|
Frederick Rutland
Frederick Joseph Rutland, (21 October 1886 – 28 January 1949) was a British pioneer of naval aviation. A decorated pilot in the First World War, he earned the nickname "Rutland of Jutland" for his exploits at the Battle of Jutland in 1916. He later worked for the Japanese and was interned by the British authorities during the Second World War. "Rutland of Jutland" He joined the Royal Navy as a boy seaman in 1901. He was graded as Flight Sub-Lieutenant in the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) in December 1914, awarded his aviator's certificate by the Royal Aero Club on 26 January 1915 after training at Eastchurch and promoted to Lieutenant on 7 January 1916. At Jutland he served as a pilot on the seaplane tender HMS ''Engadine''. On 30 May 1916, ''Engadine'' carried two Short Type 184 and two Sopwith Baby floatplanes and was attached to the 3rd Light Cruiser Squadron. ''Engadine'' accompanied the cruisers when the Battlecruiser Fleet sortied from Rosyth that evenin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Livock
Group Captain Gerald Edward Livock (11 July 1897 – 27 January 1989) was an English officer of the Royal Naval Air Service and Royal Air Force, who served from the beginning the First World War until the end of Second, and was also an archaeologist and cricketer. A right-handed batsman and wicket-keeper, he played first-class cricket for various teams between 1923 and 1934. Early life and background Livock was born in Newmarket, Suffolk, the son of a veterinary surgeon, and was educated at Cheltenham School. He had just turned 17 when the First World War broke out in August 1914, and his father was keen for his son to join him in his practice. However, young Livock had other ideas, and on 27 October 1914 he was commissioned into the Royal Naval Air Service as a probationary flight sub-lieutenant, and was posted to HMS ''Pembroke'', for duty with the RNAS at Hendon. There, at the Grahame-White School, he learned to fly the Grahame-White Type XV biplane, and on 20 December 1914 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Type 184
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It was first flown in 1915 and remained in service until after the armistice in 1918. A Short 184 was the first aircraft to sink a ship using a torpedo, and another was the only British aircraft to take part in the Battle of Jutland. Design and development Torpedo-dropping trials had been undertaken using a Gnome powered Short Admiralty Type 166 but this had proved insufficiently powerful, and so in September 1914 a new specification was formulated for an aircraft to be powered by the Sunbeam Mohawk engine currently being developed. Design proposals were invited from Sopwith, J. Samuel White and Short Brothers. Horace Short's response when the requirements were explained him by Murray Sueter, the director of the naval air department, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Air Arm Museum
The Fleet Air Arm Museum is devoted to the history of British naval aviation. It has an extensive collection of military and civilian aircraft, aero engines, models of aircraft and Royal Navy ships (especially aircraft carriers), and paintings and drawings related to naval aviation. It is located on RNAS Yeovilton airfield, and the museum has viewing areas where visitors can watch military aircraft (especially helicopters) take off and land. At the entrance to the museum are anchors from and , fleet carriers which served the Royal Navy until the 1970s. It is located north of Yeovil, and south of Bristol. Exhibits The museum's main display is divided into four areas: Hall 1 This hall contains a display about the development of naval aviation from the early days of airships and fabric-covered wooden biplanes to modern jet aircraft and helicopters, including the front section of the fuselage of Short 184 ''8359'', built locally by Westland Aircraft in Yeovil and flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of Britain and its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'." Originally housed in the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill, the museum opened to the public in 1920. In 1924, the museum moved to space in the Imperial Institute in South Kensington, and finally in 1936, the museum acquired a permanent home that was previously the Bethlem Royal Hospital in Southwark. The outbreak of the Second World War saw the museum expand both its collections and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
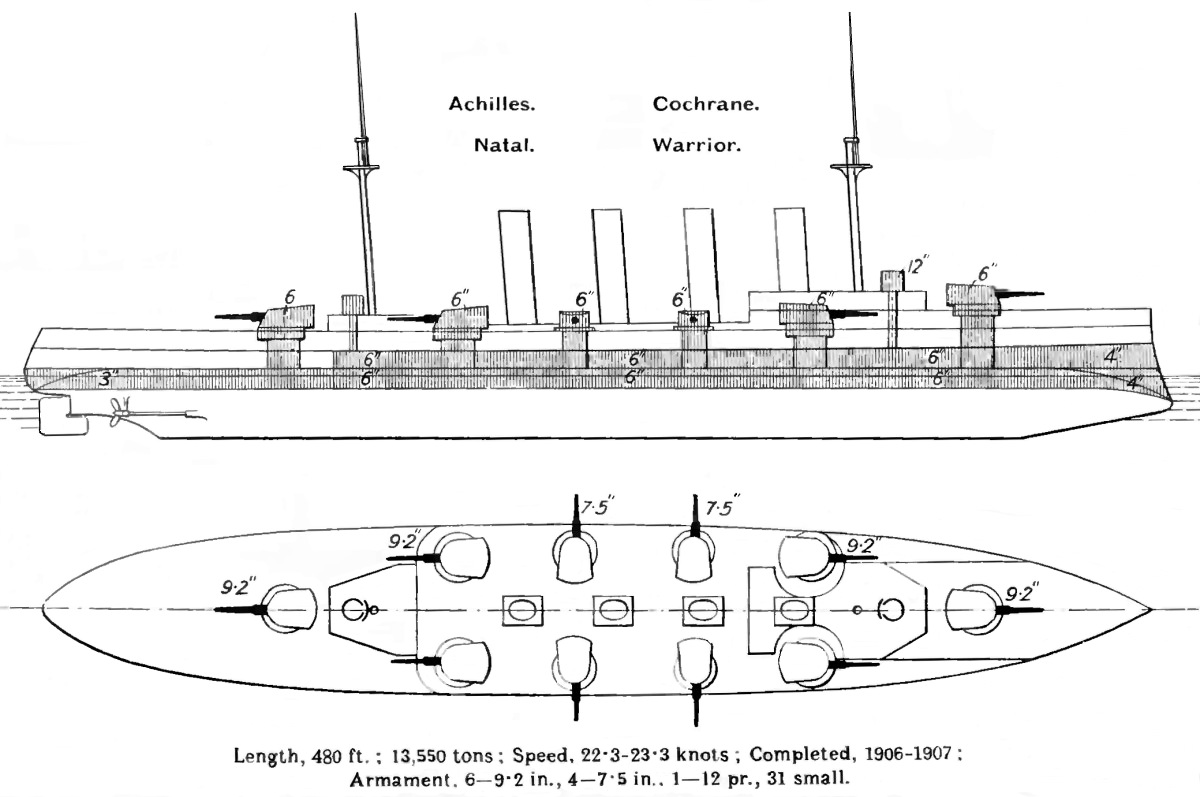
HMS Warrior (1905)
HMS ''Warrior'' was a armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was stationed in the Mediterranean when the First World War began and participated in the pursuit of the German battlecruiser and light cruiser . ''Warrior'' was transferred to the Grand Fleet in December 1914 and remained there for the rest of her career. She was heavily damaged during the Battle of Jutland in 1916, after which she withdrew and was later abandoned and sank in a rising sea. Description ''Warrior'' displaced as built and fully loaded. The ship had an overall length of , a beam of and a draught of . She was powered by four-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, driving two shafts, which developed a total of and gave a maximum speed of .Roberts, p. 34 The engines were powered by 19 Yarrow water-tube boilers and six cylindrical boilerss. The ship carried a maximum of of coal and an additional of fuel oil that was sprayed on the coal to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser which combined an armored belt with the long range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a light armored deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannon and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of face-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previously. Varying in size, the armored cruiser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Battle Squadron (United Kingdom)
The 5th Battle Squadron was a squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships. The 5th Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Second Fleet. During the First World War, the Home Fleet was renamed the Grand Fleet. History First World War August 1914 In August 1914, the 5th Battle Squadron was based at Portland, and consisted of a number of pre-dreadnought battleships. These were: * * * * * * * * Following the loss of HMS ''Bulwark'' in 1914, and were transferred from the 6th Battle Squadron. With the commissioning of the five fast battleships of the ''Queen Elizabeth'' class, the remaining pre-dreadnoughts were sent to the Mediterranean. herself was delayed in joining the squadron, instead taking part in the Dardanelles Campaign until May 1915. Battle of Jutland In 1916, the 5th Battle Squadron—under the command of Rear Admiral Hugh Evan-Thomas— was temporarily transferred to David Beatty's Battlecruiser Fleet. On 31 May, four s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiing
Taxiing (rarely spelled taxying) is the movement of an aircraft on the ground, under its own power, in contrast to towing or pushback where the aircraft is moved by a tug. The aircraft usually moves on wheels, but the term also includes aircraft with skis or floats (for water-based travel). An airplane uses taxiways to taxi from one place on an airport to another; for example, when moving from a hangar to the runway. The term "taxiing" is not used for the accelerating run along a runway prior to takeoff, or the decelerating run immediately after landing, which are called the takeoff roll and landing rollout, respectively. Etymology As early as 1909 aviation journalists envisioned aeroplanes to replace the taxicab in traffic-congested cities. Some aviators and some linguists report that around the year 1911 the slang word "taxi" was in use for an "airplane". They suggest that the way aircraft move under power before they take off or after they land reminded someone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(6857765499).jpg)