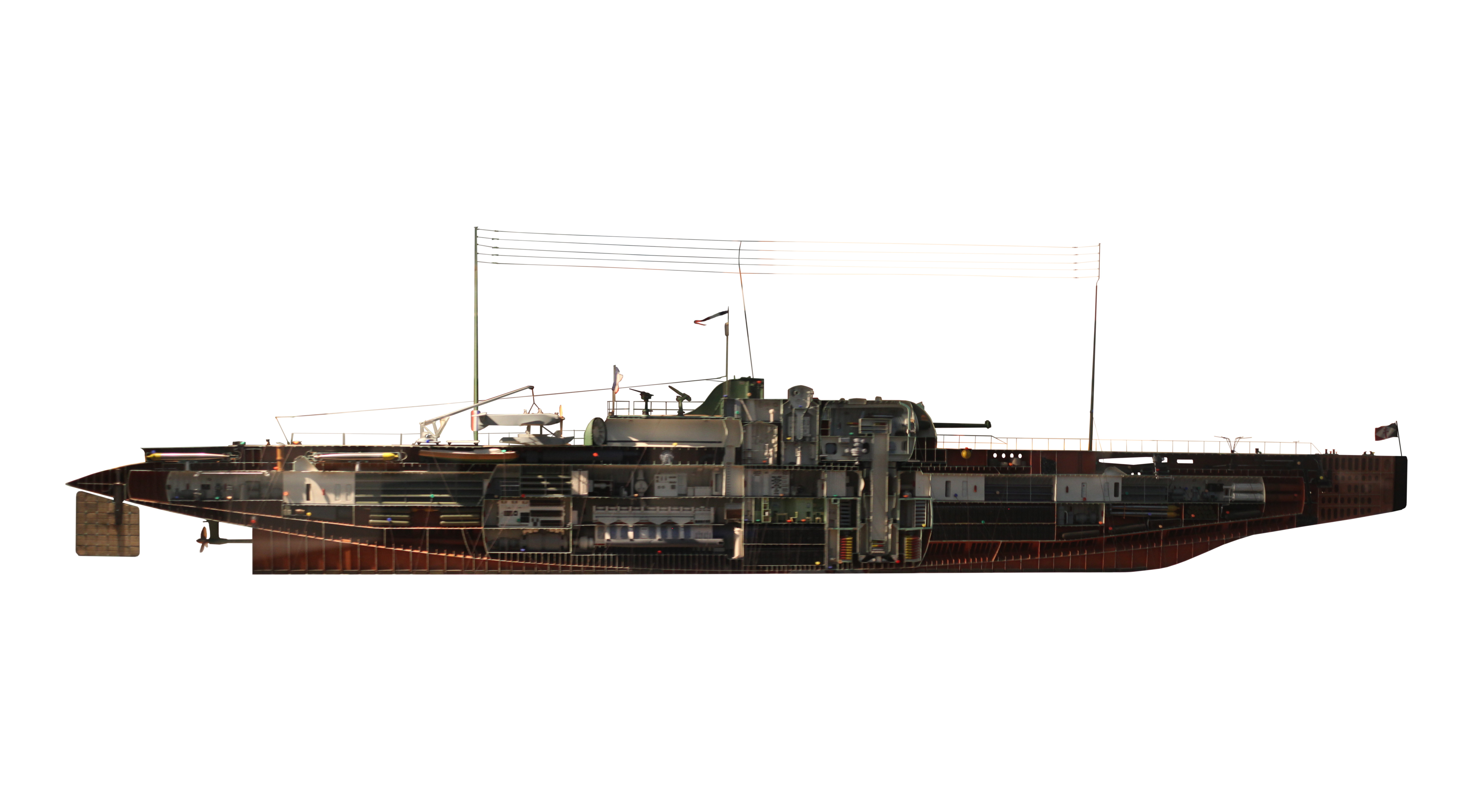
''Surcouf'' was a large French gun-armed cruiser submarine of the mid 20th century. She carried two 203 mm guns as well as anti-aircraft guns and (for most of her career) a floatplane. ''Surcouf'' served in the French Navy and, later, the Free French Naval Forces during the Second World War. ''Surcouf'' disappeared during the night of 18/19 February 1942 in the Caribbean Sea, possibly after colliding with the US freighter ''Thompson Lykes'', although this has not been definitely established. She was named after the French privateer and shipowner Robert Surcouf. She was the largest submarine built until surpassed by the first Japanese I-400 class aircraft carrier submarine in 1944. Design The Washington Naval Treaty had placed strict limits on naval construction by the major naval powers in regard to displacements and artillery calibers of battleships and cruisers. However, no agreements were reached in respect of light ships such as frigates, destroyers or submarines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Surcouf
Robert Surcouf (; 12 December 1773 – 8 July 1827) was a French privateer, businessman and slave trader who operated in the Indian Ocean from 1789 to 1808 during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Capturing over 40 prizes, he later amassed a large fortune from a variety of commercial activities, such as ship-owning, privateering, slave trading and owning land.Alain Roman; summary oRobert Surcouf, www.netmarine.net Surcouf started his maritime career as an officer on the ships ''Aurore'', ''Courrier d'Afrique'' and ''Navigateur''. Having risen to the rank of captain, he illegally engaged in slave trading onboard the slave ship ''Créole''. Surcouf then captained the merchantman ''Émilie'', on which he engaged in commerce raiding despite lacking a letter of marque. He preyed on British shipping, capturing several merchantmen including the East Indiaman '' Triton'', before returning to the Isle de France where his prizes were confiscated. Surcouf then retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces in the world recognised as being a blue-water navy. The French Navy is capable of operating globally and conducting expeditionary missions, maintaining a significant Standing French Navy Deployments, overseas presence. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the United States Navy, U.S., Royal Navy, U.K., People's Liberation Army Navy, China, Russian Navy, Russia, Italian Navy, Italy, Indian Navy, India, and Spanish Navy, Spain with its flagship being the only Nuclear marine propulsion, nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use Aircraft catapult, catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Motions
Ship motions are the six degrees of freedom that a ship, boat, or other watercraft can experience. Reference axes The '' vertical/Z axis'', or ''yaw axis'', is an imaginary line running vertically through the ship and through its centre of mass. A yaw motion is a side-to side movement of the bow and stern of the ship. The '' transverse/Y axis'', ''lateral axis'', or ''pitch axis'' is an imaginary line running horizontally across the ship and through the centre of mass. A pitch motion is an up-or-down movement of the bow and stern of the ship. The '' longitudinal/X axis'', or ''roll axis'', is an imaginary line running horizontally through the length of the ship, through its centre of mass, and parallel to the ''waterline''. A roll motion is a side-to-side or port-starboard tilting motion of the superstructure around this axis. Rotational There are three special axes in any ship, called longitudinal, transverse and vertical axes. The angular movements around them—a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Director (military)
A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew. Naval warships For warships of the 20th century, the director is part of the fire control system; it passes information to the computer that calculates range and elevation for the guns. Typically, positions on the ship measured range and bearing of the target; these instantaneous measurements are used to calculate rate of change values, and the computer ("fire control table" in Royal Navy terms) then predicts the correct firing solution, taking into account other parameters, such as wind direction, air temperature, and ballistic factors for the guns. The British Royal Navy widely deployed the Pollen and Dreyer Fire Control Tables during the First World War, while in World War II a widely used computer in the US Navy was the electro-mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Observer
An artillery observer, artillery spotter, or forward observer (FO) is a soldier responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire support onto a target. An artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry unit. Spotters ensure that indirect fire hits targets which those at a fire support base cannot see. History Historically, the range of artillery steadily increased over the centuries. In the era of bombards or ''Steinbüchse'', the gunner could usually still fire directly on the target by line-of-sight. As ranges increased, methods of employing indirect fire were developed. This made a forward observer essential in order to be able to use artillery effectively. The proximity of the observer to the target depended on the terrain and battlefield situation. Elevated observation posts could be used as an aid to facilitate communication between the guns and the observers. The development of optical and communication aids for observation advanced significantly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conning Tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armoured, from which an officer in charge can conn (nautical), conn (conduct or control) the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and ground tackle. It is usually located as high on the ship as is practical, to give the conning team good visibility of the entirety of the ship, ocean conditions, and other vessels. The naval term "conn" may derive from the Middle English ''conne'' (study, become acquainted with) or French ''conduire'' from Latin ''conducere'' (conduct). Surface ships On surface ships, the conning tower was a feature of all battleships and armored cruiser, armoured cruisers from about 1860 to the early years of World War II. Located at the front end of the superstructure, the conning tower was a heavily armored cylinder, with tiny slit windows on three sides providing a reasonable field of view. Designed to shield j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Cruiser
A heavy cruiser was a type of cruiser, a naval warship designed for long range and high speed, armed generally with naval guns of roughly 203 mm (8 inches) in calibre, whose design parameters were dictated by the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922 and the London Naval Treaty of 1930. Heavy cruisers were generally larger, more heavily armed and more heavily armoured than light cruisers while being smaller, faster, and more lightly armed and armoured than battlecruisers and battleships. Heavy cruisers were not considered capital ships, unlike battlecruisers, battleships, and fleet carriers. Heavy cruisers were assigned a variety of roles ranging from commerce raiding to serving as 'cruiser-killers,' i.e. hunting and destroying similarly sized ships. The heavy cruiser is part of a lineage of ship design from 1915 through the early 1950s, although the term "heavy cruiser" only came into formal use in 1930. The heavy cruiser's immediate precursors were the light cruiser design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of French Possessions And Colonies
From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire existed mainly in the Americas and Asia. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the second French colonial empire existed mainly in Africa and Asia. France had about 80 colonies throughout its History of France, history, the second most colonies in the world behind only the United Kingdom, British Empire. Around 40 countries gained independence from French colonial empire, France throughout its history, the second most in the world behind only the British Empire. Over 50% of the world’s borders today, were drawn as a result of British and French imperialism.Lovejoy, Paul E. (2012). Transformations of Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa. London: Cambridge University Press. France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India, following Spanish and Portuguese successes during the Age of Discovery, in rivalry with Britain. A series of wars with Britain during the 18th century and earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Submarines Of France
The submarines of France include Nuclear submarine, nuclear attack submarines and nuclear ballistic missile submarines of various List of submarine classes, classes, operated by the French Navy as part of the Submarine forces (France), French Submarine Forces. France also builds Scorpène-class submarines for international buyers; the Brazilian submarine Álvaro Alberto, a nuclear-powered boat, will be developed from this platform. Each French Navy vessel, including French submarines have for military awards and decorations their respective fanion insignia. In service Nuclear attack submarines * *# (1992–present) *# (1993–present) * *# French submarine Suffren, ''Suffren'' (Q284/S635) (2020–present) *# French submarine Duguay-Trouin, ''Duguay-Trouin'' (S636) (2023 - present) *# French submarine Tourville, ''Tourville'' (S637) (2024 - present) (working up to full operational status as of late 2024) Nuclear ballistic missile submarines * *# (1997–present) *# (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Naval Treaty
The Washington Naval Treaty, also known as the Five-Power Treaty, was signed during 1922 among the major Allies of World War I, Allies of World War I, which agreed to prevent an arms race by limiting Navy, naval construction. It was negotiated at the Washington Naval Conference in Washington, D.C. from November 1921 to February 1922 and signed by the governments of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and India), United States, French Third Republic, France, Kingdom of Italy, Italy, and Empire of Japan, Japan. It limited the construction of battleships, battlecruisers and aircraft carriers by the signatories. The numbers of other categories of warships, including cruisers, destroyers, and submarines, were not limited by the treaty, but those ships were limited to 10,000 tons displacement (ship), displacement each. The treaty was finalized on February 6, 1922. Ratifications of it were exchanged in Washington on August 17, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
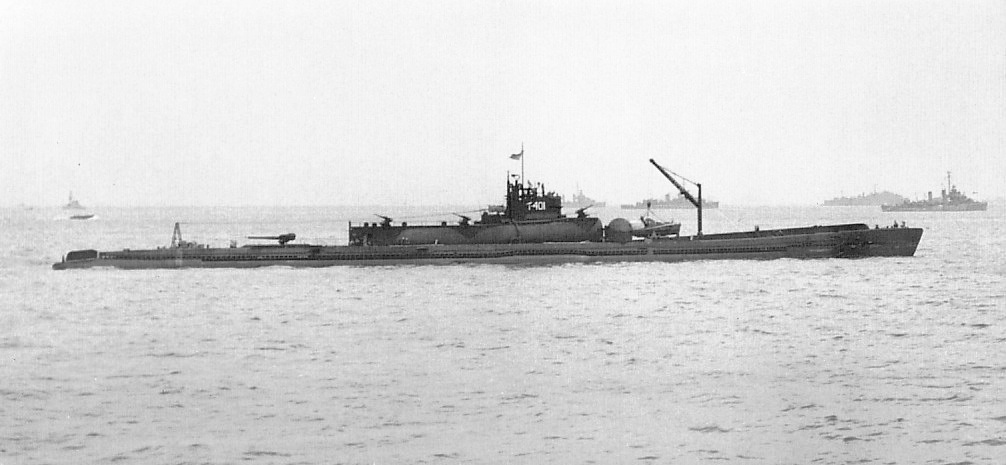
I-400-class Submarine
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) submarines were the largest submarines of World War II, with the final completed submarine being finished roughly a month before the end of the war. The ''I-400s'' remained the largest submarines ever built until the construction of nuclear ballistic missile submarines in the 1960s. The IJN called this type of submarine , shortened from . They were submarine aircraft carriers able to carry three Aichi M6A ''Seiran'' aircraft underwater to their destinations. They were designed to surface, launch their planes, then quickly dive again before they were discovered. They also carried torpedoes for close-range combat. The ''I-400'' class was designed with the range to travel anywhere in the world and return. A fleet of 18 boats was planned in 1942, and work started on the first in January 1943 at the Kure, Hiroshima arsenal. Within a year the plan was scaled back to five, of which only three ( ''I-400'' at Kure, and and ''I-402'' at Sasebo) were comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |