|
Freemasonry In Cuba
Freemasonry in Cuba has a long history in three primary eras; the Captaincy General of Cuba, Spanish era of Cuba, the Republic of Cuba (1902–1959), Republican era of Cuba, and the Cuba, Communist–Republican era of Cuba. Many of the independence fighters and Revolutionary, revolutionaries in the history of Cuba were members of the Freemasonry, Freemasons, including Carlos Manuel de Céspedes, Francisco Javier de Céspedes, José Martí, Ignacio Agramonte, and others. Freemasonry in Cuba can trace its origins back to 1762, with various lodges forming and evolving over the centuries, however, the Grand Lodge of Cuba dates back to August 1, 1876. Despite being expelled from the Conference of North America in 1962, following the Cuban Revolution, the Grand Lodge of Cuba is recognized as "Regular and Correct," by the majority of Lodges around the world. As of a survey in 2010, the islands of Cuba have 316 Masonic Lodges. The Grand Lodge of Cuba is unique in that it allows Woman, wom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola (Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital. Cuba is the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti and the Dominican Republic, with about 10 million inhabitants. It is the largest country in the Caribbean by area. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited as early as the 4th millennium BC, with the Guanahatabey and Taino, Taíno peoples inhabiting the area at the time of Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narciso López
Narciso López de Urriola (November 2, 1797 – September 1, 1851) was a Venezuelan-born adventurer and Spanish Army general who is best known for his expeditions aimed at liberating Cuba from Spanish rule in the 1850s. His troops carried a flag that López had designed, which later became the flag of Cuba. Following his final failed attempt he was captured and garroted for treason in Havana. Life in Venezuela, Cuba, and Spain Narciso López was born in Caracas, Venezuela, to a wealthy merchant family of Basque origin; his father was Pedro Manuel López and his mother was Ana Paula de Oriola (sometimes spelled Urriola). He had one sister, Maria Asunción López. As a young teenager, he was forcibly recruited in 1814 by the ruthless Spanish General José Tomás Boves from the ranks of the defeated independence forces that had been abandoned by a fleeing Simón Bolívar at the city of Valencia. When still a young man, he fought for the Spanish at the Battle of Queseras de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Cuba (1902-1959)
The Cuban coat of arms is the official heraldic symbol of Cuba. It consists of a shield, in front of a fasces crowned by the Phrygian cap, all supported by an oak branch on one side and a laurel wreath on the other. The coat of arms was created by Miguel Teurbe Tolón in 1849. The current version is not exactly the same as the original, since some elements related to annexationist ideas were removed. The design specifications of the shield were established by decree by the first president of Cuba, Tomás Estrada Palma, on 21 April 1906. This emblem is currently the only communist state not to feature socialist heraldry. Official blazon Cuban law details the official blazon of the state coat of arms as follows: ''The coat of arms is a symbol of the nation that is formed by two arches of equal circles, cut turning concavities to each other, as in an ogival shield. It's split at two thirds of its height, where a horizontal line divides it. It consists of three spaces or fields: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narciso Valdés
Narciso may refer to: Given name * Narciso Clavería y de Palacios, Spanish architect * Narciso Clavería y Zaldúa, Governor General of the Philippines * Narciso dos Santos, Brazilian former footballer * Narciso Durán, Franciscan friar and missionary * Narciso López, Venezuelan adventurer * Narciso Mina, Ecuadorian footballer * Narciso Rodriguez, American fashion designer * Narciso Ramos, Filipino journalist * Narciso Vernizzi, Brazilian sports journalist * Narciso Yepes, Spanish classical guitarist Surname * Antonio Narciso, Italian footballer * Frederick Narciso, American poker player Other *Narciso (opera), an opera by Domenico Scarlatti *Narciso (drag queen), Italian drag queen See also *Chicho Chicho is a Spanish male nickname. It can be a pet name for many different Spanish names, including Francisco and Narciso. Notable people known by this nickname include: * Cándido Sibilio * Chicho Frumboli, also known as Mariano Frúmboli, Argen ..., Spanish nickname sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castillo De Los Tres Reyes Del Morro
The Castillo de los Tres Reyes del Morro (), also known as Castillo del Morro (Morro Castle), is a fortress guarding the entrance to the Havana harbor. The design is by the Italian engineer Battista Antonelli (1547–1616). Originally under the control of Spain, the fortress was captured by the British in 1762 and returned to Spain under the Treaty of Paris (1763) a year later. The Morro Castle was the primary defense in the Havana harbor until La Cabaña was completed in 1774. History Perched on the promontory on the opposite side of the harbor from Old Havana, it can be seen from miles as it dominates the entrance to the harbor. Built in 1589 in response to raids on the city, el Morro protected the entrance of the harbor with a chain strung out across the water, known as the Boom (navigational barrier), boom defense to the fort at Castillo San Salvador de la Punta, La Punta. The Morro fortress shares its name with Castillo de San Pedro de la Roca in Santiago de Cuba and the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marta Abreu
Doña Marta de los Ángeles González Abreu y Arencibia (13 November 1845 – 2 January 1909) was a Cuban philanthropist and one of the most influential figures of her time in central Cuba. She is recognized for her extensive charitable works in her hometown of Santa Clara, as well as her substantial financial contributions to the Cuban independence movement against Spanish colonial rule. Abreu is partly responsible for the creation of the Lone Star flag of the Republic of Cuba, referred to as the Narciso López flag. Being the single-largest financial supporter of the Mambises and the Mambí Army, Abreu was named the "Patroness of Cuba." Early life and philanthropic works Born in Santa Clara, Cuba, Marta Abreu was the daughter of Don Pedro Abreu and Rosalía Arencibia, members of a wealthy and influential family, the Viscount of Los Remedios. Her father, Pedro Abreu, inherited and expanded a significant fortune. Her wealth enabled Marta Abreu to travel to Europe and the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emilia Casanova De Villaverde
Emilia Casanova de Villaverde (1832–1897) was a Cuban political activist, most notable for her involvement in the Cuban independence movement. She founded La Liga de las Hijas de Cuba, one of the first all-women's organizations dedicated to the Antillean emancipation struggle. Early life and career Emilia Casanova de Villaverde was born into an elite Creole slaveholding family in Cuba in 1832. Despite her affluent Creole upbringing, de Villaverde did not share her father's conservative views. At a banquet during her youth, with Spanish authorities in attendance, she defiantly made a toast to Cuban freedom from Spanish colonial power. By 1825, most of Spain's colonies in the Americas gained independence except for Cuba and Puerto Rico, which remained under Spanish rule. Cuban elites believed that Spanish colonialism would help maintain Cuba's domination of the sugar industry and prevent a slave uprising similar to the Haitian Revolution in 1791. Over the years, many inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Flag Masonic Origins
Cuban or Cubans may refer to: Related to Cuba * of or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean * Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent ** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof * Cuban Americans, citizens of the United States who are of Cuban descent * Cuban Spanish, the dialect of Cuba * Culture of Cuba * Cuban cigar * Cuban cuisine ** Cuban sandwich People with the surname * Brian Cuban (born 1961), American lawyer and activist * Mark Cuban (born 1958), American entrepreneur See also * * Kuban (other) * List of Cubans * Demographics of Cuba * Cuban Boys, a British music act * Cuban eight, a type of aerobatic maneuver * Cuban Missile Crisis * Cubane Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a Cube (geometry), cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substanc ..., a synthetic hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
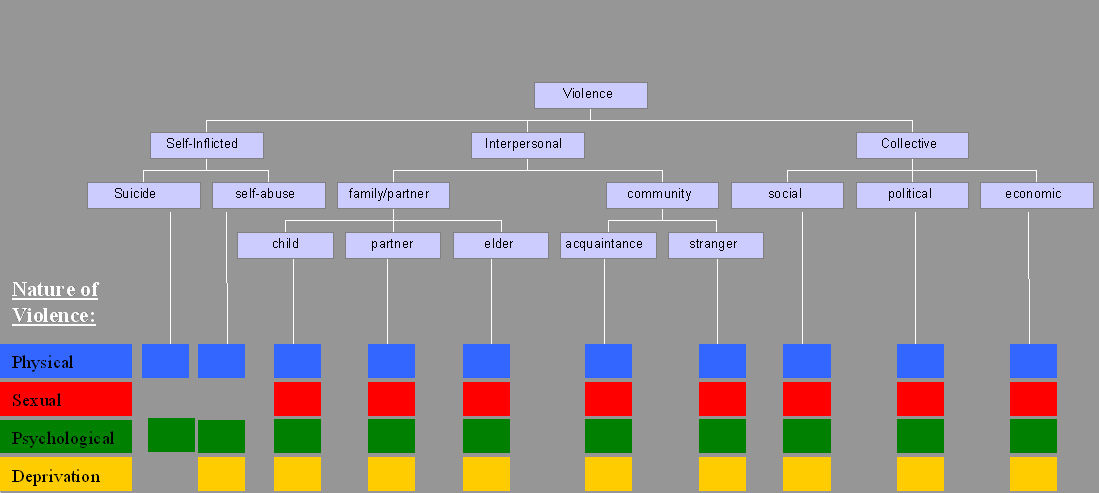
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Of Providence
The Eye of Providence or All-Seeing Eye is a symbol depicting an eye, often enclosed in a triangle and surrounded by rays of light or a halo, intended to represent Providence, as the eye watches over the workers of mankind. A well-known example of the Eye of Providence appears on the reverse of the Great Seal of the United States, which is depicted on the United States one-dollar bill. Use by governments and confederations United States In 1782, the Eye of Providence was adopted as part of the symbolism featured on the reverse side of the Great Seal of the United States. It was first proposed as an element of the Great Seal by the first of three design committees in 1776, and it is thought to be the suggestion of the artistic consultant Pierre Eugene du Simitiere.Bureau of Public Affairs. July 2003.The Great Seal of the United States" Washington: U.S. Department of State Archive; See alsoGreat Seal" Bureau of Public Affairs. 2002. Both retrieved 6 June 2020. At the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five-pointed Star
A five-pointed star (☆), geometrically an equilateral concave decagon, is a common ideogram in modern culture. Comparatively rare in classical heraldry, it was notably introduced for the flag of the United States in the Flag Act of 1777 and since has become widely used in flags. It has also become a symbol of fame or "celebrity, stardom" in Western culture, among other uses. History of use Early history The Egyptian hieroglyph representing "star" had five points (N14 Gardiner's sign list#N, N14), while the dingir, "star" sign in Mesopotamian cuneiform had eight. Sopdet, the Egyptian personification of the star Sirius, is always shown with the five-pointed star hieroglyph on her head. The five-pointed star is the oldest symbol of Italy. Venus (mythology), Venus (once considered a star instead of a Venus, planet) represented the West and was, in Classical mythology, the symbol of the Italian peninsula, which was western to Greece. The star (or ''mullet (heraldry), mullet'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |