|
Free State Of Brunswick
The Free State of Brunswick () was a Administrative divisions of Weimar Germany, state of the German Reich in the time of the Weimar Republic. It was formed after the abolition of the Duchy of Brunswick in the course of the German revolution of 1918–1919. Its capital was Braunschweig (Brunswick). In 1933 it was ''de facto'' abolished by Nazi Germany. The free state was disestablished after the World War II, Second World War in November 1946. History The Duchy of Brunswick had been established after the 1814 Congress of Vienna, as a sovereign successor state of the German Confederation. It roughly comprised the incoherent territory of the former Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, stretching from Holzminden on the Weser River in the west to County of Blankenburg, Blankenburg in the Harz mountain range and Calvörde (Amt), Calvörde in the east.Wolfgang Meibeyer: ''Die Landesnatur. Territorium - Lage - Grenzen'', in Horst-Rüdiger Jarck / Gerhard Schildt (eds.), ''Die Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers (other than the Ottoman Empire) and other stakeholders. The Congress was chaired by Austrian Empire, Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and was held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars through negotiation. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could European balance of power, balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More generally, conservative leaders like Metternich also soug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Hanover
The House of Hanover ( ) is a European royal house with roots tracing back to the 17th century. Its members, known as Hanoverians, ruled Hanover, Great Britain, Ireland, and the British Empire at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. Originating as a cadet branch of the House of Welf (also "Guelf" or "Guelph") in 1635, also known then as the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, the Hanoverians ascended to prominence with Hanover's elevation to an Electorate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1692. In 1714 George I, prince-elector of Hanover and a descendant of King James VI and I, assumed the throne of Great Britain and Ireland, marking the beginning of Hanoverian rule over the British Empire. At the end of this line, Queen Victoria's death in 1901, the throne of the United Kingdom passed to her eldest son Edward VII, a member of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, through his father Albert, Prince Consort. The last reigning members of the House of Hanover lost the Duchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
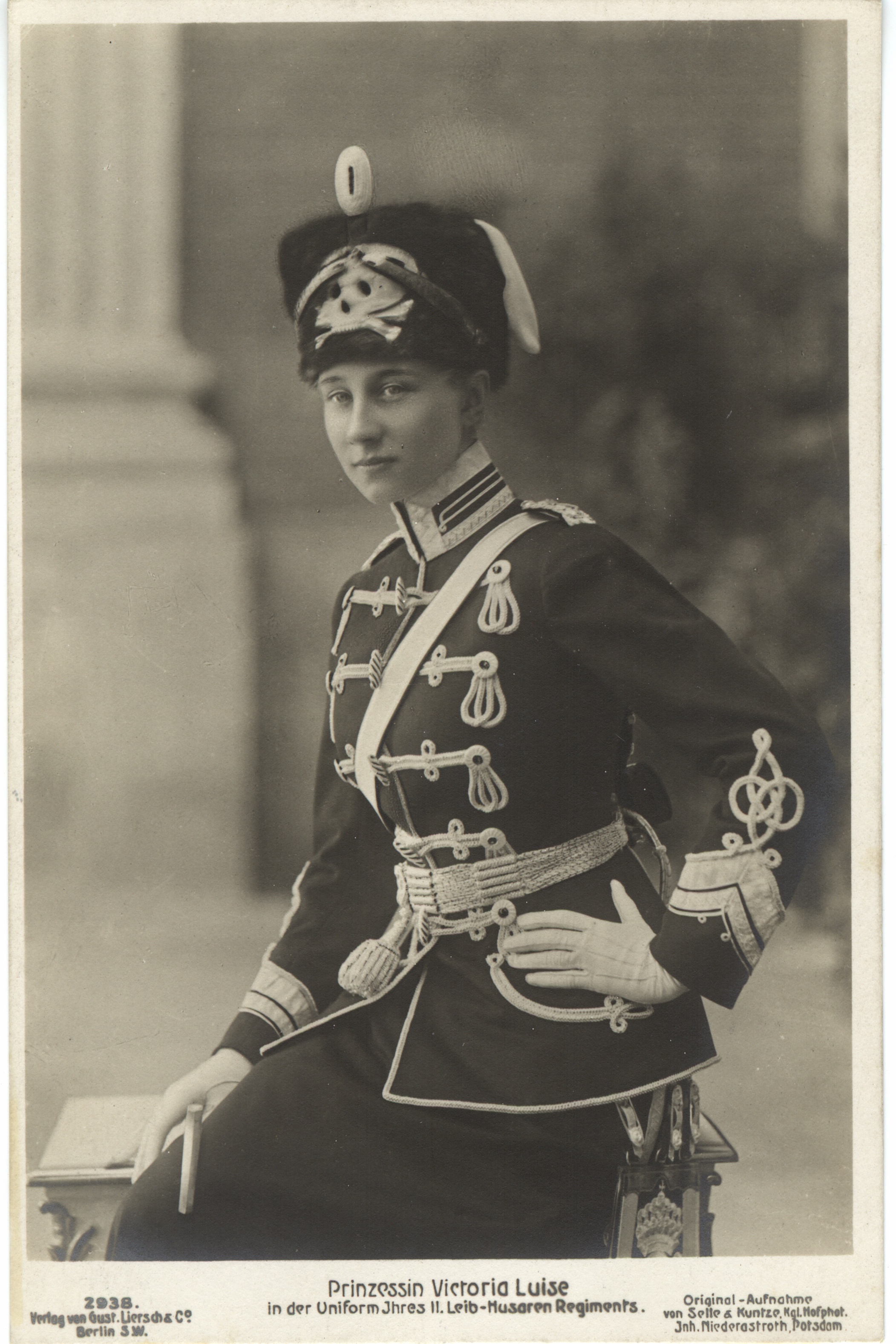
Ernest Augustus, Duke Of Brunswick
Ernest Augustus (Ernest Augustus Christian George; ; 17 November 1887 – 30 January 1953) was Duke of Brunswick from 2 November 1913 to 8 November 1918. He was a grandson of George V of Hanover, thus a Prince of Hanover and a Prince of the United Kingdom. He was also a maternal grandson of Christian IX of Denmark and the son-in-law of German Emperor Wilhelm II. The Prussians had deposed King George from the Hanoverian throne in 1866, but his marriage ended the decades-long feud between the Prussians and the Hanoverians. Early life Ernest Augustus was born at Penzing (Vienna), Penzing near Vienna, the sixth and youngest child of Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover, former Crown Prince Ernest Augustus of Hanover and his wife, Princess Thyra of Denmark. His great-grandfather, Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover, Prince Ernest Augustus, Duke of Cumberland, the fifth son of George III of the United Kingdom, became king of Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover in 1837 because Salic Law barre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (), also known as Prussian Saxony (), was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg. It was formed by the merger of various territories ceded or returned to Prussia in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna: most of the former northern territories of the Kingdom of Saxony (the remainder of which became part of Brandenburg or Silesia), the former French Principality of Erfurt, the Duchy of Magdeburg, the Altmark, the Principality of Halberstadt, and some other districts. The province was bounded by the Electorate of Hesse (the province of Hesse-Nassau after 1866), the Kingdom of Hanover (the province of Hanover after 1866) and the Duchy of Brunswick to the west, Hanover (again) to the north, Brandenburg to the north and east, Silesia to the south-east, and the rump kingdom of Saxony and the small Ernestine duchies to the south. Its shape was very irregular and it entirely surrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover () was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and joined 38 other sovereign states in the German Confederation in June 1815. The kingdom was ruled by the House of Hanover, a cadet branch of the House of Welf, in Personal union of Great Britain and Hanover, personal union with Great Britain between 1714 and 1837. Since its monarch resided in London, a viceroy, usually a younger member of the British royal family, handled the administration of the Kingdom of Hanover. The personal union with the United Kingdom ended in 1837 upon the accession of Queen Victoria because semi-Salic law prevented females from inheriting the Hanoverian throne while a dynastic male was still alive. Her uncle Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover, Ernest Augustus thus became the ruler of Hanover. His only son succeeded h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Hanover
The Province of Hanover () was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1866 to 1946. During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation. After Hanover voted in favour of mobilising confederation troops against Prussia on 14 June 1866, Prussia saw this as a just cause for declaring war; the Kingdom of Hanover was soon dissolved and annexed by Prussia. The private wealth of the dethroned House of Hanover was then used by Otto von Bismarck to finance his continuing efforts against Ludwig II of Bavaria. In August 1946, the British military administration recreated the State of Hanover based on the former Kingdom of Hanover but, three months later, it was merged into the new States of Germany, state () of Lower Saxony along with the states of Free State of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Free State of Brunswick, Brunswick, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. Prussia formed the German Empire when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by 1932 Prussian coup d'état, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians who were conquered by the Teutonic Knightsan organized Catholic medieval Military order (religious society), military order of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvörde (Amt)
The Amt of Calvörde is a historical Amt in the District of Helmstedt, Brunswick, in today's Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It formed an exclave that was surrounded by the Province of Saxony, Prussia, and in 1944 it was moved to the District of Haldensleben, Province of Saxony The Province of Saxony (), also known as Prussian Saxony (), was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg. It was formed by the merger of various territories ceded .... Its capital was Calvörde; it had a population of 4,600 (1933). Municipalities in 1939: * Berenbrock * Calvörde * Dorst * Elsebeck * Jeseritz * Lössewitz * Parleib * Uthmöden * Velsdorf * Zobbenitz References {{DEFAULTSORT:Calvorde (Amt) Helmstedt (district) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harz
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German word ''Hardt'' or ''Hart'' (hill forest). The name ''Hercynia'' derives from a Celtic name and could refer to other mountain forests, but has also been applied to the geology of the Harz. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of above sea level. The Wurmberg () is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony. Geography Location and extent The Harz has a length of , stretching from the town of Seesen in the northwest to Eisleben in the east, and a width of . It occupies an area of , and is divided into the Upper Harz (''Oberharz'') in the northwest, which is up to 800 m high, apart from the 1,100 m high Brocken massif, and the Lower Harz (''Unterhar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Blankenburg
The County of Blankenburg () was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was Blankenburg, it was located in and near the Harz mountains. History County of Blankenburg About 1123 Lothair of Supplinburg, then Duke of Saxony, had Blankenburg Castle erected in the Eastphalian Harzgau region. His vassal Poppo I of Blankenburg, a relative of Lothair's wife Richenza of Northeim, is documented as count over the Eastern Harzgau since 1128. He later also appeared as a ''ministerialis'' of the Welf duke Henry the Lion. After Poppo's death around 1161, his sons divided their heritage: Conrad took his residence at Regenstein Castle, north of Blankenburg, and became the ancestor of the noble House of Regenstein, while his brother Siegfried I retained Blankenburg Castle. In 1180 Henry the Lion was deposed by an intervention of his Hohenstaufen cousin Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, allied with many Saxon vassals and former supporters of Duke Henry. However, the then ruling Counts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ... via two highly Saline water, saline, Estuary, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east–west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of ''Weser''), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main (river), Main, however, is the longest if the Weser-Werra are considered separate). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |